C++
ノ亅 示 言果
+


優點
- APCS愛用
- 長姐愛用
- 海的女兒愛用
缺點
- 下載麻煩
- 設定麻煩
- 打開麻煩


點它

點它們
怎麼執行

build and run
檢查檔案是否變更/檢查語法是否正確
執行程式

學校練習題目的測資平台

先用學校的gmail登入
和皮卡丘一樣會電人的社師
加入課程

先點自己
找到加入課程輸入課程代碼
課程代碼:X+_0R_
點選現在的課程

按他

就可以點喜歡的題目練習了
怎麼將程式碼交給JMJ測資


點它
點選現在所用的語言
將所寫的code複製貼上到這
起手式
起手式
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
return 0;
}
控制輸入輸出
設定命名空間
程式的「入口點」
程式正常結束
變數
變數名稱 = 資料
就像數學上 設x=??
「設定變數」就是給一個名字,儲存資料或數值,讓你之後可以用這個名字來操作。也就是你給資料取的「暱稱」。
- 宣告變數的型態
- 變數名稱
- 分號
步驟
宣告變數
| int | float | double | char | string | bool |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 整數 |
浮點數 (7位以內小數) |
浮點數(16位以內小數) |
字元 (單個字母符號或數字) |
字串 (一個以上的字母符號或數字) |
布林值 (判斷True(1)/ False(0)) |
告訴程式要用甚麼型態儲存變數
變數名稱
- 不能用特殊字
- 開頭不能是數字
- 不能有空格
- 只能用英文字母、數字、底線
_ - 有意義的變數名稱
整數
int 變數名 =整數 ;
int age =15;
int year = 2025 ;-
全名:整數(Integer)
-
功能:表示整數數值
浮點數
float 變數名 =小數 ;
float hight = 180.5 ;
float weight = 50.0 ;-
全名:單精度浮點數 (Single Precision Floating Point)
-
功能:表示具有小數點的數字
字符
char 變數名稱 = 字符
char ans = 'A' ;
char grade = 'b' ;-
全名:字符(Character)
-
功能:儲存任何一個 ASCII 字符
布林值
bool 變數名稱 = 字串
bool isFinished = false;
bool isAdult = true;-
全名:布林值(Boolean)
-
功能:用來表示真或假的值
-
true=1 / flase=0 兩種
int(整數)
- 只表示整數,精確,沒有小數。
float(浮點數)
- 可表示小數,近似,約 7 位十進位有效數字。
對比
Vs.
char(字符)
- 單一字元(1 個位元組的「碼元」)
string(字串)
- 可變長字串(擁有並管理一段連續的
char序列)
Vs.
輸入輸出
輸入
cin >> 用來存取輸入內容的變數 ;cin : 從鍵盤讀取(輸入)
範例.
int a , b;
cin >> a >> b ;float a , b;
cin >> a >> b ;依照想要輸入內容的類別先宣告欲儲存輸入的變數
整數
浮點數
char a , b;
cin >> a >> b ;字元
string a , b;
cin >> a >> b ;字串
輸出
cout << 變數/數字 ;
cout<< " 字串 " ;cout : 在屏幕上印出你想要列印的內容
範例.
cout << 520 ; //520
cout << 1314 ; //1314int a=10;
char b='A';
cout<<a<<b; //10A在cout<<後放欲想輸出的內容
整數
變數
cout<<"賺大錢"; //賺大錢文字
cout<<endl;
cout<<520<<endl<<1314;換行
- 用雙引號 " " 將字串包起來
a033.
a176.
題目練習
運算子
算術運算子
+ |
加法 | 3 + 2 |
5 |
- |
減法 | 5 - 3 |
2 |
* |
乘法 | 4 * 2 |
8 |
/ |
除法(浮點) | 7 / 2 |
3.5 |
/ |
整除(取整) | ||
% |
取餘數 | 7 % 2 |
1 |
** |
(冪次) | 2 3 |
8 |

