Hydrography of Mesopotamia:
Assyria and Babylonia
Sebastian Borkowski M.A.
Prof. Dr. Mirko Novák
Dr. Susanne Rutishauser
Dr. Eveline C. Zbinden
Prof. Dr. Andreas Zischg
Seminar Paper
- 9000–12000 characters including spaces and bibliography
- on a specific topic not directly related to the presentation
- This counts for 50% of the final grade
- The paper may be written in either German or English
- Deadlines:
- Determining the topic: April 30
- Submission: July 31
example: 27'000 characters including spaces
Topics (selection)
- Climate change in upper regions (Turkey)
- Sea level changes
- Changes delta progression
- Marsh formation in antiquity
- Iraqi marshlands
- Modern hydraulic projects in Iraq (and Turkey)
- Organisation of irrigation and water management in the early Old Babylonian period
- Impact of salinization in agriculture and coping strategies
- human labour & hydraulic technologies in the 3rd millenium BCE
- compilation of an German-English-Arabic Glossary of modern hydrographic and hydraulic terminology
Presentation and Handout
- Prepare and give an interdisciplinary presentation (40 min) on a topic in a group, including a handout (2000–5000 characters with spaces and bibliography).
- A draft of the handout must be submitted to all lecturers one week before the presentation.
- The final version of the handout must be uploaded to Ilias into the folder "handout" until Sunday evening before the presentation, a PDF (and pptx) of the presentation on the day of the presentation.
- Handout and presentation count for 40% of the final grade (group assessment).
Quotations
- You can find the document "Richtlinien und Empfehlungen zum wissenschaftlichen Schreiben und Präsentieren für die Vorderasiatische Archäologie und Altorientalische Philologie sowie für die Prähistorische Archäologie" on Ilias within the folder "Administration".
- Quotations inclusive page number
- Wilkinson 2007: 80.
- Wilkinson, T.J. (1990): Early Channels and Landscape Development around Abu Salabikh, a Preliminary Report, Iraq 52: 75–83.
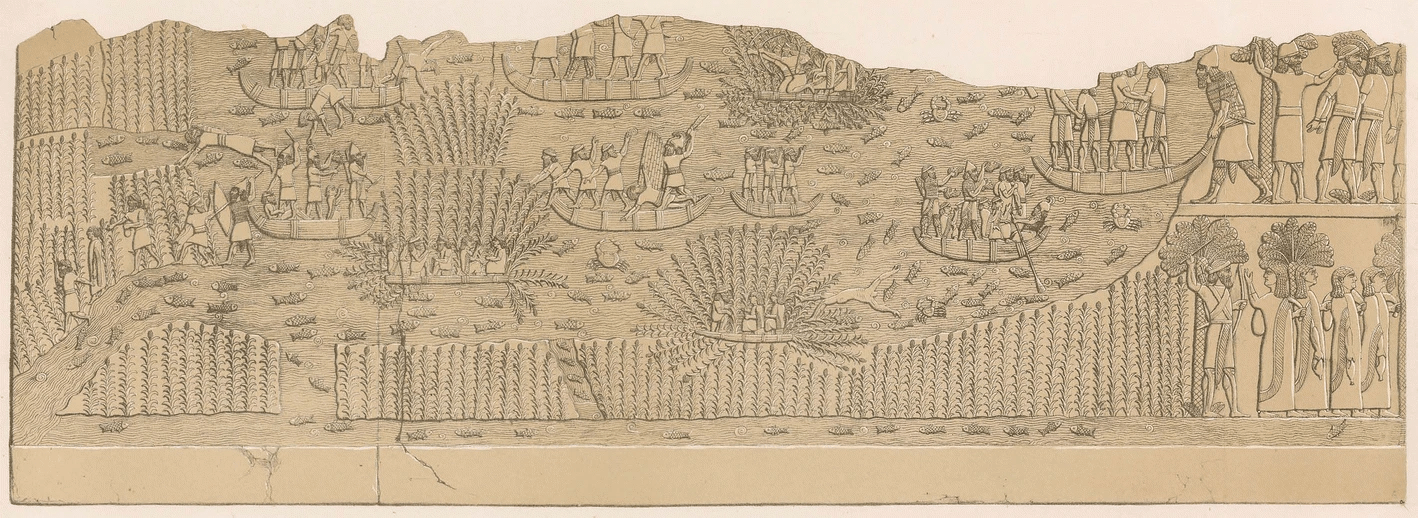
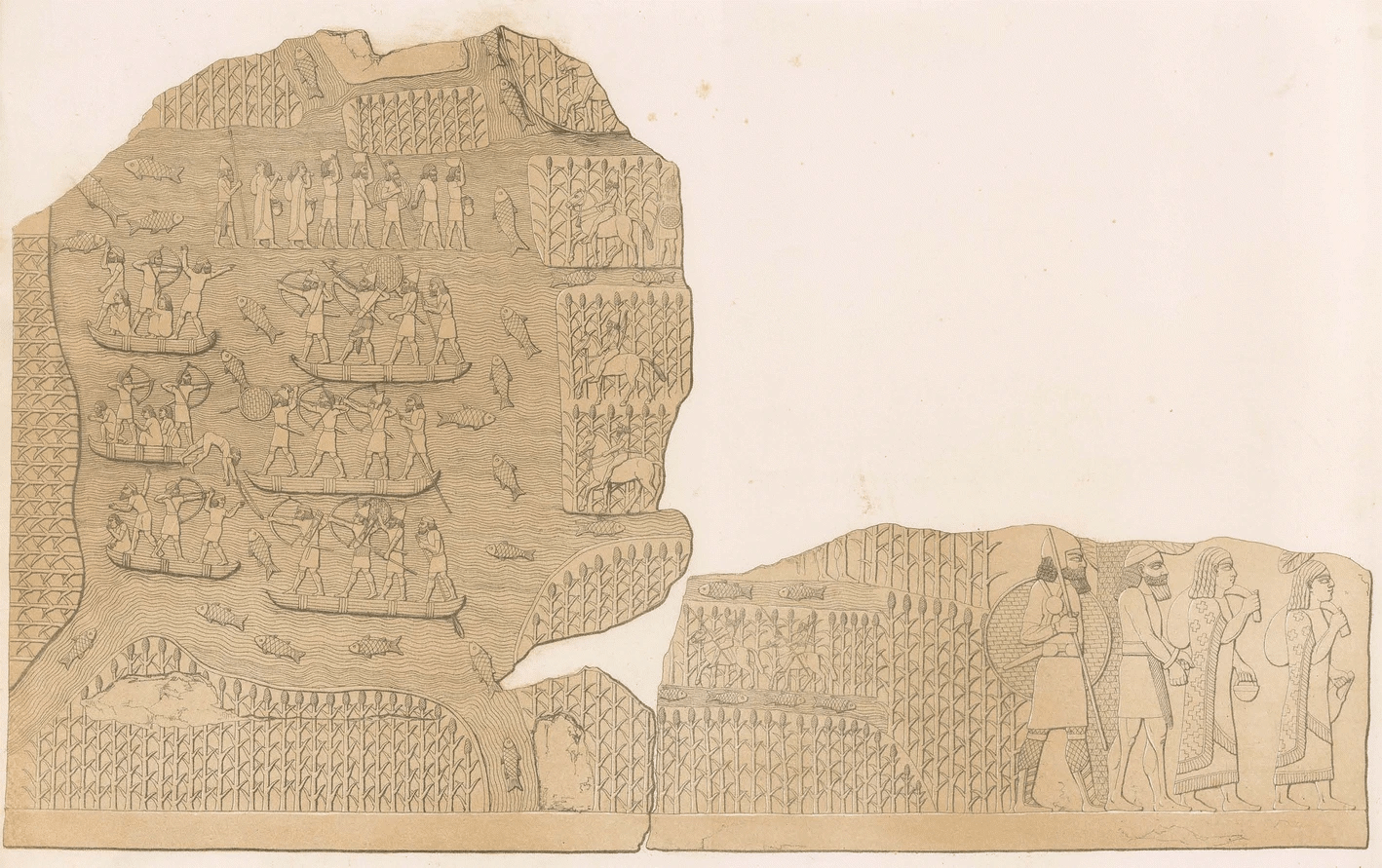
Marshes on wall panel
343794001, © The Trustees of the British Museum. Shared under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-SA 4.0) licence.
Marshes on wall panel
1613413114, © The Trustees of the British Museum. Shared under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-SA 4.0) licence.
Marshes on wall panel
312724001, © The Trustees of the British Museum. Shared under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-SA 4.0) licence.
