

Next.js
Next.js
Introductie


Next.js
Next.js enables you to create high-quality web applications with the power of React components.
- Full-stack framework
- Extremely popular:
13 million weekly downloads on npm - Not without controversy

Next.js
- Why Next.js and not a competitor?
-
TanStack Start
- Still in beta
-
Remix
- Unclear where it's going
-
TanStack Start

Next.js
- Built on top of React
- Consists of:
- Compiler
- Command Line Interface (CLI)
- Node.js runtime
- Full-stack, thus allows us to write front-end and
back-end code in the same project

Next.js
-
Installation
- ⚠️ Specifieer v15.5.2 want Next.js verandert snel!
npx create-next-app@15.5.2
What is your project named? my-first-next-app
Would you like to use TypeScript? Yes
Which linter would you like to use? ESLint
Would you like to use Tailwind CSS? Yes
Would you like your code inside a `src/` directory? Yes
Would you like to use App Router? (recommended) Yes
Would you like to use Turbopack? (recommended) Yes
Would you like to customize the import alias (`@/*` by default)? No
Next.js
- create-next-app genereert:
- Configuration files:
- Next.js
- ESLint
- TypeScript
- PostCSS
- .gitignore
- Configuration files:

Next.js
- create-next-app genereert:
-
public folder
- publieke assets: images, videos, fonts ...
-
next-env.d.ts
- ensures Next.js types are picked up by the TypeScript compiler
-
public folder

Next.js
- create-next-app genereert:
-
src/app
- favicon.ico
- globals.css
- layout.tsx
- page.tsx
-
src/app
Next.js
Rendering environments


Rendering environments
- We moeten eens praten over full-stack
- Client(-side) rendering → client components
-
Server(-side) rendering → server components (RSC)
- Static (build time)
- Dynamic (request time)

Rendering environments
-
Client-side rendering
- Large bundles
- Resource-intensive
- No SEO
- Less secure

Rendering environments
-
Server-side rendering
- Smaller bundles
- Resource efficient
- SEO
- More secure

Rendering environments
- ⚠️ Maar server components kunnen NIET:
- Luisteren naar browser events
- Web APIs aanspreken
- State beheren
- Effects gebruiken
- ...

Rendering environments
- Daarom, als vuistregel:
- Server components: zo veel mogelijk
-
Client components: enkel wanneer nodig
- ⚠️ Hou client components zo klein mogelijk

Rendering environments
- Hoe herken je het type component in Next.js?
- Standaard: server
- Expliciet markeren met directives

Rendering environments
- Onthou ook alvast volgende concepten:

Streaming

Streaming
- Server stuurt initieel een fallback UI
- Skeleton loaders/screens
- Spinners
- ...
- Ondertussen wordt data opgehaald en de
actual UI samengesteld- Zodra opgehaald: server stuurt de actual UI
- Hydration (React)

Streaming

Streaming

Streaming
- Why skeleton loaders/screens?
- Prevent users from thinking the site isn’t working
- Illusion of a shorter wait time
- Reduce cognitive load
Next.js
Routing - part 1


Routing
- Next.js heeft 2 verschillende routing-mechanismen:
- App Router ✅
-
Pages Router❌
- Waarom kiezen wij App Router?
- Meer flexibiliteit 👍
-
"Pages Router is still supported but
App Router is recommended" 👍 - Complexer 👎

Routing
- ⚠️ Als je de documentatie van Next.js bekijkt, let er dan altijd op dat je App Router selecteert

Routing
- Filesystem-based routing
- De naamgeving en structuur van onze files en folders bepaalt hoe de routing werkt
- cf. TanStack Router (PGM4)
- Convention > configuration

Routing
- Belangrijkste routing files (.tsx)
- page
- layout
- loading
- not-found
- error
- route

Routing
- Belangrijkste routing folders
- src
- app
- pages
- public

Routing
- ⚠️ Gebruik geen <a> tags voor interne links
- Dit negeert de Next.js-router en zal steeds alle assets (JS, CSS ...) opnieuw downloaden
→ gebruik steeds <Link> - Voor externe links kan je wel <a> gebruiken
- Dit negeert de Next.js-router en zal steeds alle assets (JS, CSS ...) opnieuw downloaden

Prefetching
-
Prefetching makes navigation feel instant
- When a <Link> enters the viewport,
it is automatically prefetched
- When a <Link> enters the viewport,