X
比較運算子
== |
是否相等 | 5 == 5 |
|
!= |
是否不相等 | 5 != 3 |
|
> |
是否大於 | 7 > 5 |
|
< |
是否小於 | 3 < 5 |
|
>= |
是否大於等於 | 5 >= 5 |
|
<= |
是否小於等於 | 3 <= 5 |
簡化
- x=x+1 ➭ x+=1
- x=x-1 ➭ x-=1
- x=x*1 ➭ x*=1
- x=x/1 ➭ x/=1
- x=x%1 ➭ x%=1

a014.
b001.
題目練習
次方/根號
#include<cmath>導入函示庫
提供了執行各各種數學運算的函數,包括基本
算術、三角函數、指數、對數和取整函數等
次方
pow ( 底數 , 次方 ) ;#include<iostream>
#include<cmath>
using namespace std;
int main(){
pow(2,3); //8
pow(4,0.5); //2
return 0;
}根號
sqrt ( 底數 ) ;#include<iostream>
#include<cmath>
using namespace std;
int main(){
sqrt(4); //2=pow(4,0.5)
return 0;
}if/else
if
if (條件){
//要執行的程式碼 ;
}

else if
else if (條件){
//要執行的程式碼;
}
如果不符合if的條件但符合這裡的條件,就會執行
else
else{
//要執行的程式碼 ;
}

其他(不符合上面所有if和elif的條件)


你可以有很多選擇
///假設都符合條件
if(true){ //流麻
cout<<"買!";
}
if(true){ //徽章
cout<<"買!";
}
if (true){ //拍立得
cout<<"買!";
}
if(true){ //金屬胸章
cout<<"買!";
}結果:

if
金錢有限只能選一個
if(true){ ///假設都符合條件
cout<<"you") ;
}
else if(true){ //薄巧
cout<<"薄巧";
}結果:you

比起薄巧我更喜歡你
elif
if:還有錢
else if:如果前面買了現在這個就沒錢買了
if
elif
VS.
int x=5,y=10;
if (y==10){
cout<<"a";
}
if (x==5){
cout<<"b";
}int x=5,y=10;
if (y==10){
cout<<"a";
}
elif(x==5){
cout<<"b";
}a
b
a
&& / ||
&&
Vs.
||
int x=5,y=10;
if (x==5 && y!=10){
cout<<"a";
}int x=5,y=10;
if(x==5 || y!=10){
cout<<"a";
}a


題目練習
a021.
b008.
迴圈

用途
- 執行相同的程式碼多次
- 處理大量資料(如總和、最大值、找資料)
- 根據條件持續執行,直到滿足條件才停止
- 輸入大量資料,使用迴圈接收一堆數字,而不是寫很多次 cin
for (初始化;條件化;變化){
//要重複執行的code;
}- 初始化:設定迴圈開始前的變數。通常是計數器。
- 條件:每次迴圈執行前會檢查此條件,若條件為 true,則續 執行迴圈,若為 false 則結束迴圈。
- 迭代:在每次執行完程式碼後,會執行這段程式碼來更新變 數,通常是計數器增加或減少。
for (初始化;條件化;變化){
//要重複執行的code;
}1.
2.
3.
4.


要扣$
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
for (int i=0;i<520;i++){
cout<<"公關姐姐我愛你!"<<endl;
}
return 0;
}當你情人節告白,不用1314行,更不用520行,只要3行,輸出幾遍我愛你都可以


#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
for(int i=0;i<6;i++){
cout<<i<<" ";
}
return 0;
}請學妹們來想想,最後的輸出會是怎樣的呢?
Ans:0 1 2 3 4 5



#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
for(int i=5;i<-1;i--){
cout<<i<<" ";
}
return 0;
}請學妹們來想想,最後的輸出會是怎樣的呢?
Ans:5 4 3 2 1 0


題目練習
b038.
b030.

while(條件){
//要重複執行的code;
}- 條件:每次迴圈執行前,都會檢查這個條件。如果符合,則繼續執行迴圈;如果不符合,則跳出迴圈。
while(條件){
//要執行的code;
}1
2


#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int i=0;
while(i<=5){
cout<<i<<" ";
i++;
}
return 0;
}請學妹們來想想,最後的輸出會是怎樣的呢?
Ans:0 1 2 3 4 5



題目練習
a078.
a063.