Marshes on wall panel
Marshes on wall panel
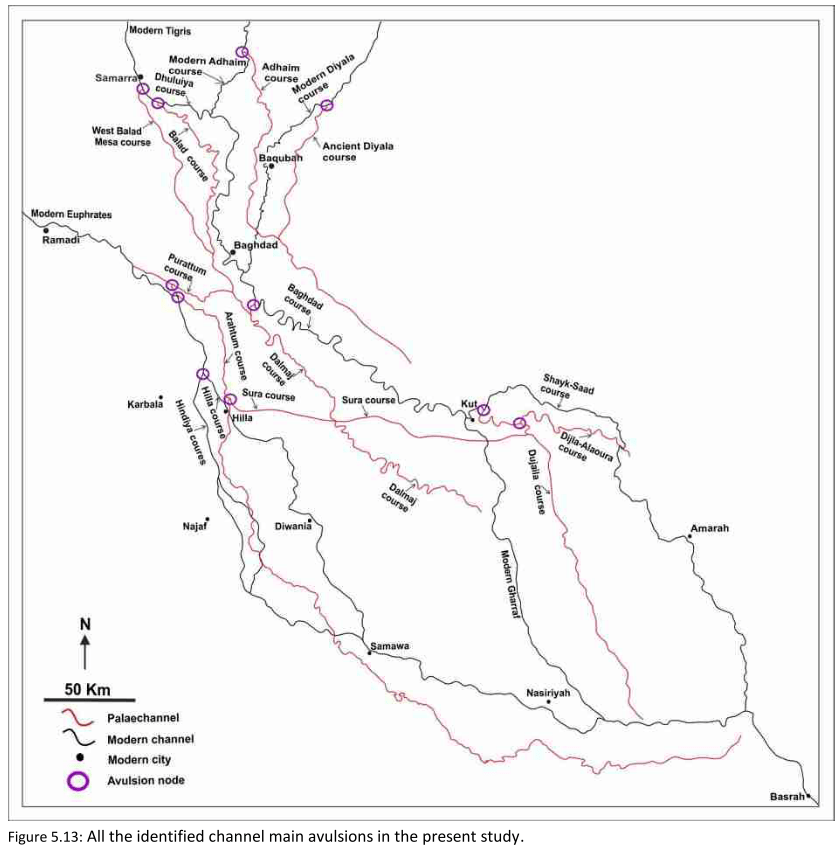
Main Paleochannels
Jotheri, J. (2016): Holocene avulsion history of the Euphrates and Tigris rivers in the Mesopotamian floodplain. PhD thesis, Durham, Fig. 5.13
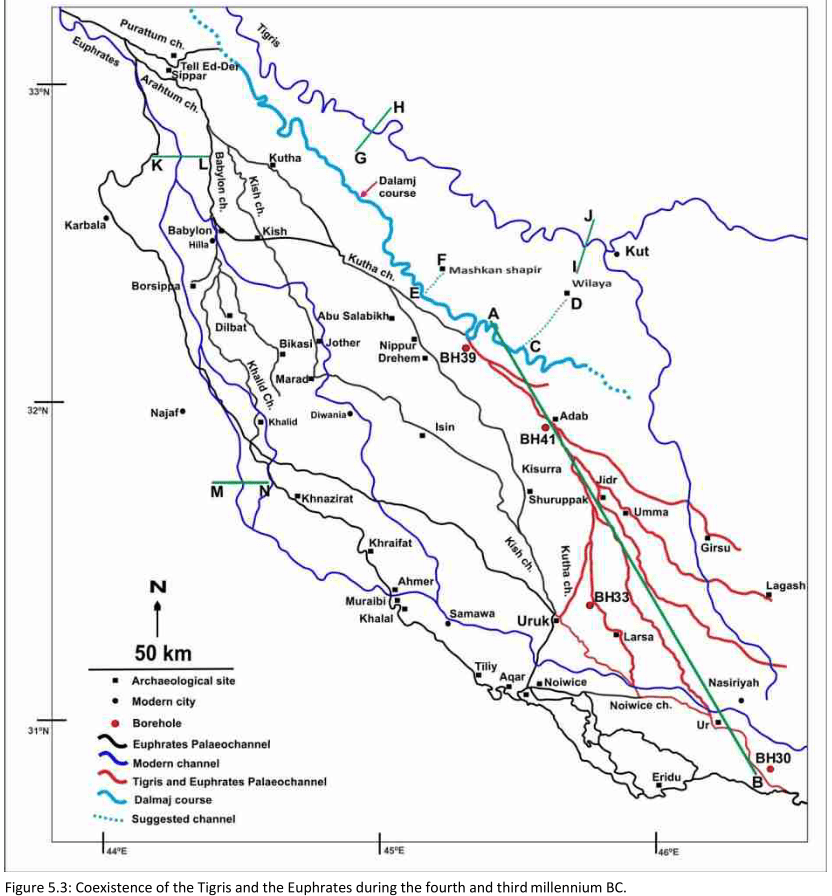
Main Paleochannels
Jotheri, J. (2016): Holocene avulsion history of the Euphrates and Tigris rivers in the Mesopotamian floodplain. PhD thesis, Durham, Fig. 5.3.