Prefetching
-
Prefetching makes navigation feel instant
- Runs only in production
- To make a production build:
npm run build
npm run start
Routing - terminologie
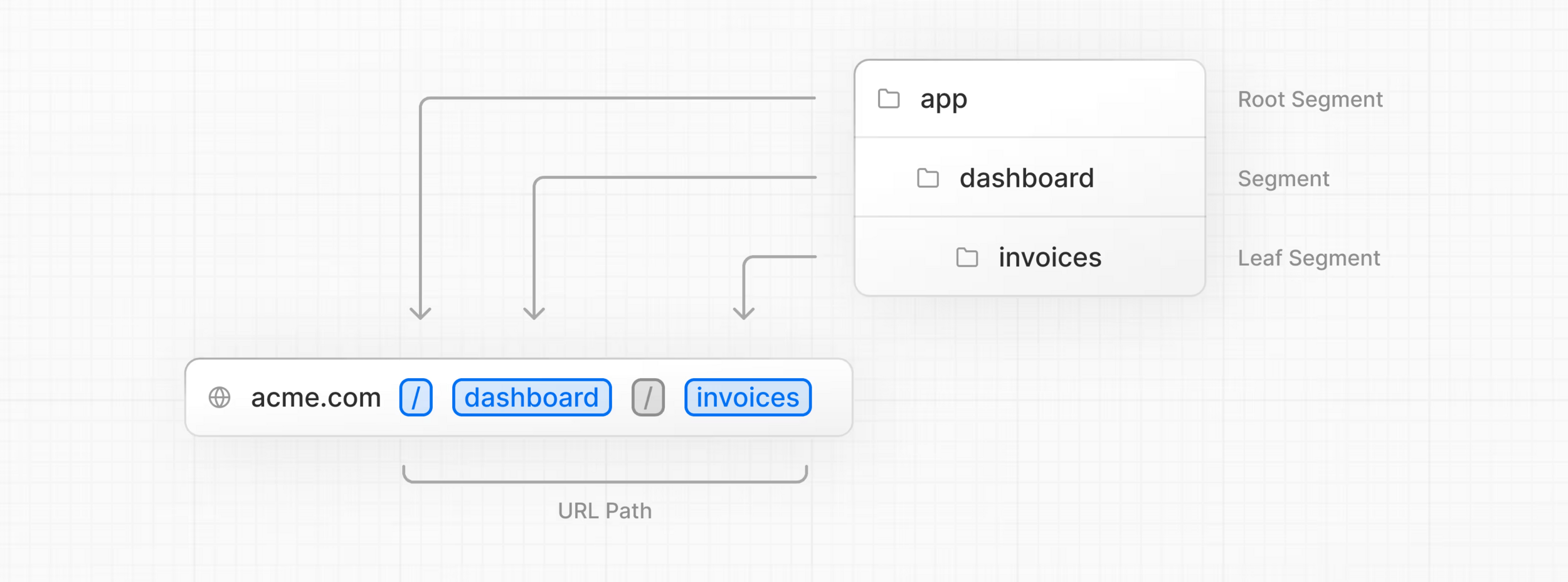