#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
for(int i=0;i<6;i++){
if i==3:
continue;
cout<<i<<" ";
}
return 0;
}#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
if i==3:
break;
cout<<i<<" ";
}
return 0;
}Ans:0 1 2
Ans:0 1 2 4 5
題目練習
a026.
一維陣列
定義:一維陣列是一種線性陣列,其中元素的存取是以
行或列索引的單一下標表示。
如果有效的元素索引從0開始,則常數B只是陣列第一個元素的位址。因此C語言指定陣列的索引一定從0開始;許多開發人員會將該元素稱為「第零」而不是「第一」。
甚麼是一維陣列???
簡單來說就像放一堆資料的長條櫃子!
- 櫃子第0個="Terry"
- 櫃子第1個="Hoyou"
- 櫃子第2個="Vivian"
- 櫃子第3個="Ktlai"
0
1
2
3
Terry
Hoyou
Vivian
Ktlai
如果以C++來表示
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main(){
string team[4]={"Terry","Hoyou","Vivain","Ktlai"};
cout<<team[0]<<endl;
cout<<team[1]<<endl;
cout<<team[2]<<endl;
cout<<team[3];
return 0;}理論已知,如何實踐?
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
宣告 陣列名稱[陣列長度]={陣列裡存放的東東};
return 0;}這個陣列想要放甚麼資料型態的物品
取名規則同變數
櫃子想要有幾格
櫃子也可以空著(默認是0)
有陣列後,要如何存取資料??
陣列名[資料對應位置]==放在這個櫃子的資料
int a[10]={};
a[0]=1;
a[1]=3;
a[2]=12;
a[4]=4;
cout<<a[0]+a[1];Q :輸出是什麼??
A: 4
Why?????????????????????????????????????
1+3=4
有沒有覺得這樣一個一個放東西很麻煩(𖦹.𖦹)
那就用loop解決煩惱٩(๑•̀ω•́๑)۶
a[101]={};
cin>>a[0]>>a[1]>>.......>>a[100];int a[101]={};
for (int i=0;i<101;i++) {
cin>>a[i];
}是不是方便很多?!♥(。→v←。)♥
同理可得ε(*・ω・)_/゚:・☆
int a[10]={0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9};
for (int i=0;i<10;i++) {
cout>>a[i];
}真的很方便!OK(ゝω・´★)
手癢養的,快來實踐看看



進入課程開始練習吧
字元字串
甚麼是字元字串,可以吃嗎?
字串string
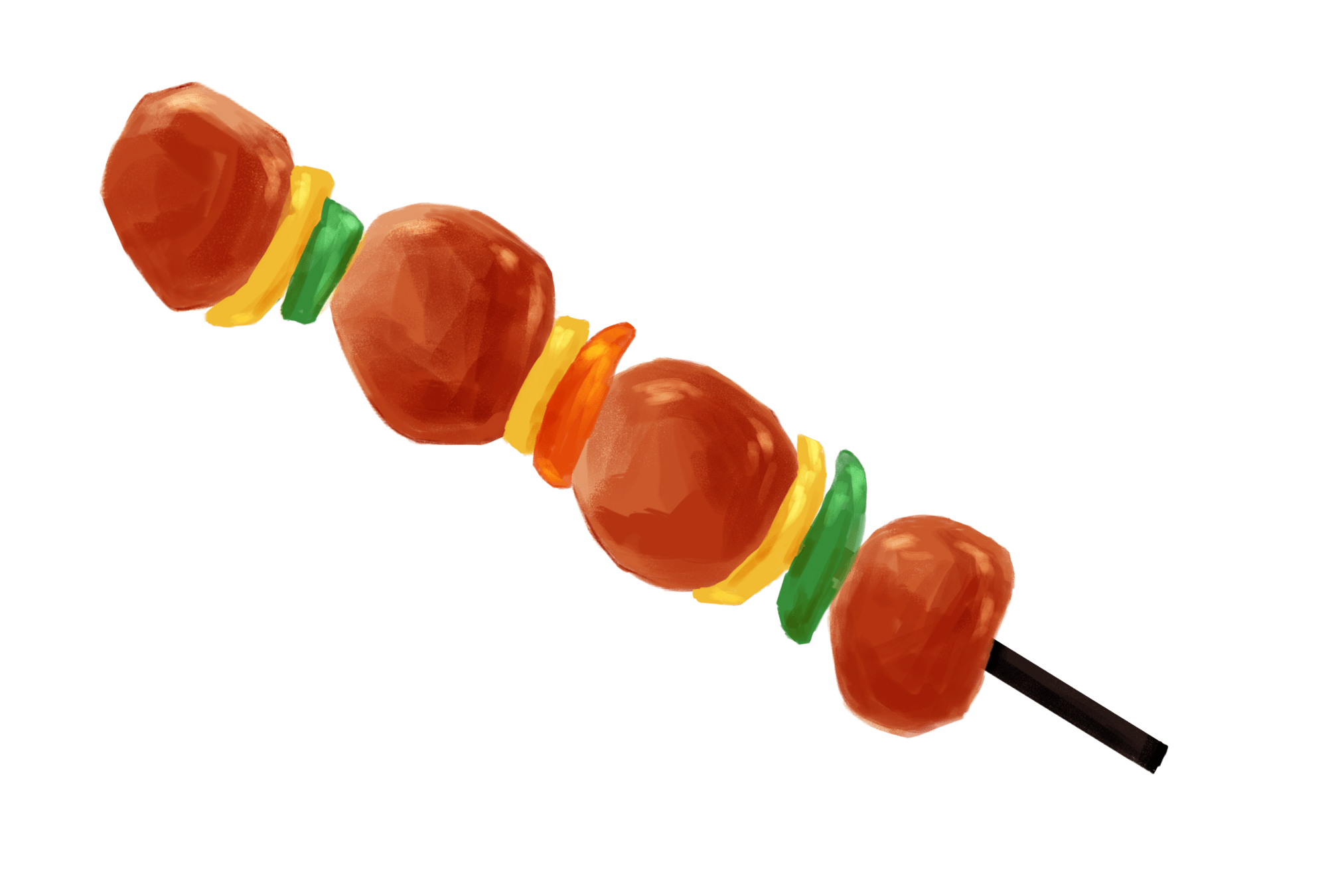
把它想像成烤肉串!
- 這串烤肉串是由雞肉、青椒、彩椒組成的
- 烤肉串[0]=雞肉!!!!!!!!
- 烤肉串[1]=黃色彩椒 : (
- 烤肉串[2]=青椒 :( ( ( (
有沒有覺得他跟一維陣列有點像,因為它也是陣列:字元陣列
字元char
把它想像成烤肉串上的食材!
雞

