

NestJS Introductie
NestJS Introductie
NestJS


Definitie
Nest (NestJS) is a framework for building efficient, scalable Node.js server-side applications. It uses progressive JavaScript, is built with and fully supports TypeScript (yet still enables developers to code in pure JavaScript) and combines elements of OOP (Object Oriented Programming), FP (Functional Programming), and FRP (Functional Reactive Programming).

Installatie CLI
$ npm i -g @nestjs/cli
$ nest new project-name
App Structure


App Structure
-
app.controller.ts
- Een basale controller met één route
-
app.controller.spec.ts
- De unit tests van onze controller
-
app.module.ts
- De root module van onze applicatie
-
app.service.ts
- Een basale service met één methode

App Structure
-
main.ts
- De start file van onze applicatie die de core functionaliteiten zal initialiseren. We gebruiken hiervoor de NestFactory instantie.
import { NestFactory } from '@nestjs/core';
import { AppModule } from './app.module';
async function bootstrap() {
const app = await NestFactory.create(AppModule);
await app.listen(3000);
}
bootstrap();
Platform
const app = await NestFactory.create<NestExpressApplication>(AppModule);
Start je applicatie
- Met NPM
- npm run start
- Met yarn
- yarn start
Navigeer met je browser naar http://localhost:3000/.
Je krijgt nu Hello World! te zien.
NestJS Introductie
NestJS Building Blocks


Overzicht
- Controllers
- Providers (e.g. services)
- Modules
- Middleware
- Pipes
- Exception Filters

"Controllers are responsible for handling incoming requests and returning responses to the client."
Controllers

Controllers
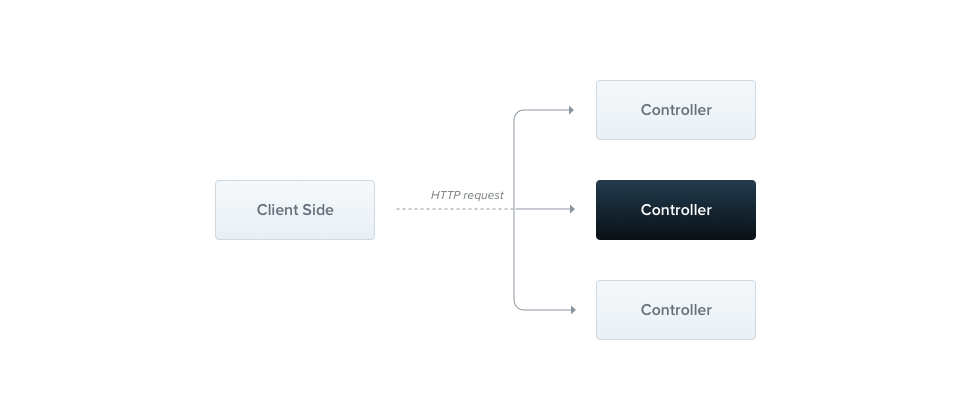

Controllers
import { Controller, Get } from '@nestjs/common';
@Controller('cats')
export class CatsController {
@Get()
findAll(): string {
return 'This action returns all cats';
}
}De response code is altijd 200, tenzij
- we een error hebben
- anders meegegeven via decorator

Controllers
Routing
import { Controller, Get, Req } from '@nestjs/common';
import { Request } from 'express';
@Controller('cats')
export class CatsController {
@Get('all')
findAll(@Req() request: Request): string {
return 'This action returns all cats';
}
}https://localhost:3000/cats/all

Controllers
Route Parameters
@Get(':id')
findOne(@Param() params): string {
console.log(params.id);
return `This action returns a #${params.id} cat`;
}Voeg de @Param decorator toe voor alle parameters of voor individuele parameters
@Get(':id')
findOne(@Param('id') id: string): string {
return `This action returns a #${id} cat`;
}