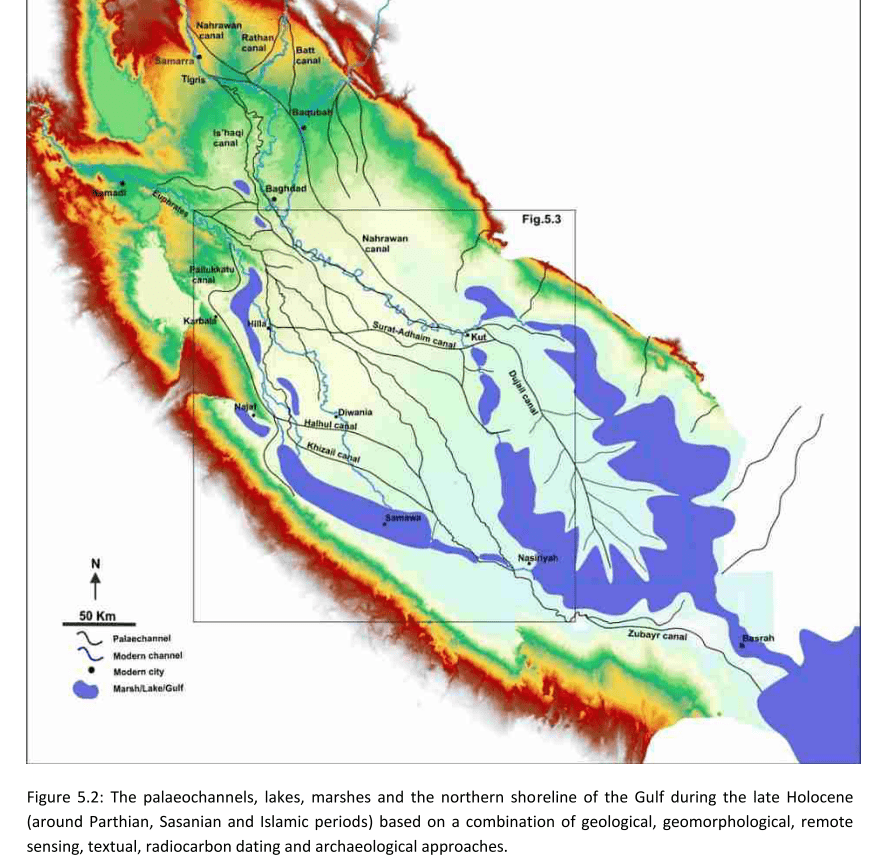
Main Paleochannels
Jotheri, J. (2016): Holocene avulsion history of the Euphrates and Tigris rivers in the Mesopotamian floodplain. PhD thesis, Durham, Fig. 5.2.
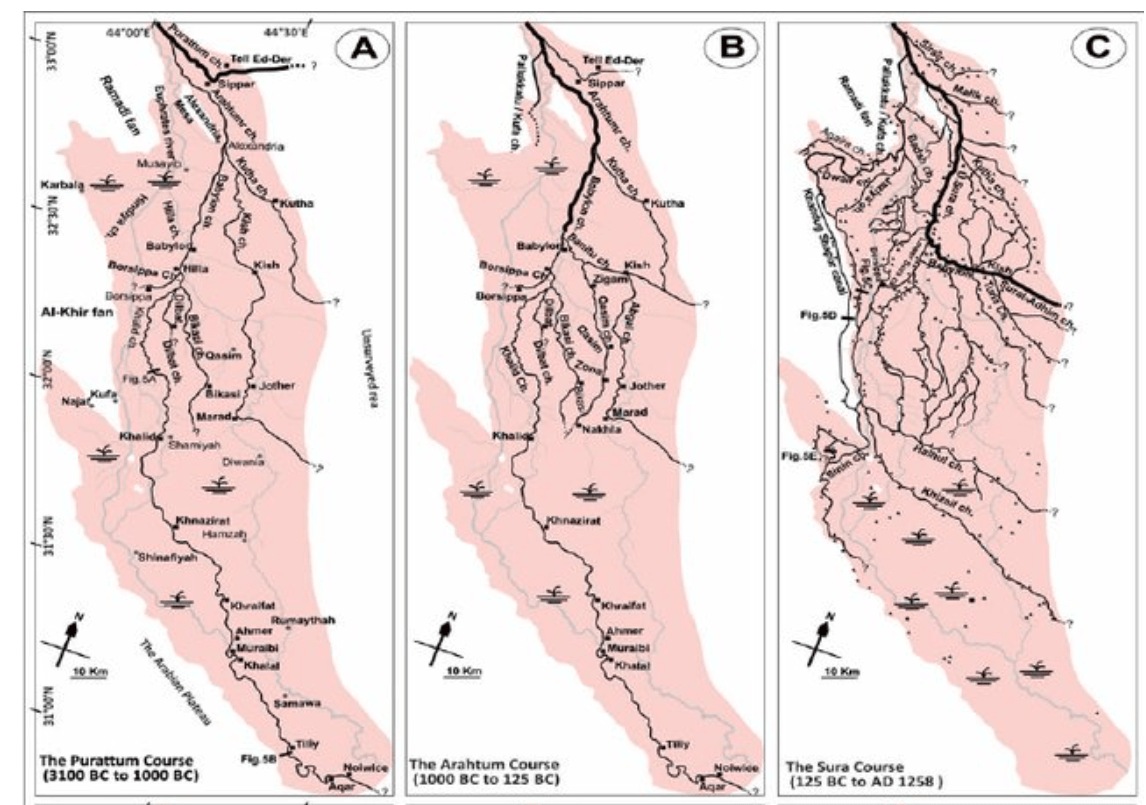
Purattum, Arahtum and Sura Course
Jotheri, J./Allen, M.B./Wilkinson, T.J. (2016): Holocene Avulsions of the Euphrates River in the Najaf Area of Western Mesopotamia. Impacts on Human Settlement Patterns, Geoarchaeology 31: 3, 175–193, Fig. 6 A-C.