Routing - voorbeeld
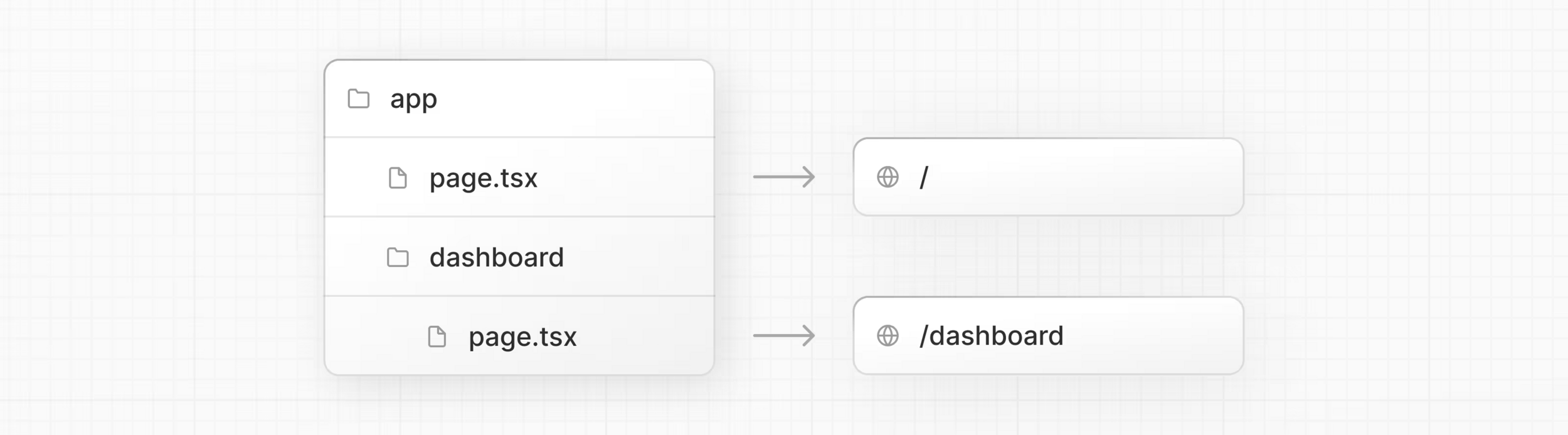

Routing - voorbeeld
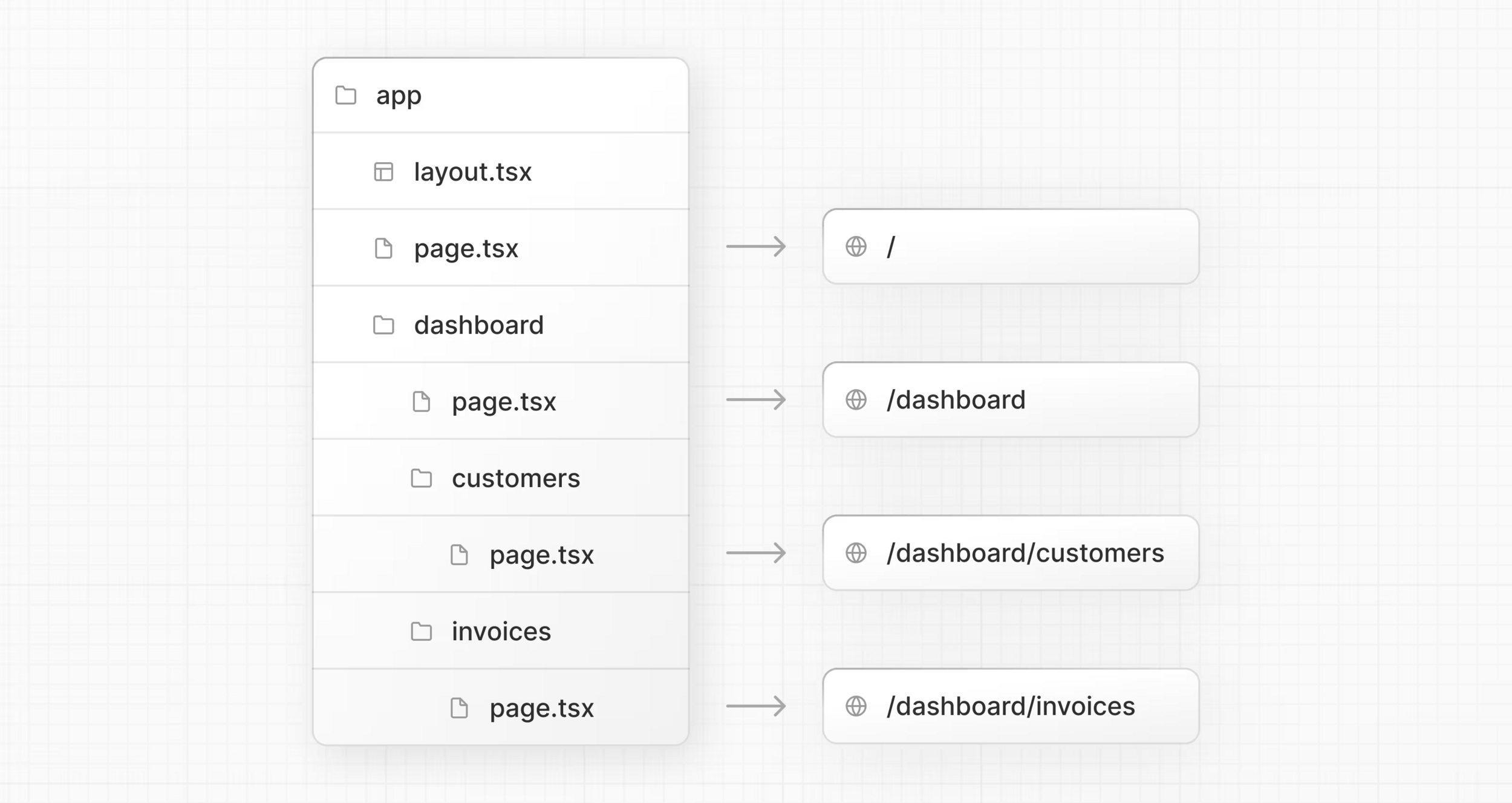

Routing - layouts
-
layout.tsx
- UI shared between multiple pages
- applies to leaf routes if no separate layout.tsx present
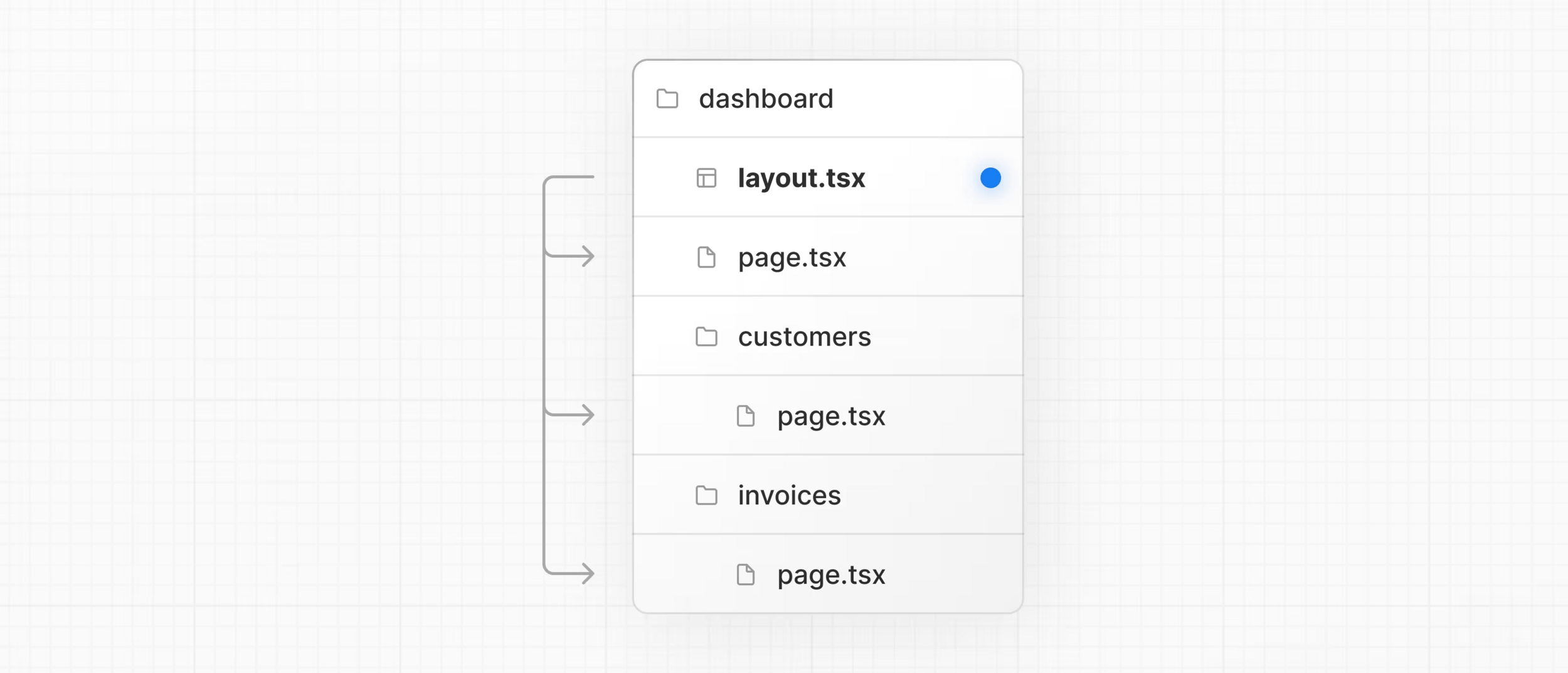

Routing - layouts
-
app/layout.tsx
- Root layout: required
- automatically generated with create-next-app

Routing
- Styling active links
-
usePathname
- Only works client-side
-
Often done with clsx or classnames
- ⚠️ Extra dependency → management cost
-
usePathname