Controllers
HTTP Methods: @GET, @POST, @PUT, @DELETE
import { Controller, Get, Post } from '@nestjs/common';
@Controller('cats')
export class CatsController {
@Post()
create(): string {
return 'This action adds a new cat';
}
@Get()
findAll(): string {
return 'This action returns all cats';
}
}
Controllers
@Body
@Post()
async create(@Body() createCatDto: CreateCatDto) {
return 'This action adds a new cat';
}Maak een Data Transfer Object aan of DTO in een afzonderlijke dto folder. Geef het de filename create-cat.dto.ts.
export class CreateCatDto {
name: string;
age: number;
breed: string;
}
Controllers
Status Code
@Post()
@HttpCode(204)
create() {
return 'This action adds a new cat';
}
Controllers
Asynchrone Calls -> Out Of The Box
@Get()
async findAll(): Promise<any[]> {
return [];
}
Controllers
Voeg Controllers toe aan je AppModule
import { Module } from '@nestjs/common';
import { CatsController } from './cats/cats.controller';
@Module({
controllers: [CatsController],
})
export class AppModule {}
"Many of the basic Nest classes may be treated as a provider – services, repositories, factories, helpers, and so on. The main idea of a provider is that it can be injected as dependency; this means objects can create various relationships with each other, and the function of "wiring up" instances of objects can largely be delegated to the Nest runtime system."
Providers

Providers
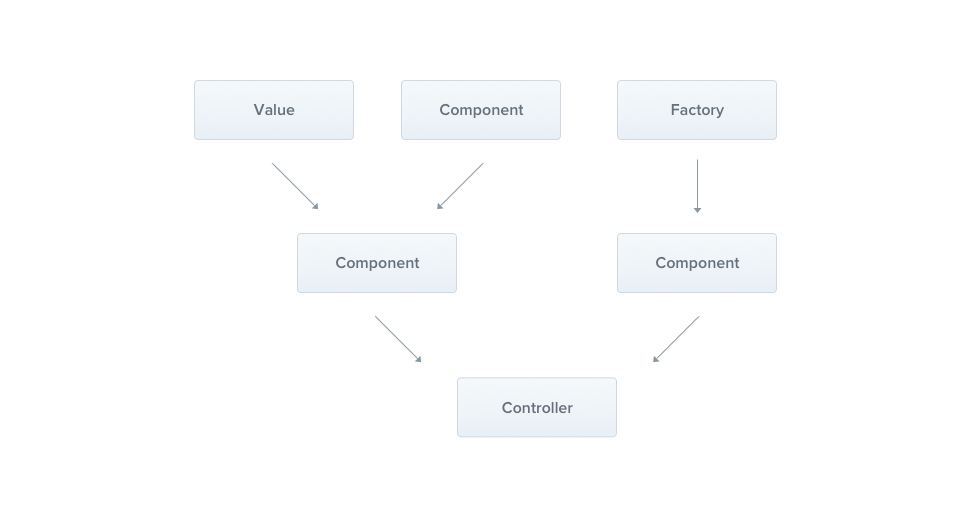
Providers zijn plain JavaScript classes die worden gedeclareerd in een module.

Services
import { Injectable } from '@nestjs/common';
import { Cat } from './interfaces/cat.interface';
@Injectable()
export class CatsService {
private readonly cats: Cat[] = [];
create(cat: Cat) {
this.cats.push(cat);
}
findAll(): Cat[] {
return this.cats;
}
}
Services
- Maak een service aan met de CLI: nest g service cats
- De CatsService is een basic klasse, met een @injectable() decorator.
- De CatsService maakt gebruik van de Cat interface:
export interface Cat {
name: string;
age: number;
breed: string;
}
Service in een Controller
import { Controller, Get, Post, Body } from '@nestjs/common';
import { CreateCatDto } from './dto/create-cat.dto';
import { CatsService } from './cats.service';
import { Cat } from './interfaces/cat.interface';
@Controller('cats')
export class CatsController {
constructor(private catsService: CatsService) {}
@Post()
async create(@Body() createCatDto: CreateCatDto) {
this.catsService.create(createCatDto);
}
@Get()
async findAll(): Promise<Cat[]> {
return this.catsService.findAll();
}
}De CatsService wordt geïnjecteerd door de constructor. In dit geval is de catService private.

