AUTOMATION II: FEEDBACK
Ryan: FYS Computational Reasoning Fall 2025
Lecture content licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
See also
See Also
PLAYLIST
Notes (Google Drive)
IMage Gallery
Software tools
Excel PID Drone Simulation (.xlsx)
NetLogo Simulations
Google Docs version (lame)
Resources
Automation
STOP+THINK:What's the "AUTOMAT" Part?
These things were "AUTOMATIC" in that humans supplied the energy or the power but the device could carry out the sequence of activities "on its own."
The Secret: built-in CONTROL
AKA GOVERNANCE
from Kubernetes (κυβερνήτης, Greek for "governor", "helmsman" or "captain" or "steerer"; becomes gubernet- in Latin)
Earliest usages were more social than technical: governance of society
GOVERNANCE
Cybernetics

Cybernetics : the study of the control of systems.

TWO KINDS OF Automation
Instruction Following
Goal Seeking
An automatic machine is one that, once turned on, operates without human intervention.
components of a GOAL-SEEKING automatic machine
Set Point: the goal
Actuator: generates force
Mechanism: transmit and focus force
Sensor: detects states
Controller: Compares sensor output to goal and adjusts actuator
Stop+Think: automatic kettle?

Set Point: ?
Controller: ?
Sensor: ?
Mechanism: ?
Actuator: ?
100C/212F
thermocouple
spring and thermocouple
linkage from thermocouple to spring latch
arrangement of steam tube, thermocouple, spring, latch
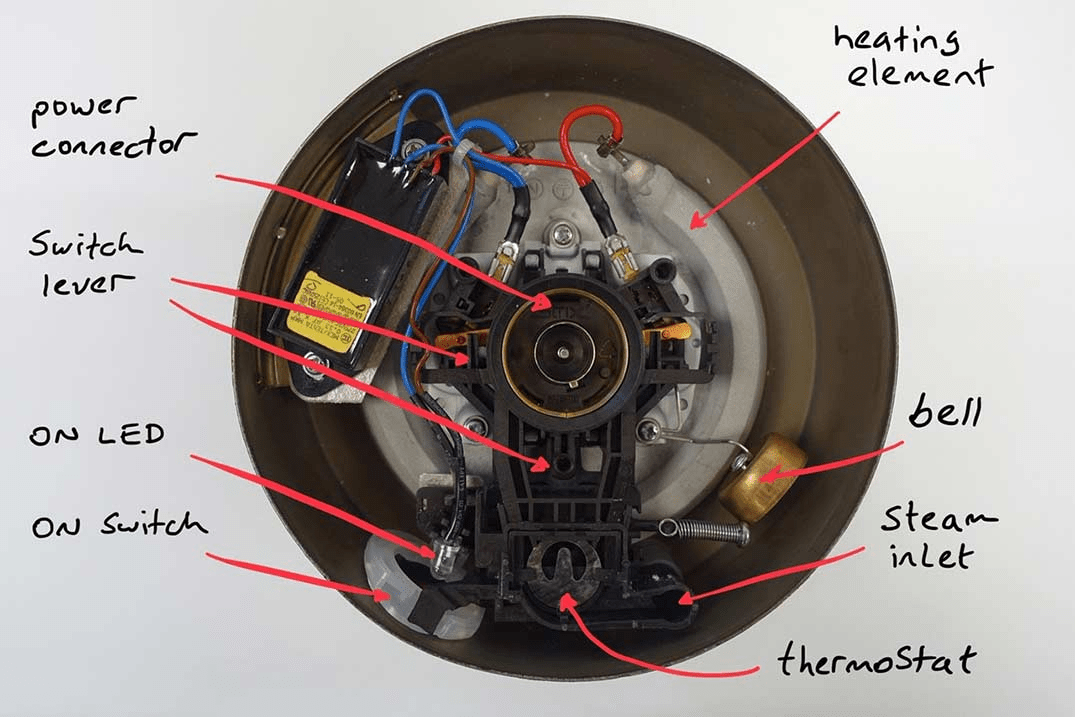
A paddle or rocker switch turns on the kettle. An LED is often used to show the kettle is operating. The switch operates a sprung lever that closes an electrical circuit to connect power to the heating element. An automatic mechanism turns the kettle off. There's a steam vent and tube leading down from the top of the water chamber to a bimetallic thermostat. When the kettle boils, steam whooshes down this tube. It heats the thermostat and makes it flip open, switching off the heating element and stopping the water from boiling. Some models have a small bell that rings when the contacts disengage. Kettles that heat water to a user-selectable temperature (below boiling) use a more complicated electronic switch and thermostat.
Automation as Sequence
centrifugal governor
