REPETITION
OUTTAKES
Backtracking
Brute force in sensibility but...
...abandoning before exhaustive search
Useful when "dead ends" are recognizable
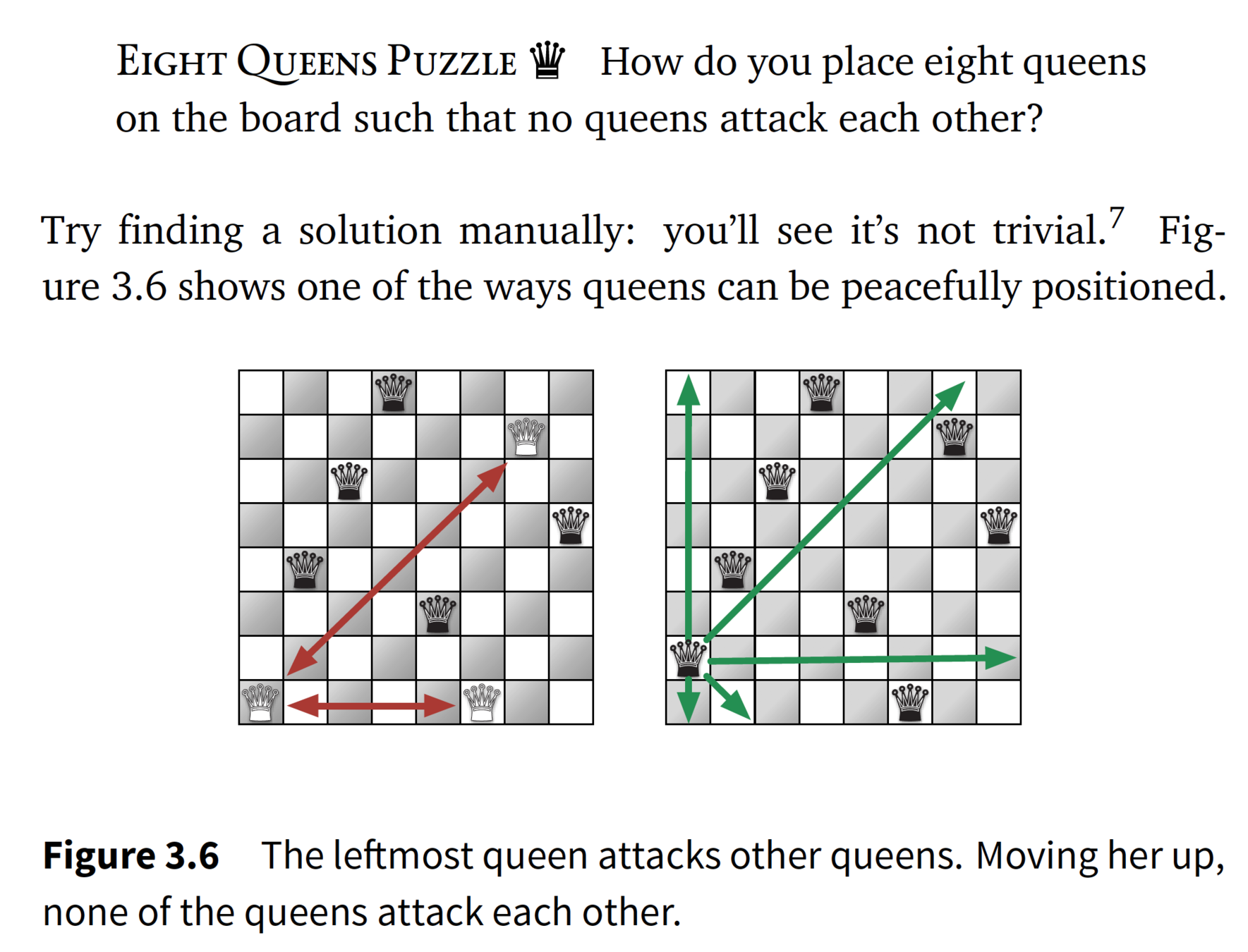
function queens(board) if board.has_8_queens //done return board for each position in board.unattacked_positions //try next open position board.place_queen(position) //is there a solution from here? solution ← queens(board) if solution //a returned solution is "true" return solution //no solution from last placement:backtrack board.remove_queen(position) //if all open positions have been tried return false
See Also
Finis
Back to Merge Sort
How many mergings?
6 repetitions of 52
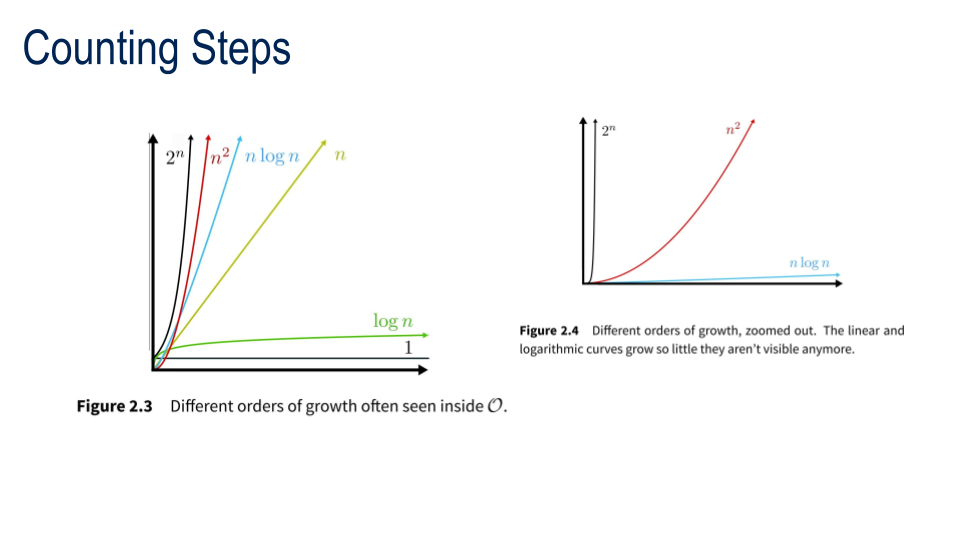
LOG N repetitions of N
NLOGN
Simple Iteration: Merge Sort
Complexity Take Away: Some tasks are a little harder than linear, but not as bad as the next level of complexity.