青椒、彩椒

當然,你可以DIY自己的烤肉串
+
+
+
=
+
轉換成烤肉串字元陣列
0
1
2
3
4
5
'\0'
'\0'表示字串結尾的特殊字符稱為”空字符”它的數值是 0
每個烤肉串最後都有一個籤子
在C++嘗試前,我們要
先導入函示庫!
#include<string>字符
char 變數名稱 = 字符
char ans = 'A' ;
char grade = 'b' ;-
全名:字符(Character)
-
功能:儲存任何一個 ASCII 字符
字串
string 變數名稱 = 字串
string name = "Terry" ;
string grade = "A++" ;-
全名:字元(String)
-
功能:儲存0~n個 ASCII 字符
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main(){
string ans;
ans='a'+'b'+'c';
cout<<ans; //abc
cout<<ans[2];//c
return 0;}在c++裡實作
當題目給你未知長度的字串
可以用length() || size()知道字串長度🤓👆
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main() {
string a = "hello";
cout << a.length(); //5
cout << a.size(); //5
return 0;}#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main(){
string a;
cin>>a;
for(int i=0;i<a.size();i++){
cout<<a[i];
}
cout<<endl;
for(int i=0;i<a.length();i++){
cout<<a[i];
}
cout<<endl;
for(int i=0;a[i]!='\0';i++){
cout<<a[i];
}
return 0;}
作字元陣列
由此可延伸
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main(){
string a;
cin>>a;
for(int i=0;i<a.size();i++){
cout<<a[i]<<"Happy";
}
return 0;}
其他同理自己照題目推,不懂得來問
a069
a114
練習
ASCII碼
📌 為什麼需要 ASCII?
電腦沒辦法直接存「字」,所以必須用 數字編號 來代表。
就像是每個字符都有自己的座號,
ex:當我們叫10304,就知道在叫江O慈小朋友
叫04的後11號是叫10315的張O穎小朋友
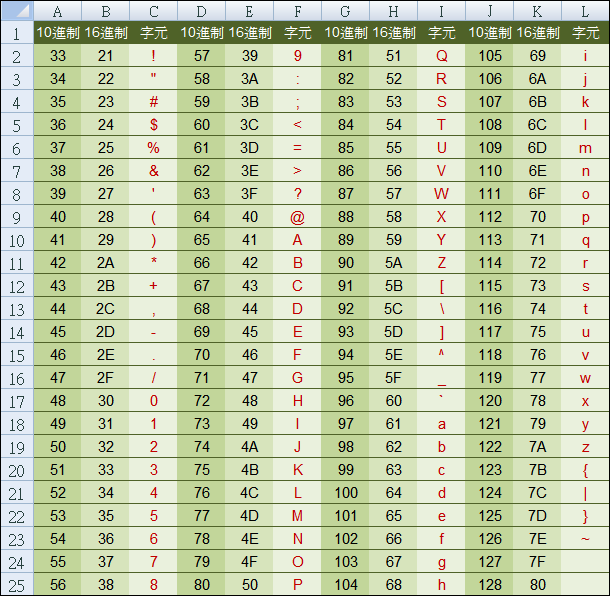
不用特別背,電腦都記著
例如我們想知道某字元是英文大寫||小寫
char a;
cin>>a;
if ('A'<=a && a<='Z') cout<<a<<"是大寫";
else if('a'<=a && a<='z') cout<<a<<"是小寫";
else cout<<a<<"不是英文字母";原理是利用他的ASCII碼大小來判斷
接下來開始練習吧!