Question
How does the centrifugal governor automatically control the speed of a steam engine?
A. When the engine speeds up, the fly balls move outward, lifting the sleeve
and closing the steam valve to slow the engine down.
B. When the engine speeds up, the fly balls move inward, lowering the
sleeve and opening the steam valve to slow the engine down.
C. When the engine slows down, the fly balls move outward, lifting the sleeve
and closing the valve to reduce steam.
D. The governor does not affect the valve; it only measures the engine’s speed.
Question:
How does the centrifugal governor automatically control the speed of a steam engine?
A. When the engine speeds up, the fly balls move outward, lifting the sleeve and closing the steam valve to slow the engine down.
B. When the engine speeds up, the fly balls move inward, lowering the sleeve and opening the steam valve to slow the engine down.
C. When the engine slows down, the fly balls move outward, lifting the sleeve and closing the valve to reduce steam.
D. The governor does not affect the valve; it only measures the engine’s speed.
✅ Correct answer: A
Question:
Why is the centrifugal governor an example of a feedback system?
A. Because it uses stored energy to keep the engine running longer.
B. Because the movement of the engine automatically provides information
that adjusts how much steam enters the engine.
C. Because it measures steam pressure but doesn’t change anything.
D. Because it needs a person to open and close the valve when the
engine speed changes.
Question
Why is the centrifugal governor an example of a feedback system?
A. Because it uses stored energy to keep the engine running longer.
B. Because the movement of the engine automatically provides information
that adjusts how much steam enters the engine.
C. Because it measures steam pressure but doesn’t change anything.
D. Because it needs a person to open and close the valve when the engine speed changes.
✅ Correct answer: B
Automation as Goal Seeking
CLOSE ENOUGH?
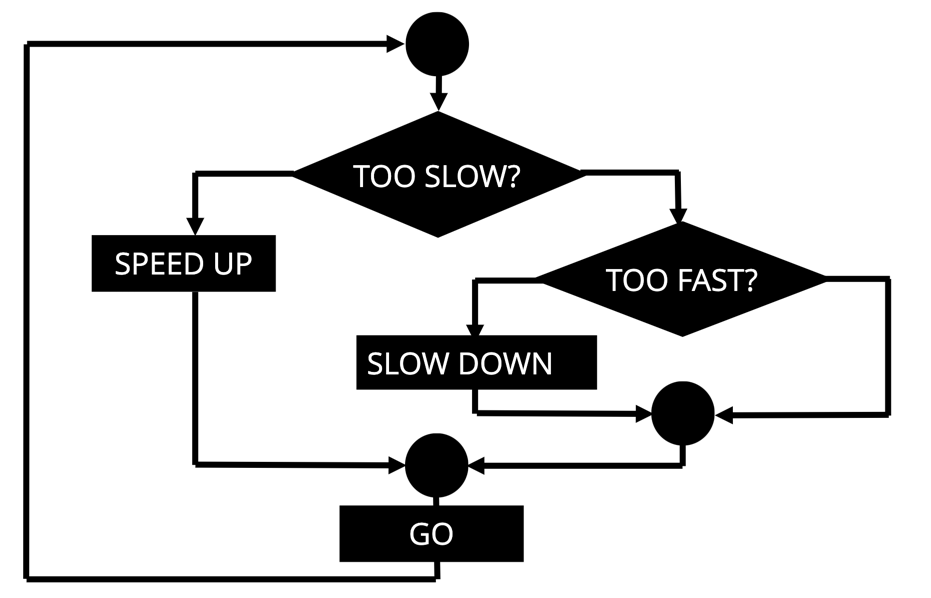
Automation as Goal Seeking: The infinite Loop of control
TOO FAST?
TOO SLOW?
SLOW DOWN
SPEED UP
GO
But where do these diamonds get the information they need to decide?