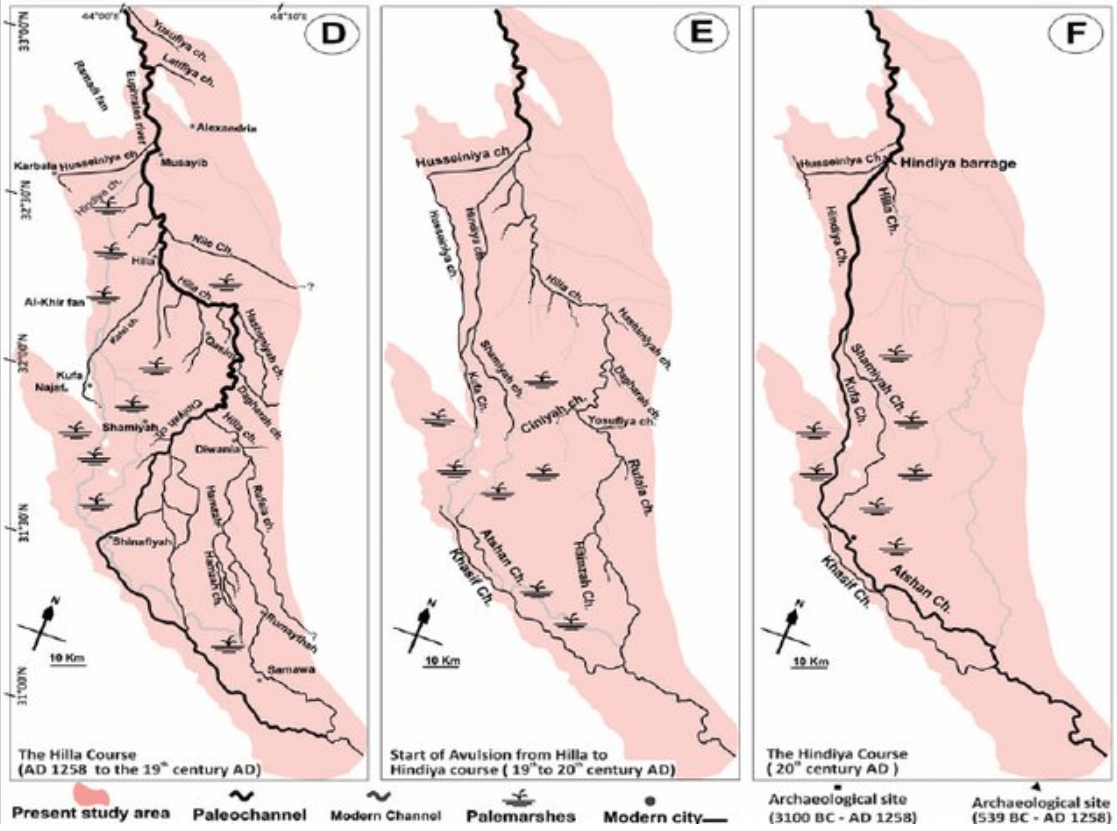
Hilla and Hindiya Course
Jotheri, J./Allen, M.B./Wilkinson, T.J. (2016): Holocene Avulsions of the Euphrates River in the Najaf Area of Western Mesopotamia. Impacts on Human Settlement Patterns, Geoarchaeology 31: 3, 175–193, Fig. 6 D-F.
Purattum
- 4.-1. mill. BCE
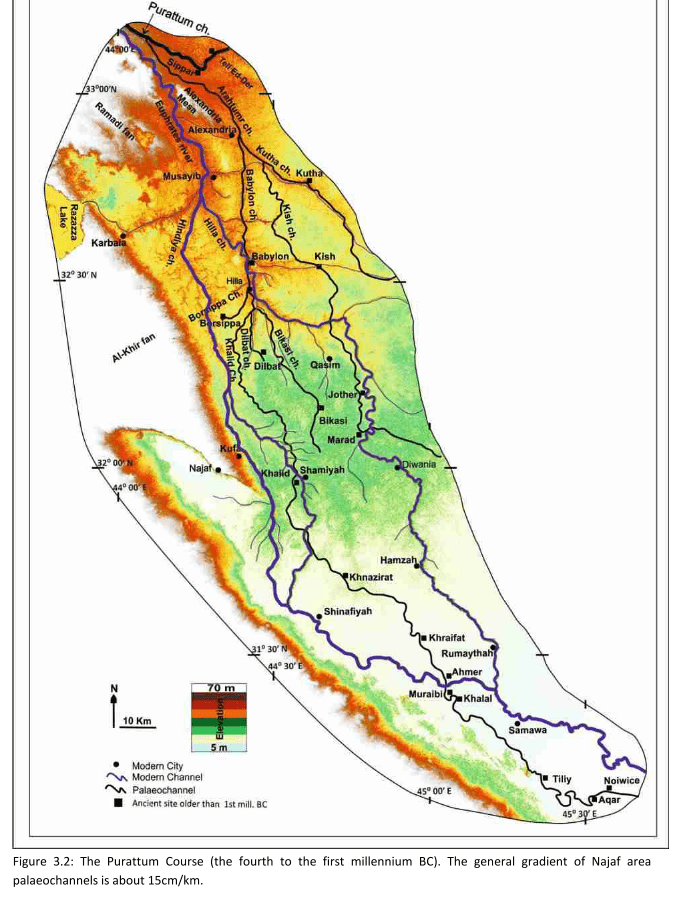
Jotheri, J. (2016): Holocene avulsion history of the Euphrates and Tigris rivers in the Mesopotamian floodplain. PhD thesis, Durham, Fig. 3.2.