Provider registratie
- We plaatsen de service in de providerse array in app.module.ts.
import { Module } from '@nestjs/common';
import { CatsController } from './cats/cats.controller';
import { CatsService } from './cats/cats.service';
@Module({
controllers: [CatsController],
providers: [CatsService],
})
export class AppModule {}
Providers


A module is a class annotated with a @Module() decorator. The @Module() decorator provides metadata that Nest makes use of to organize the application structure.
Modules

Modules
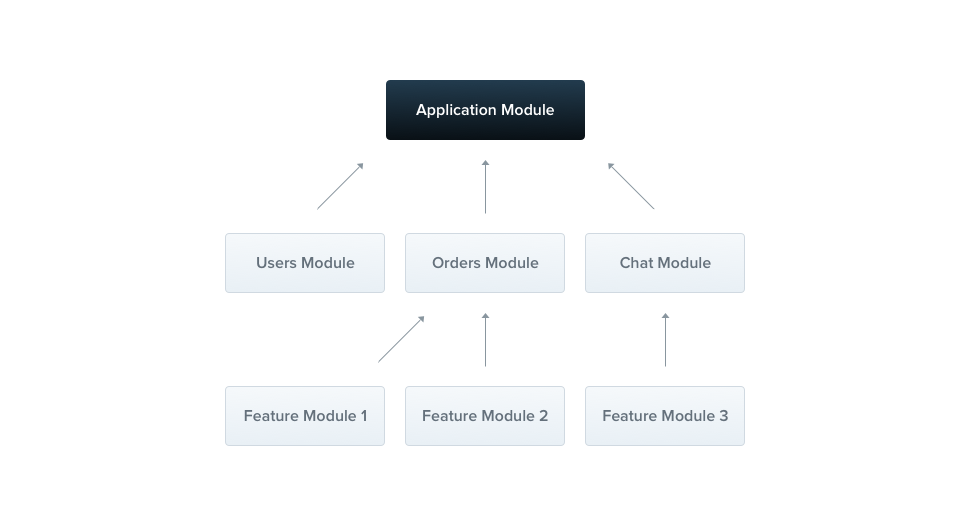

Modules
- Elke applicatie heeft minstens één module, een root module.
- De @Module decorator heeft een object met volgende properties:
- providers: één of meerdere providers
- controllers: één of meerdere controllers
- imports: lijst met te importeren providers
- exports: lijst met te exportere providers

Module
import { Module } from '@nestjs/common';
import { CatsController } from './cats.controller';
import { CatsService } from './cats.service';
@Module({
controllers: [CatsController],
providers: [CatsService],
})
export class CatsModule {}cats/cats.module.ts
Maak een service aan met de CLI: nest g module cats

Module
import { Module } from '@nestjs/common';
import { CatsModule } from './cats/cats.module';
@Module({
imports: [CatsModule],
})
export class AppModule {}app.module.ts

Modules
Deel een service provider met andere modules door ze te exporteren
import { Module } from '@nestjs/common';
import { CatsController } from './cats.controller';
import { CatsService } from './cats.service';
@Module({
controllers: [CatsController],
providers: [CatsService],
exports: [CatsService]
})
export class CatsModule {}Elke module die CatModule importeert, heeft toegang tot de CatsService.

Modules


Middleware

Middleware
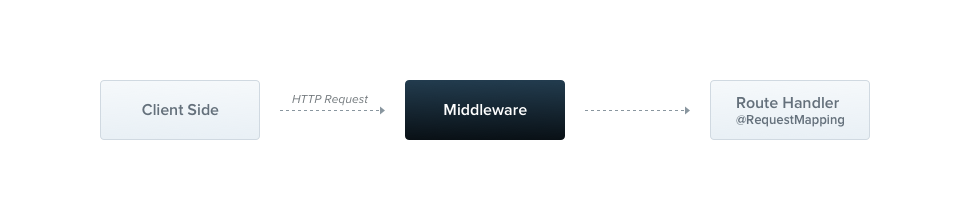

Middleware
- Schrijf middleware in een klasse met de @injectable decorator.
- De klasse implementeert de NestMiddleware interface.
import { Injectable, NestMiddleware } from '@nestjs/common';
import { Request, Response, NextFunction } from 'express';
@Injectable()
export class LoggerMiddleware implements NestMiddleware {
use(req: Request, res: Response, next: NextFunction) {
console.log('Request...');
next();
}
}
logger.middleware.ts

Middleware
import { Module, NestModule, MiddlewareConsumer } from '@nestjs/common';
import { LoggerMiddleware } from './common/middleware/logger.middleware';
import { CatsModule } from './cats/cats.module';
@Module({
imports: [CatsModule],
})
export class AppModule implements NestModule {
configure(consumer: MiddlewareConsumer) {
consumer
.apply(LoggerMiddleware)
.forRoutes('cats');
}
}Toepassen middleware in app.module.ts