Automation as Goal Seeking
TOO FAST?
TOO SLOW?
SLOW DOWN
SPEED UP
GO
SENSORS!

Centrifugal Governor
17th century
Credited to Christiaan Huygens,
adapted by James Watt 1788.
Concept: balls spin under steam pressure; faster pressure, faster spin; faster spin, pull arms down; arm motion opens pressure release; pressure decrease leads to speed decrease and valve closes

Centrifugal Governor
17th century
Credited to Christiaan Huygens,
adapted by James Watt 1788.
Concept: balls spin under steam pressure; faster pressure, faster spin; faster spin, pull arms down; arm motion opens pressure release; pressure decrease leads to speed decrease and valve closes
steam
steam
centrifugal governor

FeedBACK
3
Title Text

How does a Stampede HAPPEN?
What does the system look like over time?
What does the system look like over time?


How does a thermostat work?

One horse runs. Others say "chill out, Max."
Two horses run. Others say, "Dudes, relax."
Three horses run. Nearby others say, "Hey, something happening?" And speed up a bit.
Others see change. Start hurrying
More horses perceive the change and pick up the pace...
What's the Relationship?

????
????
What's the Relationship?

Reinforcing
Loop
Causal Loop Diagrams
Direction of Relationships
Valence of Relationships
"When A grows, B grows"
A
B
Linked Causes and Effects
"A influences B"
A
B
A
B
+
-
"When A grows, B shrinks"
STOP+THINK: Draw the causal loop diagram for "The hungrier I am, the more I eat. The more I eat, the less hungry I am.
Hungry
+
-
Eating
"The hungrier I am, the more I eat.
The more I eat, the less hungry I am."
STOP+THINK: Draw the causal loop diagram for "When things go well, I get over confident and start to cut corners. Things start slipping and I get careful and then things go better."
Things Go Well
Confidence
+
Cut Corners
+
-

decision: sensor compared to set point
sensor
STOP+THINK: where is the sensor in each diagram? where is the setting? where is the actuator?
Why does this happen?
How do Toilets work?
How Does This Work?

Why does this happen?
How do these differ?

Open vs Closed
Loop Automation
In open-loop automation the control of the process is independent of the output.
In closed loop automation, the control of the process depends on feedback based on the output of the process.
Centrifugal Governor is an example of a
Closed Loop System