N log N
WE LIKE THIS.
Chapter 3
Nested Loops
Let's Make Soup
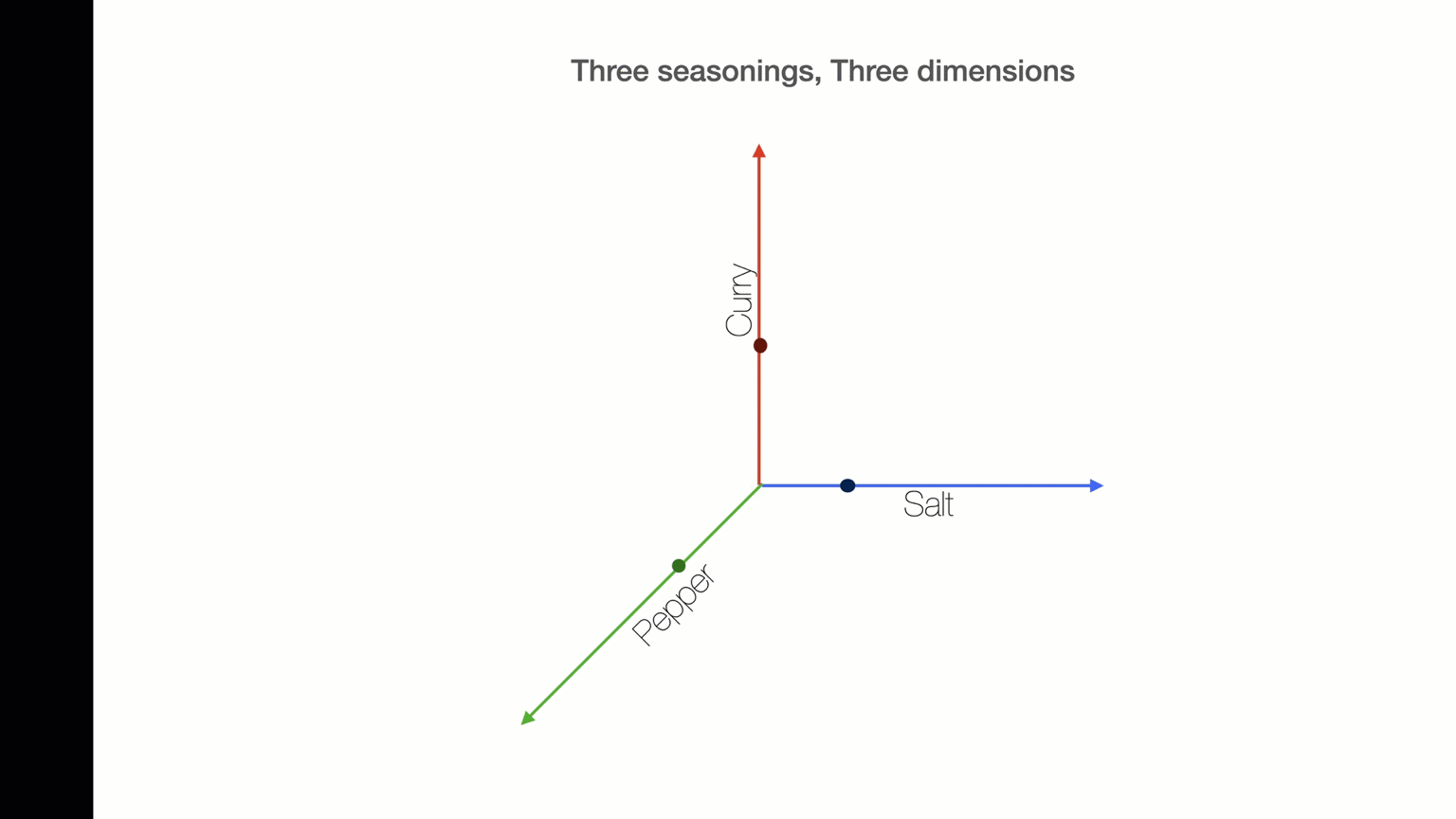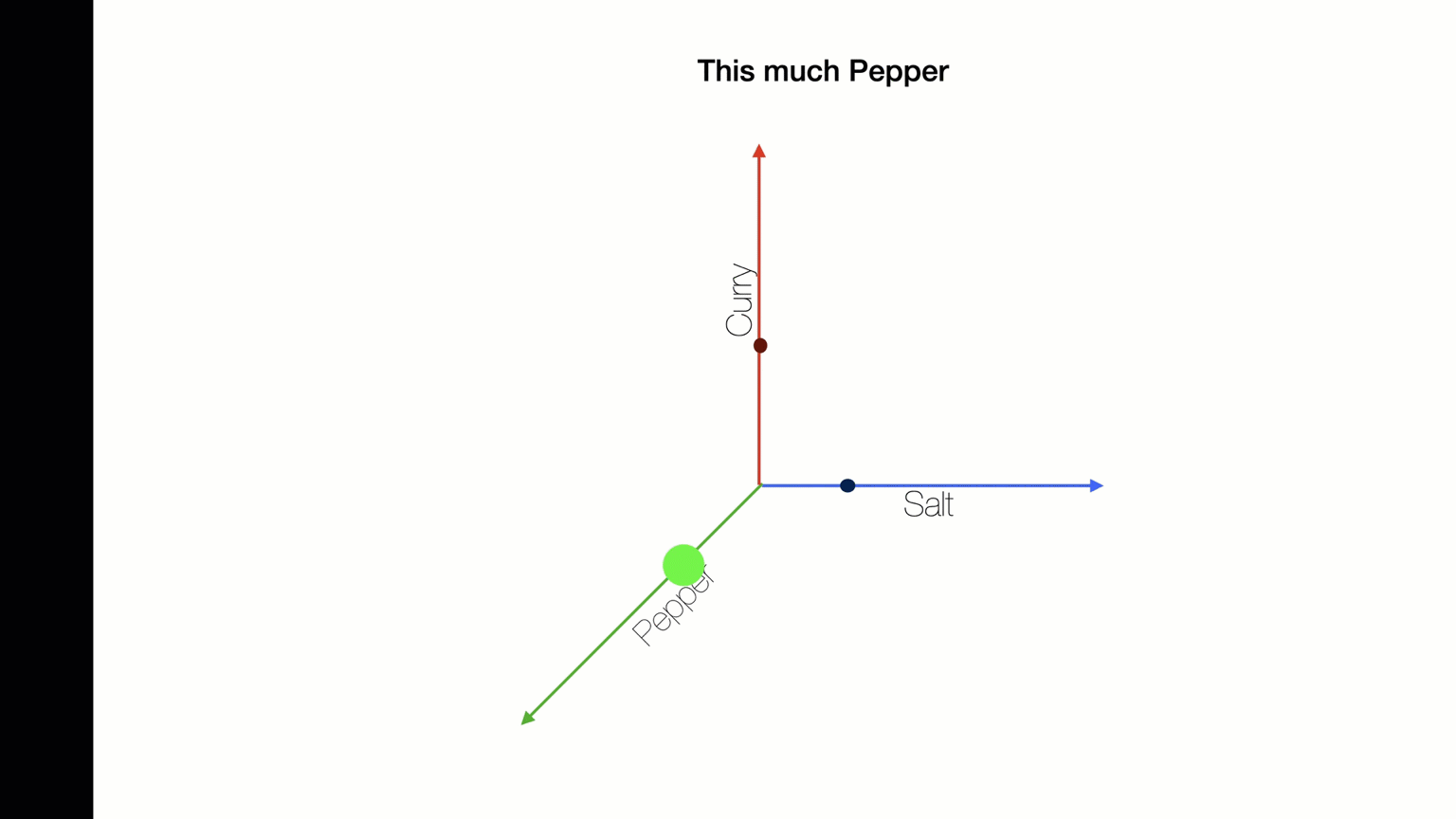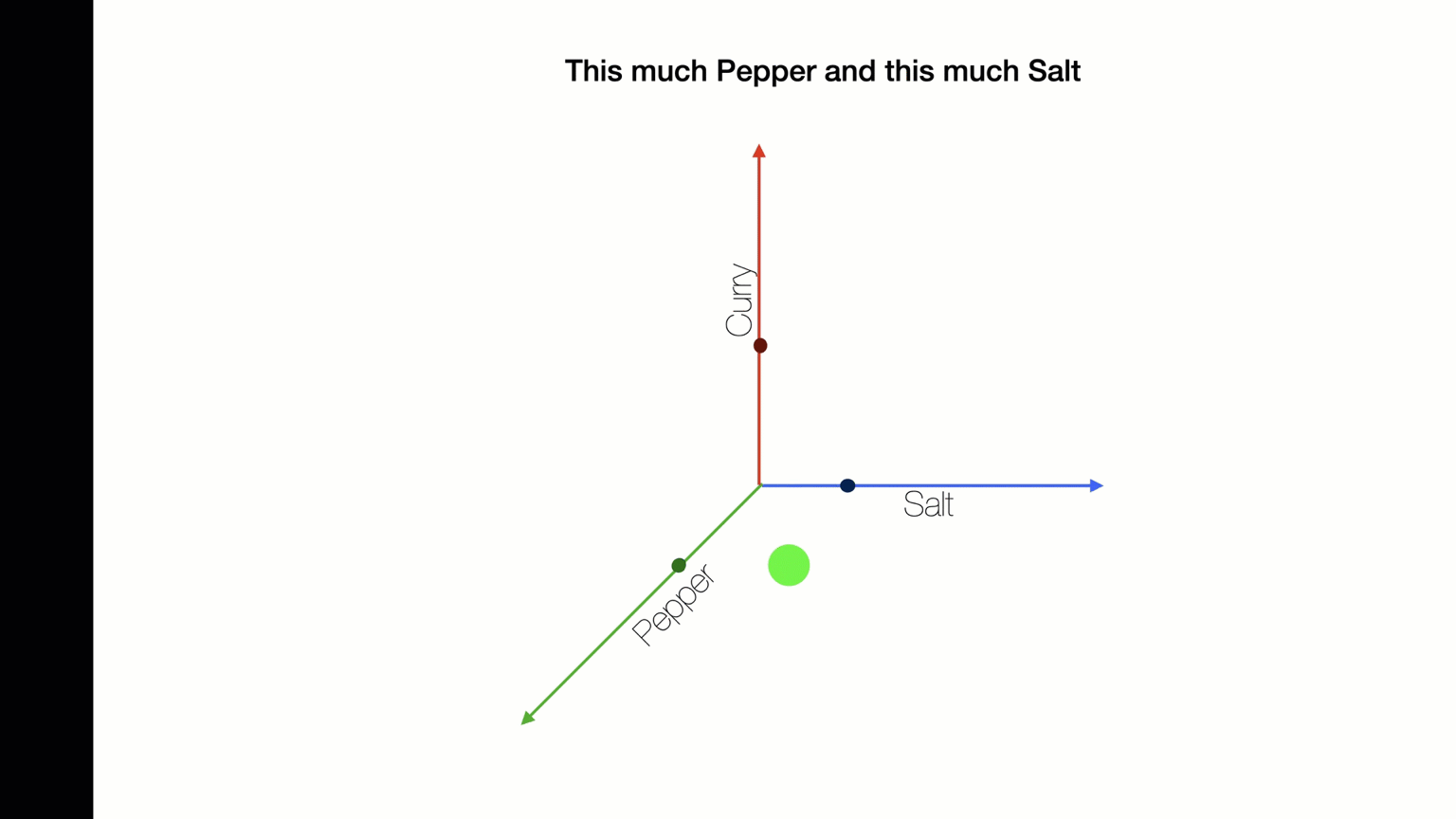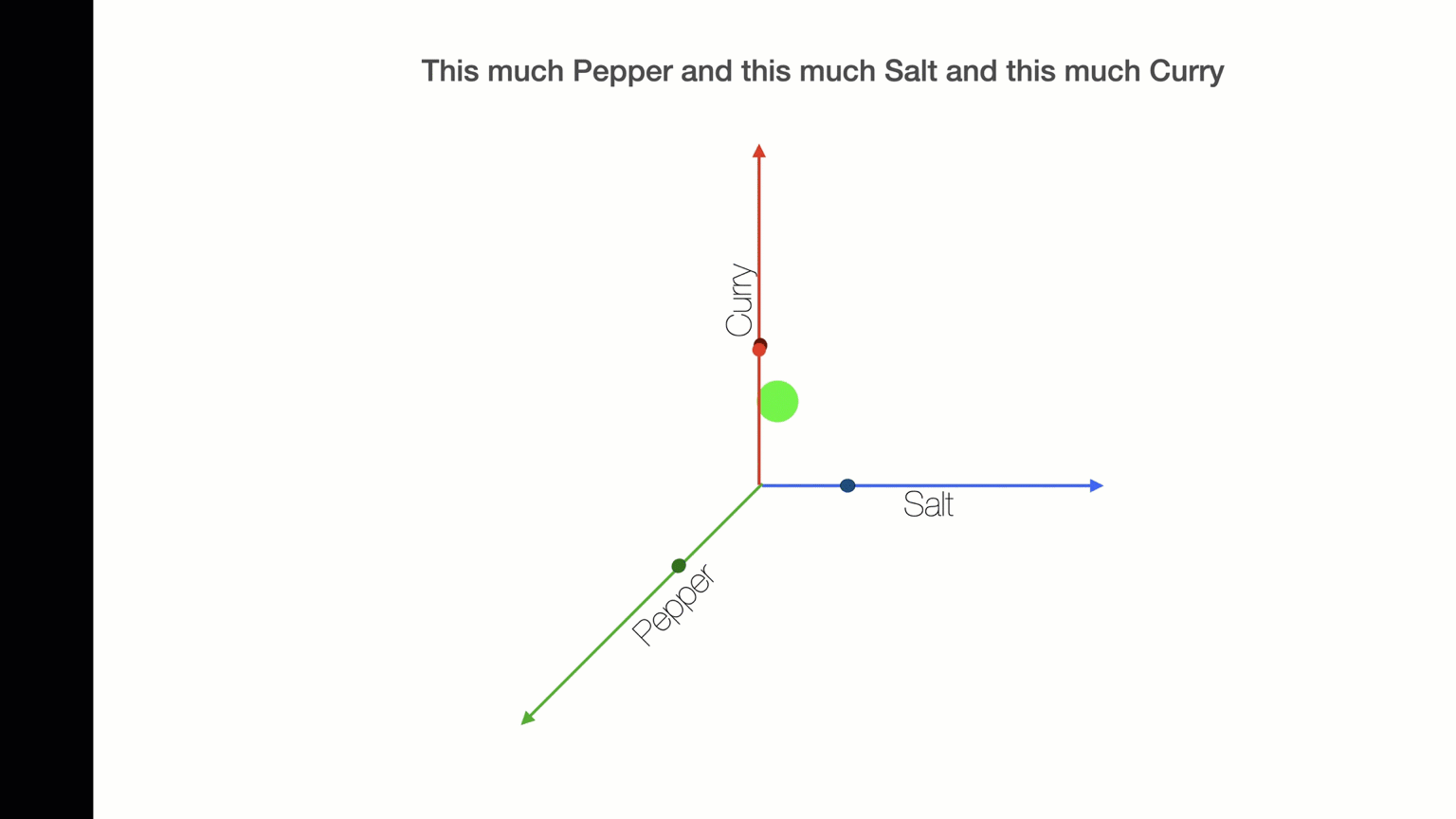