Arahtum
- 1. mill. BCE
- Banitu Channel
Jotheri, J. (2016): Holocene avulsion history of the Euphrates and Tigris rivers in the Mesopotamian floodplain. PhD thesis, Durham, Fig. 3.3.
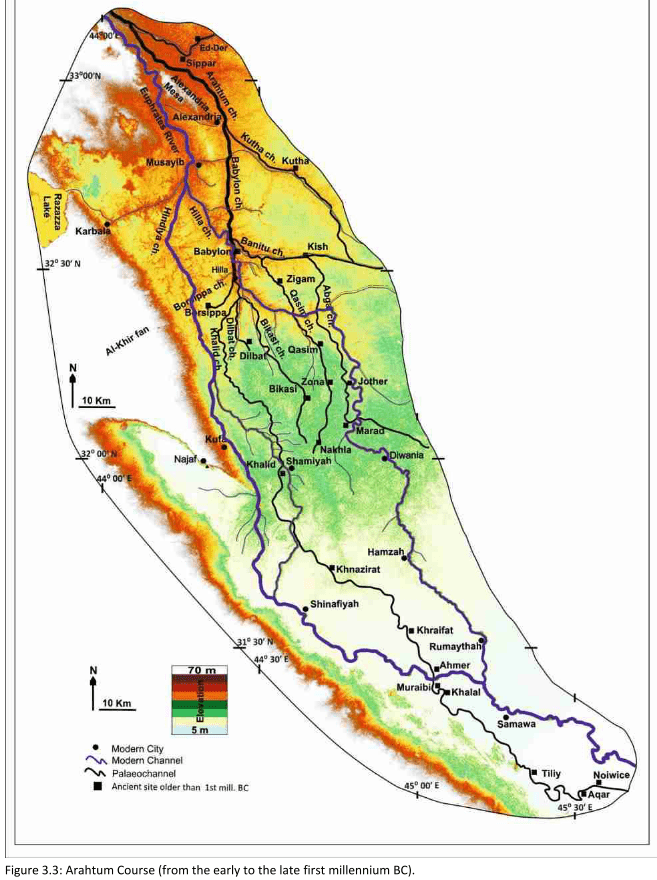
Sura
- 1. mill. BCE - 13. cent. CE
Jotheri, J. (2016): Holocene avulsion history of the Euphrates and Tigris rivers in the Mesopotamian floodplain. PhD thesis, Durham, Fig. 3.4.
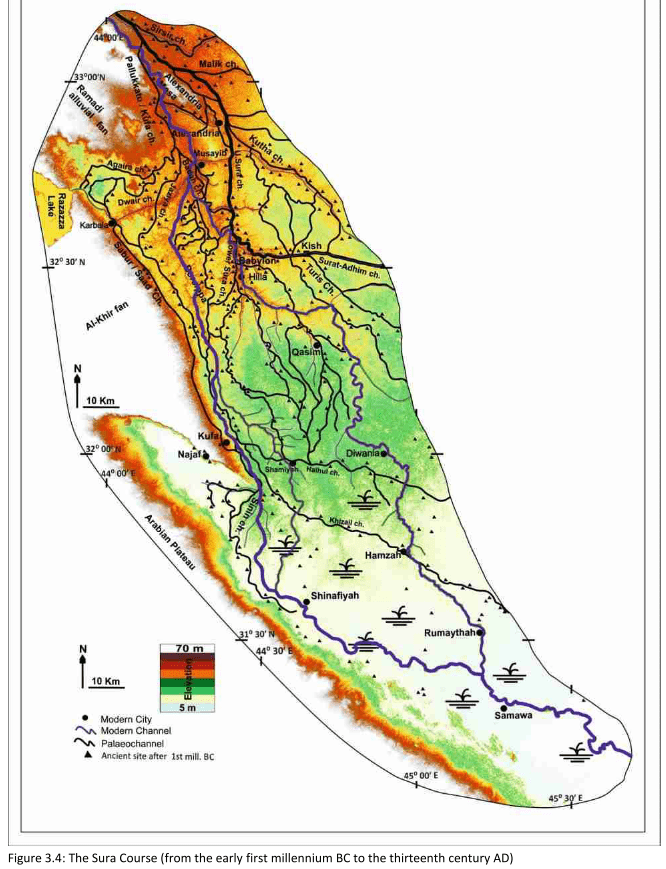
Hilla
- 13. -19. cent. CE
Jotheri, J. (2016): Holocene avulsion history of the Euphrates and Tigris rivers in the Mesopotamian floodplain. PhD thesis, Durham, Fig. 3.5.