Routing - voorbeeld
- Oefening (deel 1):
- / → homepagina
- /about → wat info over onszelf
- /users → tabel met 10 users (2 col: name + email)
-
Horizontale top nav
- Style the active link
Next.js
Data fetching


Data fetching
-
⚠️ How-to depends on the rendering environment
- Server components
- Client components

Data fetching
- ⚠️ Next.js extends the Web fetch API
- Some extra options regarding caching
- If we fetch data in a server component, by default Next.js will statically render the page
- 💥 Let's see this in action!
- To make Next.js render this dynamically,
we need to specify the cache options (see above)

Data fetching
-
Oefening (deel 2)
- / → homepagina
- /about → wat info over onszelf
- /users → tabel met name + email (https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/users)
- ⚠️ Don't forget to create an interface/type for a user
and use it appropriately!
Next.js
Routing - part 2


Dynamic route segments
- Terminology recap:
- http://localhost:3000/users/1
- Path param(eter), route param ...
- Next.js: dynamic route segment
- http://localhost:3000/users?name=abc
- Query param, URL param ...
- Next.js: search param(eter)
- http://localhost:3000/users/1

Dynamic route segments
- Convention for a dynamic route segment on id
- Folder:
[id] - Props:
{ params: Promise<{ id: string }> }
- Folder:
💥 Let's see this in action!

Dynamic route segments
/* Dynamic route segment example
* e.g. folder src/app/products/[id]/page.tsx
*/
export default async function ProductDetailPage({
params,
}: {
params: Promise<{ id: string }>;
}) {
const p = await params;
const id = p.id;
const response = await fetch(`https://dummyjson.com/products/${id}`, {
cache: "no-store",
});
const product = await response.json();
return <h2>{product.title}</h2>;
}

Dynamic route segments
-
Oefening (deel 3)
- / → homepagina
- /about → wat info over onszelf
-
/users → tabel met name + email
- name → Link naar detailpagina
- /users/:id → detailpagina (name, email, phone ...)
(https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/users/1)

Query parameters
- For retrieving search / query / URL params on a page:
-
Props:
searchParams: Promise<{ [key: string]: string | string[] | undefined }>
-
Props:
💥 Let's see this in action!

Query parameters
-
Oefening (deel 4)
- / → homepagina
- /about → wat info over onszelf
-
/users → tabel met name + email
- name → Link naar detailpagina
- filter on username with search parameter
- /users/:id → detailpagina (name, email, phone, website ..)

Query parameters
- Oefening (deel 4)
Next.js
Loading


Loading
- We can implement a loading UI with loading.tsx
- Skeleton loaders
- Spinners
- Loading message
- ...
- 💥 Let's see this in action!

Loading
- The JSONplaceholder API is super fast.
So, how can we test the loading UI?- Browser DevTools → Network → 3G
- delay

Loading
-
Oefening (deel 5)
- We have 2 pages where data is fetched
- /users
- /users/:id
- While data is fetched, show "Loading ..."
→ loading.tsx
- We have 2 pages where data is fetched

Skeleton loaders
- Options for implementing skeleton loaders?
- react-loading-skeleton
- Built-in to component library
- Do It Yourself 🔥

Skeleton loaders
- How-to:
- Copy-paste the UI from page.tsx to loading.tsx
- Replace back-end data with the skeleton
- Use your brains! 🧠
- Test to see if it's working as expected
- 💥 Let's see this in action!

Loading
-
Oefening (deel 6)
- /users → implement skeleton loader
- Use react-loading-skeleton
Next.js
Styling


Styling
We recommend using global styles for truly global CSS (like Tailwind's base styles), Tailwind CSS for component styling, and CSS Modules for custom scoped CSS when needed.
- Source: Official Next.js docs

Styling
- Why CSS Modules or Tailwind?
- Prevent style collision
- Avoid unused or duplicate CSS
- Code completion
→ VS Code extension (CSS Modules)
→ VS Code extension (Tailwind CSS IntelliSense)
- 💥 Let's see this in action!

Styling
- With CSS Modules, remember:
- Filename: component-name.module.css
- Apply lowerCamelCase for class names
- Use classes for local (component) styles
- Put global selectors in globals.css

Styling
- What approach should you take?
- Preferably the recommended one
- If not:
- Do not put everything in globals.css
- Make sure there is no collision
- Be prepared to explain the disadvantages
PGM5/2 - Next.js: introductie
By kareldesmet
PGM5/2 - Next.js: introductie
- 234