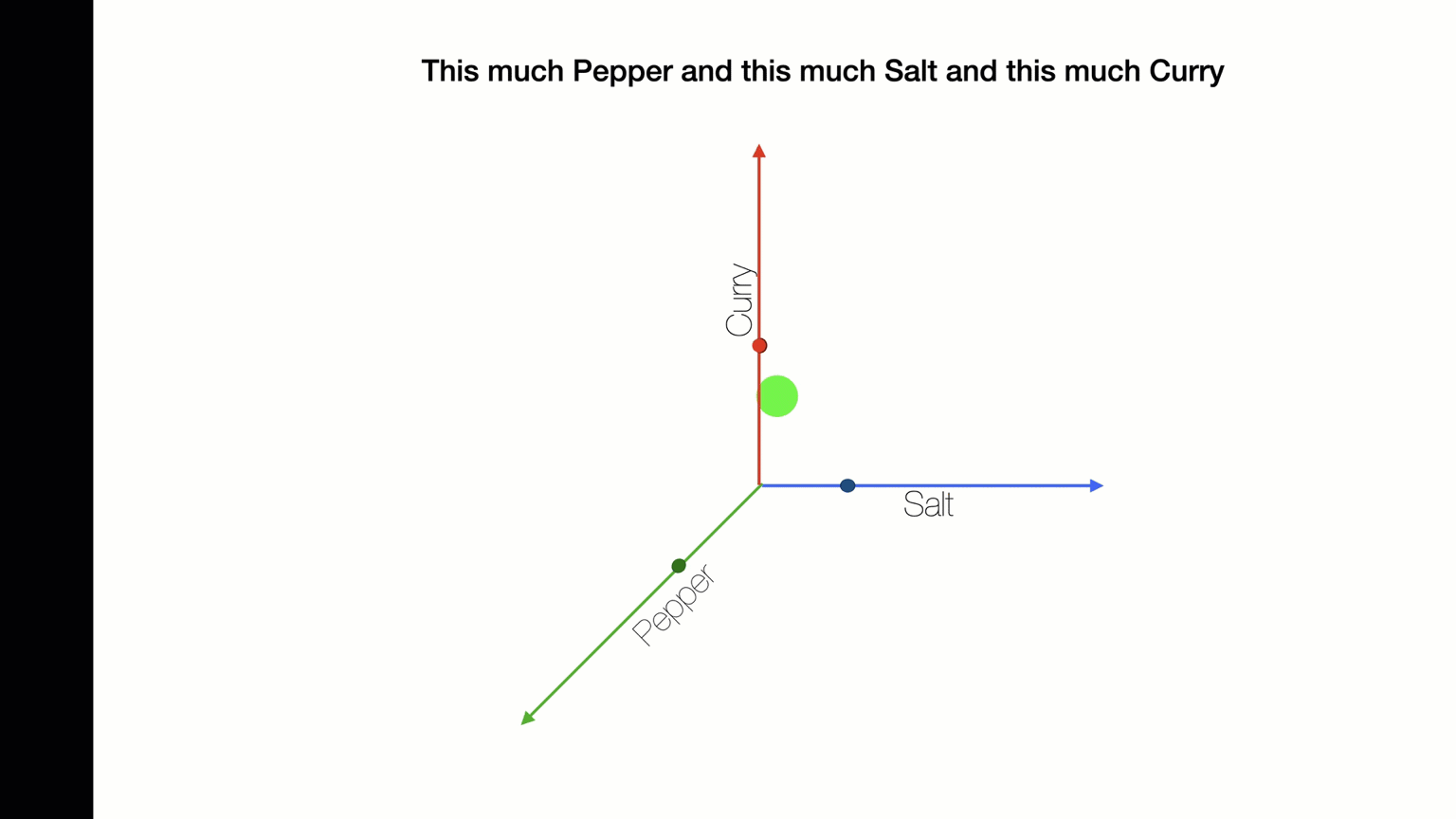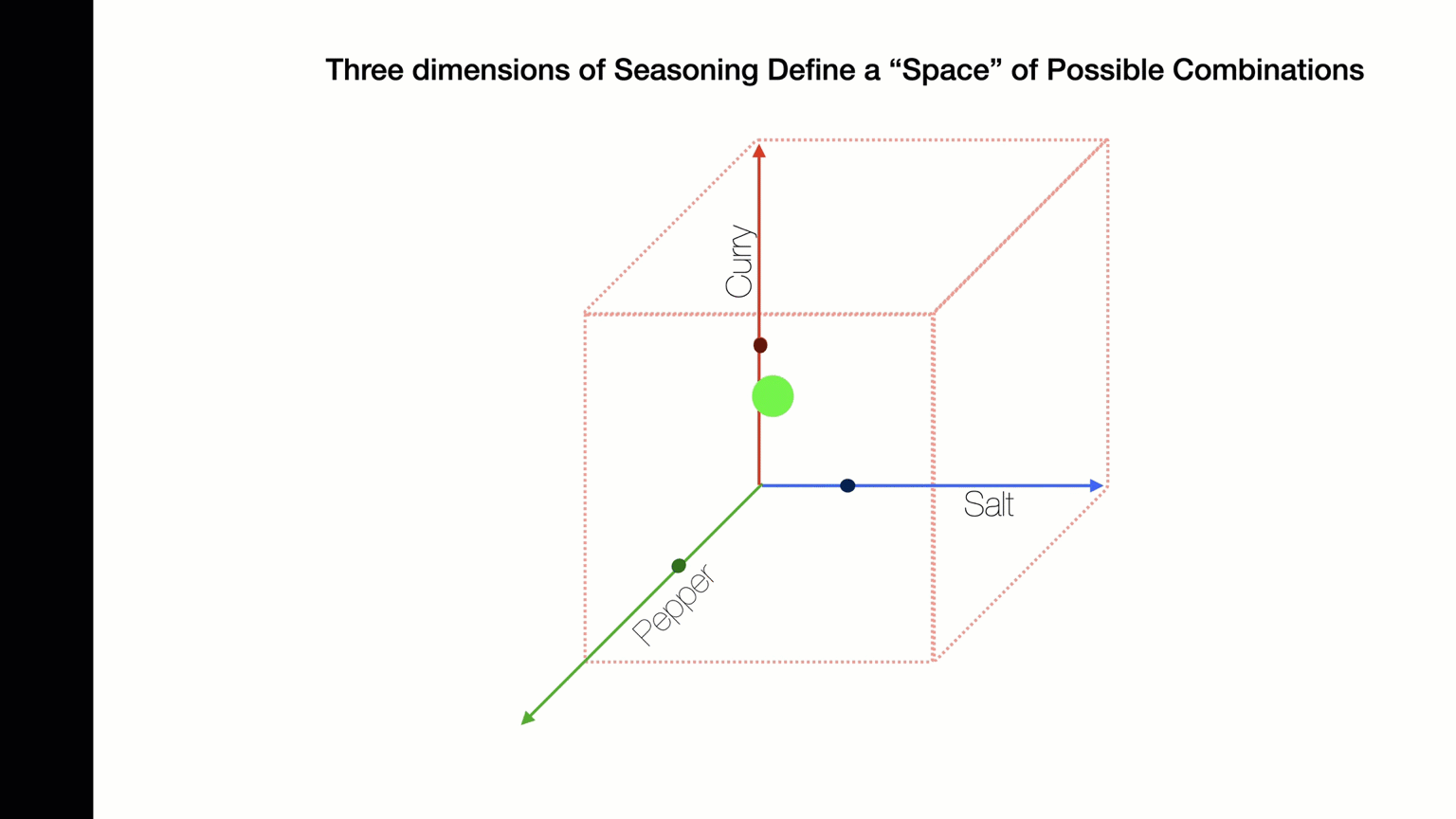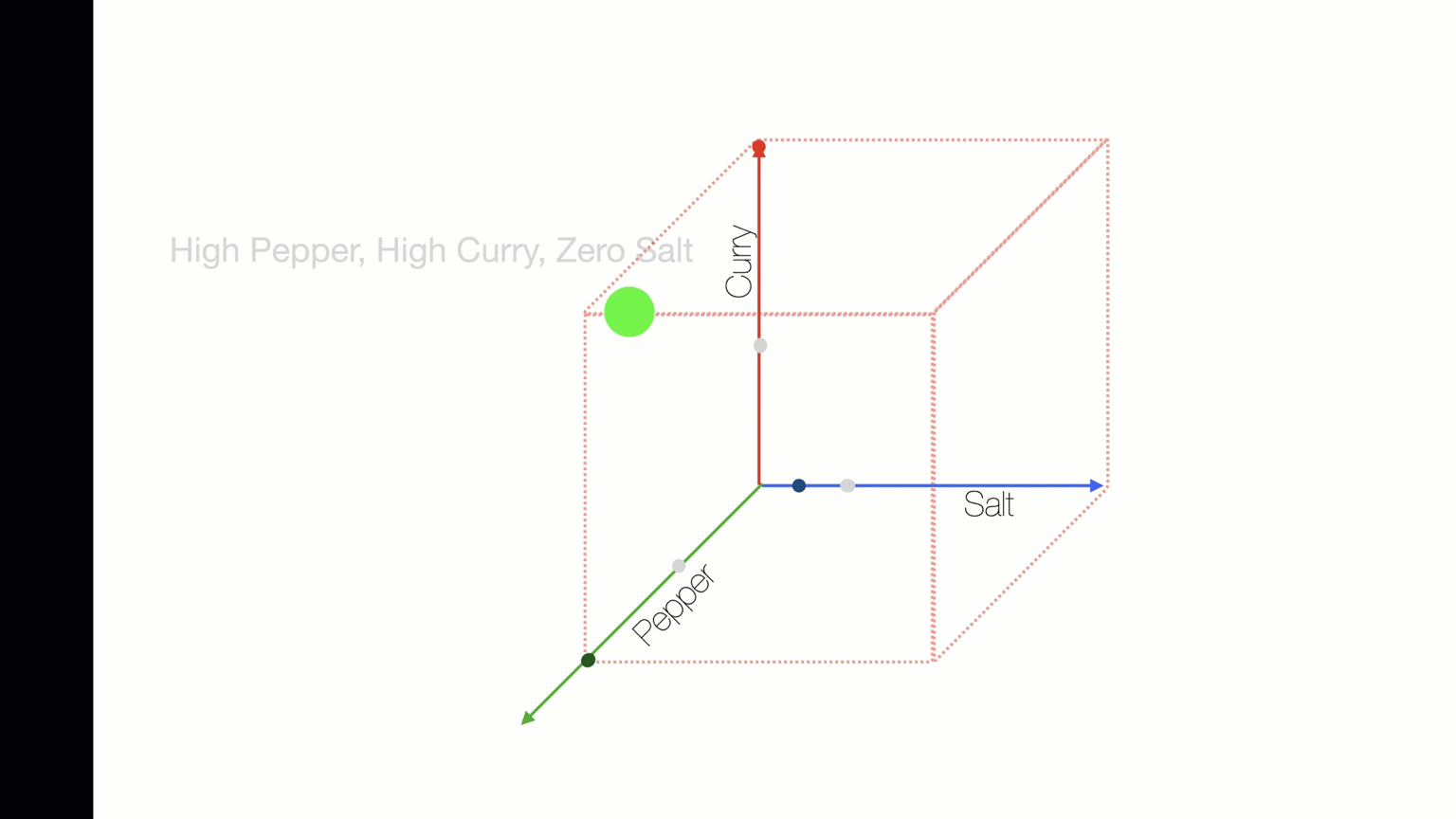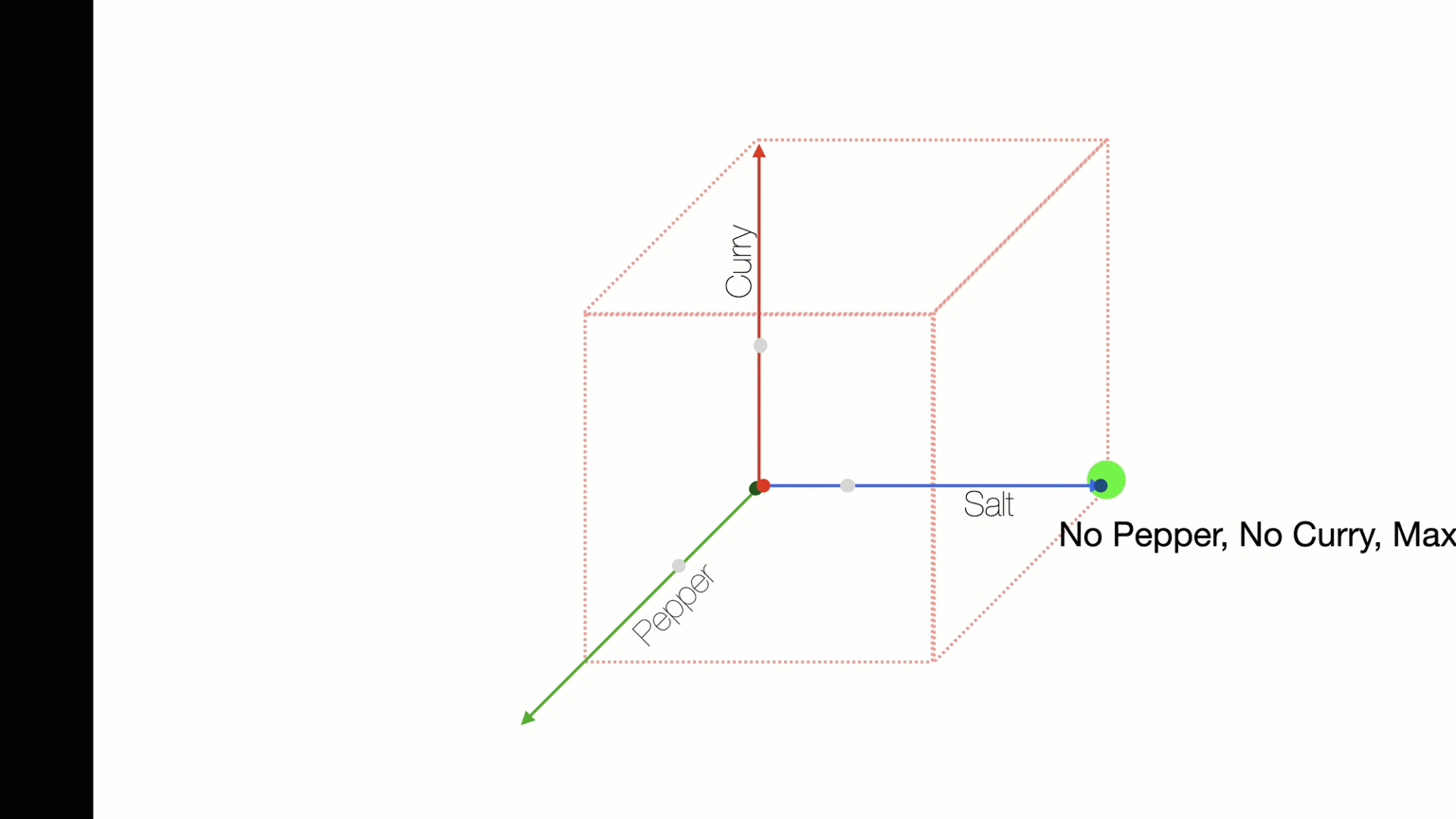


Nested Loops: Stop+Think
Nested Loops: Stop+Think
Nested Loops: Stop+Think
Nested Loops: Stop+Think
Nested Loops: Stop+Think
Chapter 4
This Leads to "Brute Force"
Brute Force
Brute Force
Def: consider every possible solution
Expensive : no clever cost-saving
Skills
Enumerating all the options
Not making it worse
Filho Example

SELL |
11 |
12 |
13 |
12 |
10 |
9 |
|
BUY |
Day |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
10 |
1 |
||||||
9 |
2 |
||||||
7 |
3 |
||||||
11 |
4 |
||||||
10 |
5 |
||||||
9 |
6 |
SELL |
11 |
12 |
13 |
12 |
10 |
9 |
|
BUY |
Day |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
10 |
1 |
1 |
2 |
3 |
2 |
0 |
-1 |
9 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
3 |
1 |
0 |
|
7 |
3 |
6 |
5 |
3 |
2 |
||
11 |
4 |
1 |
-1 |
-2 |
|||
10 |
5 |
0 |
-1 |
||||
9 |
6 |
0 |
Filho Example

STOP+THINK: What data jig would help us out here?