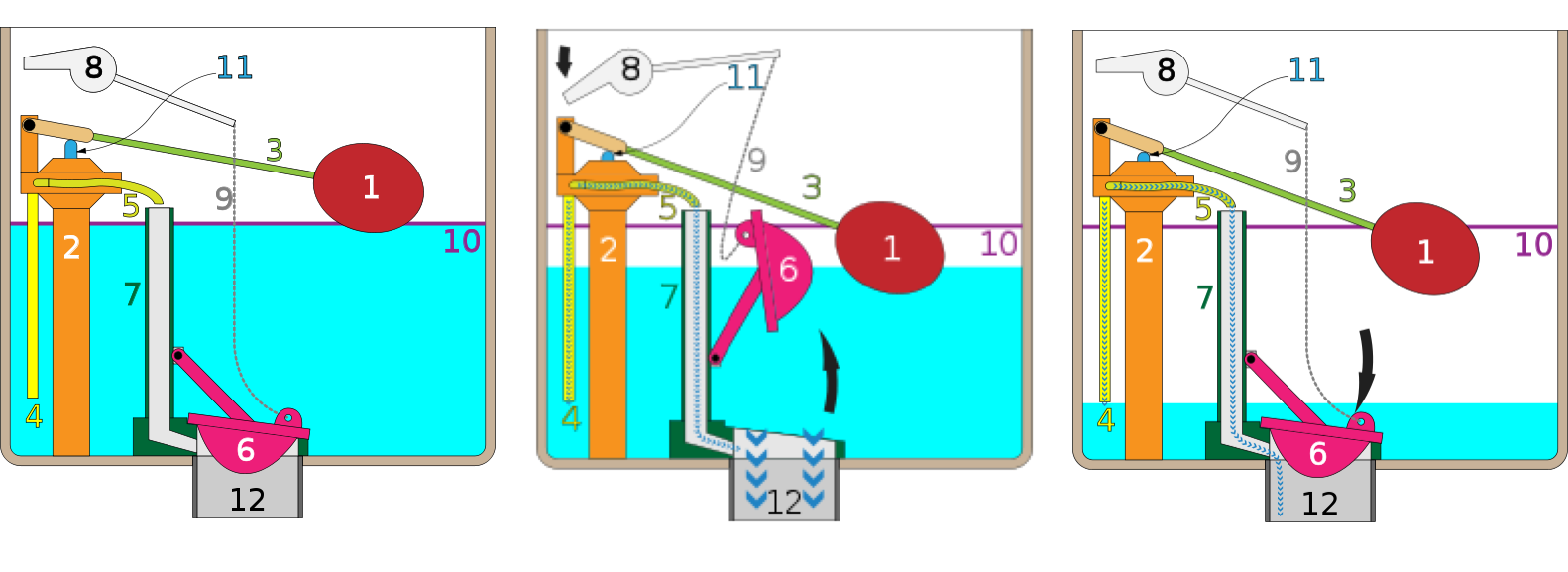
STOP+THINK: Open or Closed Loop?
Closed Loop Systems
Depend
on
Feedback
How do thermostats work?

ANSWER:
FEEDBACK
(or Lack of Feedback!)
Feedback
Evaluative information about a process that is available to a controller of that process
a system paying attention to the effect it has on the world.
Feedback
When an output is also an input
Feedback
INPUT
OUTPUT
DEF 1: a group of interacting or interdependent things
System
centrifugal governor

Biological Feedback
causal loop for insulin/glucagon

STOP+THINK: In the body, insulin is a hormone produced by beta cells of the pancreas in response to high blood glucose. It promotes absorption of glucose from the blood into cells of the liver, fat, and skeletal muscles.[8]
The pancreas releases glucagon when the amount of glucose in the bloodstream is too low. Glucagon raises the concentration of glucose and fatty acids in the bloodstream. Draw a causal loop diagram that captures the relationship between concentrations of insulin, glucose, and glucagon.
System
something about A has an effect on B
something about B has an effect on A
System
something about A has an effect on B
something about B has an effect on A
the more B panics, the more A panics
the more A panics, the more B panics

How
do you adjust
the water to be the right temperature for washing your hands?
STARTING TEMPERATURE
DESIRED TEMPERATURE
ADJUST
HOT/COLD

Tactual
Tset
More Hot
GAP=Tset - Tactual
+
_
+
+
STOP+THINK: How does increase in actual temperature affect GAP?
STOP+THINK: How does increase in desired temperature affect GAP?
STOP+THINK: Does positive GAP mean we want more cold or more hot?
More HOT means ACTUAL temperature which means GAP
larger
smaller
higher
lower
???
???
Larger GAP means water is too
hot
cold
???
Causal Loop Diagrams
Each measurable cause/effect is represented by a word or phrase
Arrows point from causes to effects
Arrows are labeled + or - to indicate positive or negative (inverse) causal relationships.
population
births
deaths
See also
- Lannon, Colleen. "Causal Loop Construction: The Basics" @ The Systems Thinker
- DonnaGurule. 2018. "Systems Thinking: Causal Loop Diagrams" (16m40s)
- The Climate Leader. 2015. "Causal Diagrams" (8m34s)

-
+
+

-
+
+


-
+
+
We might start out too cold,
add warm, still be a bit cold,
TIME
GAP
TIME
GAP
We might start out too cold,
add more warm, getting close,
just a bit more warm, ahhh, just right.
Add warm, still be a bit cold,
add more warm, now we are a bit too warm,
turn back the warm a bit, ahhh, just right.