Middleware
Gebruik forRoutes om nog specifieker middleware toe te passen:
import { Module, NestModule, RequestMethod, MiddlewareConsumer } from '@nestjs/common';
import { LoggerMiddleware } from './common/middleware/logger.middleware';
import { CatsModule } from './cats/cats.module';
@Module({
imports: [CatsModule],
})
export class AppModule implements NestModule {
configure(consumer: MiddlewareConsumer) {
consumer
.apply(LoggerMiddleware)
.forRoutes({ path: 'cats', method: RequestMethod.GET });
}
}
Middleware
Of gebruik een Controller in de forRoutes method:
import { Module, NestModule, MiddlewareConsumer } from '@nestjs/common';
import { LoggerMiddleware } from './common/middleware/logger.middleware';
import { CatsModule } from './cats/cats.module';
import { CatsController } from './cats/cats.controller.ts';
@Module({
imports: [CatsModule],
})
export class AppModule implements NestModule {
configure(consumer: MiddlewareConsumer) {
consumer
.apply(LoggerMiddleware)
.forRoutes(CatsController);
}
}
Middleware
Meerdere middleware kan je toevoegen in de apply() method:
consumer.apply(cors(), helmet(), logger).forRoutes(CatsController);
A pipe is a class annotated with the @Injectable() decorator. Pipes should implement the PipeTransform interface.
Pipes

Pipes

Pipes
- Pipes worden gebruikt voor:
- transformation: om input data te transformeren naar een gewenste vorm (bijv. van string naar integer)
- validation: om input data te evalueren. Geef de data terug als er geen probleem is, anders throw je een exception.

Pipes
Er zijn een aantal out-of-the-box types:
- ValidationPipe
- ParseIntPipe
- ParseFloatPipe
- ParseBoolPipe
- ParseArrayPipe
- ParseUUIDPipe
- ParseEnumPipe
- DefaultValuePipe

Parse[]Pipe
- Parse pipes zijn built-in transformation pipes.
- ParseIntPipe:
@Get(':id')
async findOne(@Param('id', ParseIntPipe) id: number) {
return this.catsService.findOne(id);
}GET localhost:3000/abc{
"statusCode": 400,
"message": "Validation failed (numeric string is expected)",
"error": "Bad Request"
}
ValidationPipe
- Om deze te gebruiken, installeer:
$ npm i --save class-validator class-transformer
of
$ yarn add class-validator class-transformer
Validation Pipe
- Pas main.ts aan:
async function bootstrap() {
const app = await NestFactory.create(AppModule);
app.useGlobalPipes(new ValidationPipe());
await app.listen(3000);
}
bootstrap();
Validation Pipe
Neem volgende endpoint:
@Post()
create(@Body() createUserDto: CreateUserDto) {
return 'This action adds a new user';
}import { IsEmail, IsNotEmpty } from 'class-validator';
export class CreateUserDto {
@IsEmail()
email: string;
@IsNotEmpty()
password: string;
}Valideer dto met de decorators van 'class-validator':

Validation Pipe
Wanneer er met bovenstaande regels een foute e-mail wordt ingevoerd, krijgen we volgende melding:
{
"statusCode": 400,
"error": "Bad Request",
"message": ["email must be an email"]
}Meer info over validation pipe: https://docs.nestjs.com/techniques/validation

Nest comes with a built-in exceptions layer which is responsible for processing all unhandled exceptions across an application. When an exception is not handled by your application code, it is caught by this layer, which then automatically sends an appropriate user-friendly response.
Exception Filter

Exception Filters

Exception Filters
Standaard is er een built-in global exception handler van het type HttpException. Deze genereert volgend JSON response:
{
"statusCode": 500,
"message": "Internal server error"
}
Exception Filters
We kunnen de HTTPException klasse ook gebruiken in een controller om specifieke fouten te melden:
@Get()
async findAll() {
throw new HttpException('Forbidden', HttpStatus.FORBIDDEN);
}De HTTPException neemt twee verplichte argumenten:
- response: kan een string of een object worden
- status: een HTTPStatus code

Exception Filters
De client zal volgende response teruggeven op bovenstaande endpoint:
{
"statusCode": 403,
"message": "Forbidden"
}
Exception Filters
Built-in HTTP exceptions zijn
- BadRequestException
- UnauthorizedException
- NotFoundException
- ForbiddenException
- NotAcceptableException
- RequestTimeoutException
- ConflictException
- GoneException
- More...
NestJS Introductie
By timdpaep
NestJS Introductie
- 571