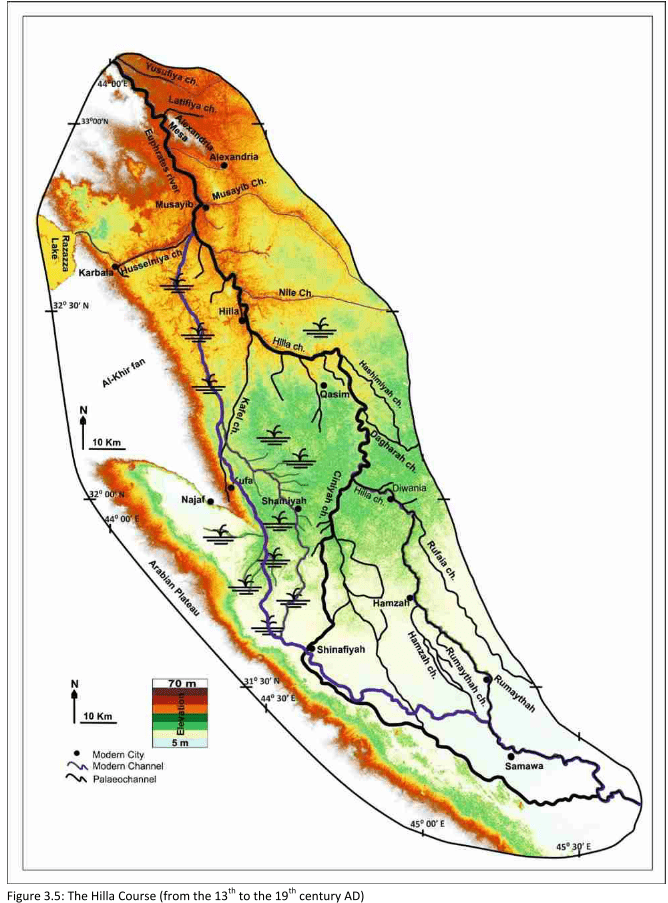
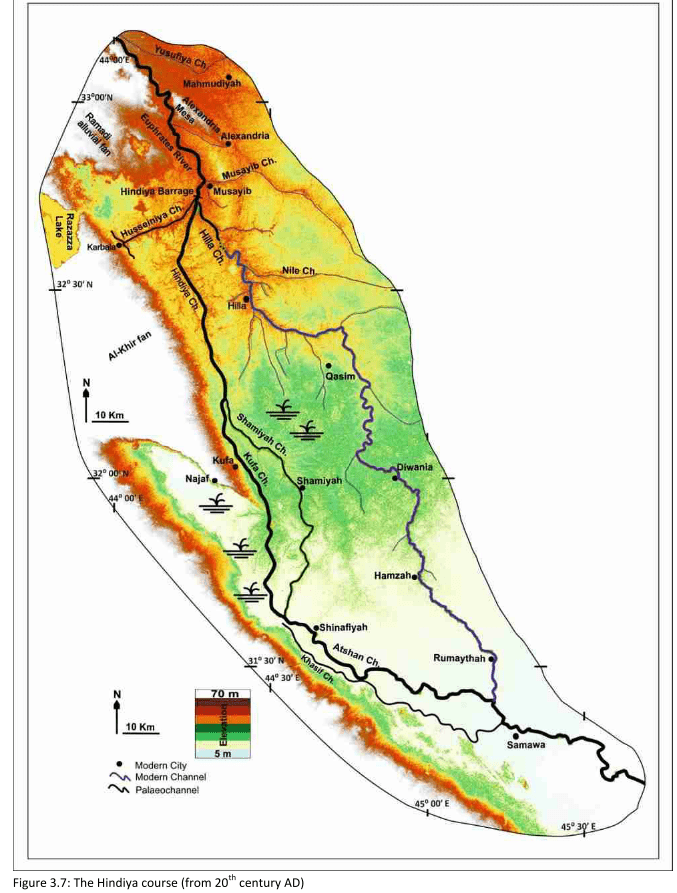
Hindiya
- 20. cent. CE
Jotheri, J. (2016): Holocene avulsion history of the Euphrates and Tigris rivers in the Mesopotamian floodplain. PhD thesis, Durham, Fig. 3.7.