buyPrices = [10, 9, 7, 11, 10, 9] sellPrices = [11, 12, 13, 12, 10, 9]
prices = [{"buy":10,"sell":11},
{"buy":9,"sell":12,
{"buy":7,"sell":13},
{"buy":11, "sell":12},
{"buy":10,"sell":10},
{"buy":9, "sell":9}]
Filho Example

STOP+THINK: Write the refinement 0 pseudocode.
loop over buy days from 1 to end
loop over sell days from buy day to end
compute profit
track days and amount of best trade
//assume data in array prices
var maxProfit = 0;
var bestBDay = 0;
var bestSDay = 0;
for (var bDay = 0; bDay < prices.length; bDay++) {
for (var sDay = bDay; sDay < prices.length; sDay++) {
var profit = prices[sDay].sell - prices[bDay].buy
if (profit > maxProfit) {
//if best so far, take notes
maxProfit = profit;
bestBday = bDay;
bestSday = sDay;
}
}
}
//Prepare results
var result = "Buy on day " + bestBday + " and sell on day " +
bestSday + " to realize profit of " + maxProfit
How much computation?
Since we don't have
to compute profit
for sell dates that
are before buy
dates we have this
triangle of numbers
and the number of
computations is
n times n/2. We would say "on the order of n2."
SELL |
11 |
12 |
13 |
12 |
10 |
9 |
|
BUY |
Day |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
10 |
1 |
1 |
2 |
3 |
2 |
0 |
-1 |
9 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
3 |
1 |
0 |
|
7 |
3 |
6 |
5 |
3 |
2 |
||
11 |
4 |
1 |
-1 |
-2 |
|||
10 |
5 |
0 |
-1 |
||||
9 |
6 |
0 |
SKILL: Enumerating All the Cases
Outtakes
The merge sort algorithm sorts a list by repeatedly splitting the list in half until reaching pairs or single elements.
If the last step generates a pair, they are put in order and then the sorted pair is returned; otherwise the single is returned.
When the results of a split are returned the two sorted lists are merged. And then the merged lists are returned and so on and so on.
If we start with 52 cards we split into 26 and 26 and then into 13s and 13s and then into 6s and 7s, and then into 3s and 3s or 3s and 4s, and finally into 2s and 1s.
Complexity Examples
O(1) - determining if a number is odd or even
O(log N) - finding a word in the dictionary
O(N) - reading a book
O(N log N) - merge sorting a deck of playing cards
O(N^2) - checking combinations of two ingredients
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/7055652/real-world-example-of-exponential-time-complexity
See Also
Introducing Logarithms
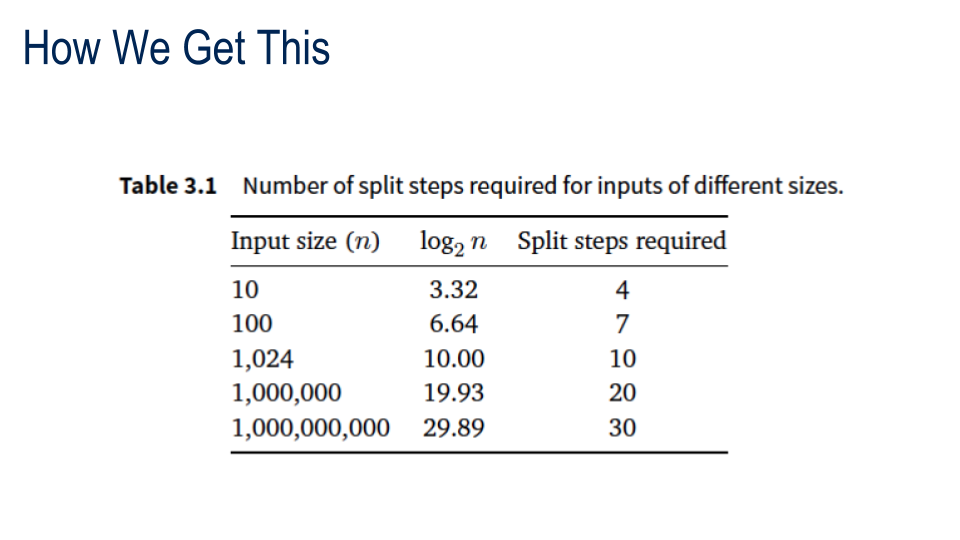
Introducing Logarithms
N > N/2 > N/4 > N/8 > ... 1 and DONE

Repetition Outtakes
By Dan Ryan
Repetition Outtakes
- 229