I keep adjusting the temp and can never get it right. Always either too hot or too cold.It takes a bit of too hot, too cold, but finally it works out.These faucets are crazy. The more I fiddle with it the more it gets too hot and then too cold.No matter what you do, the faucet has no effect.It takes a slight adjustment and then its just right.I just touched the handle and it just got hotter and hotter and hotter.




STOP+THINK: Match the system behavior trace with the description.
Types of System Behavior Behavior


Title Text

Why does THIS HAPPEN?




What ARE THE QUANTITIES?

What's the Relationship?

+
+
How does the System behave?

+
+
TIME
Horses Running
Compare these two systems

+
+
Horses Running
TIME
TIME
GAP
Two Kinds of Feedback
Positive or Reinforcing
NEGAtive or BALANCING

Reinforcing
Loop
This is a positive feedback loop. AKA a "reinforcing" (R) loop. R loops always have an even number of minus signs.

-
+
+
Balancing
Loop

Reinforcing
Loop
This is a positive feedback loop. AKA a "reinforcing" (R) loop. R loops always have an even number of minus signs.



-
+
+
Balancing
Loop
This is a negative feedback loop. AKA a "balancing" (B) loop. B loops always have an odd number of minus signs.

STOP+THINK: Draw the causal loop diagram for the centrifugal governor
STOP+THINK: Draw the causal loop diagram for the centrifugal governor

HINT: Proceed stepwise. What are the quantities of interest here?

The more open the throttle,
the faster the machine.
The faster the machine,
the higher the rotational frequency.
The higher the rotational frequency,
the higher the angle.
The higher the angle,
the less open the throttle.
The less open the throttle,
the slower the machine.
References

https://storage.googleapis.com/ltkcms.appspot.com/fs/yd/images/cover/negative-feedback-loop.base?v=1587496185
Positive Feedback
Amplifier
amplifies
sound from
microphone.
Sound comes
out of speaker
and goes into
microphone.
If amplifier affects higher
pitched sounds more then higher pitch amplification outpaces
lower pitches and we hear screeeeeeeeeeech.

https://www.joboneforhumanity.org/
What does the system look like over time?


R loops produce unconstrained growth in a system.
Two Kinds of Automation
thermo stat
temperature unchanging
How does it work?
Room Cold?
Turn Heat ON
Room warm?
Turn Heat OFF
How does a thermostat work?

SET TEMPERATURE
THERMOMETER
SWITCH
CAUSAL LOOP
SET TEMP
ACTUAL TEMP
GAP
SWITCH
HEAT
But HOW are these causally related?
CAUSAL LOOP
SET TEMP
ACTUAL TEMP
GAP
HEAT
+
-
+
HOW does the "system" behave?
balancing loop
This is a negative feedback loop. AKA a "balancing" (B) loop. B loops always have an odd number of minus signs.

TIME
TEMP
SET TEMP
ACTUAL TEMP
GAP
Furnace switches off but some heat continues to flow
Furnace ON
B loops produce systems that oscillate or settle down.
Feedback
and
System Behavior

PID CONTROL
4
Next
The Problem of Control
How to automate the process of achieving a set output goal

from "GAP" to "ERROR"
Nicolas
Minorsky
1885-1970

Expert helmspersons pay attention to what's going on, how things are changing, and where things have been so far.
I
N
S
I
G
H
T
Expert Control Takes Account of...
How far off the target am I at the moment?
Is my error increasing or decreasing?
How well or how badly have I been doing overall?
PRESENT
PAST
FUTURE
Three Ways to Think about Error
Proportion = what is the current error?
Derivative = how is error changing?
Integral = how much error has accumulated?
PAST
FUTURE
PRESENT

https://youtu.be/wkfEZmsQqiA

Tutorial
Automation II: Feedback
By Dan Ryan
Automation II: Feedback
- 95