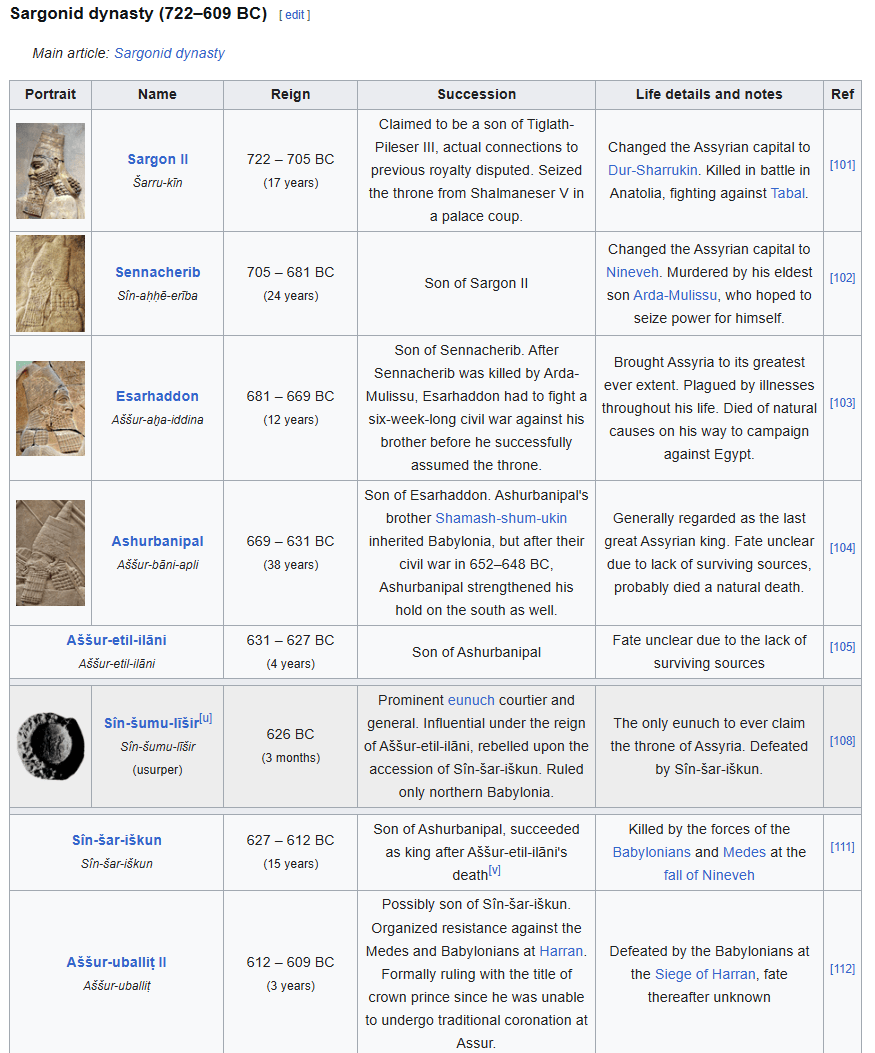
Assyrian Kinglist
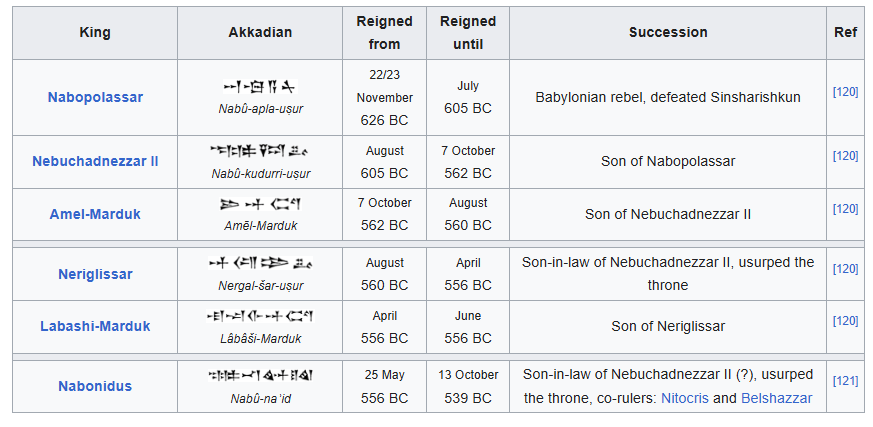
Neobabylonian KL
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_kings_of_Babylon
Homework
Wilkinson, T.J. (2013): Hydraulic Landscapes and Irrigation Systems of Sumer, in: Crawford, H.E.W. (ed.), The Sumerian world, Milton Park, Abingdon, 33–54.
Hydrography 07
By zastrugis
Hydrography 07
- 332