Document Object Model
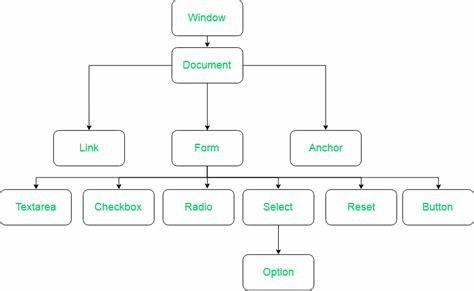
- DOM: It is a tree of nodes or elements created by the browser.
- It is a structured representation of an HTML document.
- Java Script is used to read/write/manipulate the DOM.
console.log(document);Window Object
It is the GLOBAL OBJECT in client-side java script
window.console.log("hey, there!");=
console.log("hey, there!");Document is a part of Window Object.
It includes methods like console(), prompt(), alert(), confirm() etc,.
if window.confirm(" Do you confirm to delete the file?")
{ window.console.log("file deleted");
}
else
{
window.console.log("Prevented deleting the file");
}Document Object
// gives an array of all the element nodes present in the HTML document
document.all;
// gives the number of element nodes in the HTML document
document.all.length;
// gives the <head> tag of the HTML document
document.head;
// gives you the <body> tag of the HTML document
document.body;
// gives you the DOCTYPE of the HTML document
document.doctype;
// gives you the URL of the website
document.URL;
// gives you a list of all the images in the HTML document
document.images;Like every other object in Object-oriented programming language, document object has a few properties.
DOM selectors
- Single Element selectors
- Multiple Element selectors
Single Element selectors
- document.getElementByID()
- document.querySelector()
document.getElementById()
menu = document.getElementById('menu');
console.log("\n GET ELEMENT BY ID\n",menu, typeof menu);
console.log(menu.className); // returns the className
console.log(menu.id); // returns the Id
// we can even style the elements using DOM
menu.style.backgroundColor = "#FFADA3";document.querySelector()
listItems = document.querySelector('.list-items');
console.log("\n QUERY SELECTOR\n",listItems, typeof listItems);
menu_q = document.querySelector('#menu');
list = document.querySelector('.list');
li = document.querySelector('li');
console.log(menu_q, list, li);
// >>>>>>>>>>>>> you can even select a particular element using pseudo classes
// in CSS , nested elements <<<<<<<<<<<<<
list.querySelector('.item:last-child').style.border = "solid 3px #FC34CF";
document.querySelector('.card:last-child').innerHTML = "<p> this is done using query selector where a last div is selected using pseudo classes</p><p> And this seems to replace all the inner child elements of the last .card div to two p tags with text";Multiple Element Selectors
-
document.getElementsByClassName()
- document.getElementsByTagName()
- document.querySelectorAll()
document.getElementsByClassName()
listItems = document.getElementsByClassName("list-items");
console.log(`\n GET ELEMENTS BY CLASS NAME\n ${listItems}`, listItems);
listItems[3].style.color = "#AD45E1";
// local scoping of selecting an element
listItems[2].getElementsByTagName("div")[1].style.backgroundColor = "#7FF2F3";
console.log(menu.id); // returns the Id
// we can even style the elements using DOM
menu.style.backgroundColor = "#FFADA3";
listItems = Array.from(listItems);
console.log(listItems);
listItems.forEach(function(li, i) {
console.log(li);
});document.querySelectorAll()
card = document.querySelectorAll(".card");
console.log(`\n QUERY SELECTOR ALL\n ${card}`);
console.log(card);
contactCard = document.querySelectorAll(".contact-card");
console.log(contactCard);
for (let i = 0; i < contactCard.length; i++) {
contactCard[i].style.border = "dashed 3px #FFFFFF";
}
divItems = document.getElementsByTagName("div");
console.log(`\n GET ELEMENTS BY TAG NAME\n ${divItems}`);document.getElementsByTagName()
Traversing the DOM
Moving up and down and dealing with the parents and children of the specific nodes we select is known as DOM traversing
- child Node and children
- children of children
- parent
- parent of parent
child node
Gives you a Node List of all the child nodes of the selected element, including the text nodes.
const list = document.querySelector('.list-ul');
let val = list.childNodes;
val = list.childNode[2];children
Gives you an HTML Collection of only the element nodes of the selected element.
let val = list.children;
val = list.children[3];
val.style.background = "#00DE67";children of children
const list = document.querySelector('.list-ul');
let val = list.children;
val = list.children[2].children;parent Element
let val = list.parent;
val = list.parentNode;parent of parent
let val = list.parentElement.parentElement;Creating DOM elements
- get the element you want to append the created element
- create an element
- append the created element to (1)
- get the element - document.querySelector(' ');
- create an element - document.createElement('tagName');
- append the created element - prevElement.appendChild(newElement);
// get the element
const card = document.querySelector(".card");
// create a new DOM element
const div = document.createElement('div');
// append the new created element to the card
card.appendChild(div);Replacing the DOM elements
- create an element
- get the previous element
- get the parent of the previous element
- replace the element
- create an element - document.createElement('tagName')
- get the previous element - document.getElementById('id')
- get the parent of the previous element - prevElement.parentElement;
- replace the element - parent. replaceChild('newElement', 'oldElement')
// creating a new element
const newPara = document.createElement('p');
// getting the previous element
const oldPara = document.getElementById('About');
// getting the parent of the previous element
const parent = oldPara.parentElement;
// replacing newPara with oldPara
parent.replaceChild(newPara, oldPara);Removing DOM elements
- get the element
- remove the element
// getting the element
const li = document.querySelectorAll('li');
// getting the parent element
const ul = document.querySelector('ul');
// remove the element
li[3].remove();
// remove the child element
ul.removeChild(li[4]);- get the element - document.getElementById();
- remove the element :
- remove the selected element - element.remove();
- remove the child element of the selected element - element.removeChild(child[2])
Note: u need to get the child element using DOM selectors before removing it.
TASK