bool值
在自然直覺中
1 代表:成立/真/對
0代表:不成立/假/不對
二維陣列
二維陣列使用陣列名稱與兩個索引值來指定存取陣列元素,這兩個索引值都是由 0 開始。宣告方式與一維陣列類似
為甚麼學完一維又來了二維?
何謂二維陣列於記憶體中的配置方式?其實二維陣列存取時的行與列,只是為了便於理解陣列元素索引。如果要大量儲存同一種型態、而且彼此又有密切關係的「表格式」資料,例如數學中的矩陣,這時候就應將其宣告並設定為「二維陣列」。本質是在陣列裡的陣列。
它在程式裡的資料型態
int arr[3][3]={{1,2,3},{4,5,6},{7,8,9}};int arr[3][3]={
{1,2,3},
{4,5,6},
{7,8,9}
};如果換個排版方式
是不是覺得有點像有長x寬的櫃子呢?
簡單來說
你只要會去蝦皮智取店領貨你就會了!
i
j
0
1
2
3
0
1
2
3
0-0
0-1
0-2
0-3
3-0
3-1
3-2
3-3
1-0
1-1
1-2
1-3
2-0
2-1
2-2
2-3
j
i
理論已知,如何實踐?
宣告 陣列名 [r] [c] = { } ;陣列要儲存什麼樣式的資料型態
取名規則同變數
直排
橫排
放資料的地方
怎麼將資料輸入進二維陣列?
for (int i=0;i<r;i++){//控制直排
for(int j=0;j<c;j++){ //控直橫排
cin>>arr[i][j];
}
}用雙層迴圈!
怎麼宣告二維陣列
int arr[][]={};//跟一維一樣空陣列會用0填vector
這節要鍛鍊你們自學能力,所以簡報比較短
-
vector是 C++ 中最常用的動態陣列容器。 -
元素可自動擴張(不像一般陣列大小固定)
-
支援隨機存取
-
插入、刪除、搜尋都很方便
-
需要
#include <vector>
什麼是vector?
📌 如何宣告 vector?
vector<int> v;
vector<int> v(5);
// 大小 5,每個元素預設為 0
vector<int> v(5, 10);
// 大小 5,每個值都是 10
| 操作 | 函式 | 說明 |
| ------------|-------------| ---------------|
| 新增到尾端 | push_back(x)| 加在最後 |
| 移除尾端 | pop_back() | 刪除最後一個 |
| 判斷是否為空 | empty() | true/false |
| 清空所有元素 | clear() | 全刪除 |
| 插入 | insert() | 插入到某個位置 |
| 刪除 | erase() | 刪除某位置或某區間|今天會介紹這些函式
陣列名.函式(你要處理的元素);自訂義函式
放在主程式的外面
函式
-
有名字 – 方便呼叫(像叫某人名字一樣)。
-
有輸入(參數) – 你可以把資料交給函式處理。
-
有回傳值 – 處理完的結果可以交回給主程式(也可以不回傳)。
-
能重複使用 – 寫一次,可以呼叫多次。
可重複使用的程式區塊,它能執行特定的任務,並且可以把結果回傳給呼叫它的地方。
函式
程式碼可以重複使用
- 不用一段程式碼一直「複製貼上」。
讓程式更簡潔、可讀性更高
-
把複雜問題拆成多個小任務,每個小任務用一個函式處理。
-
看程式時,不需要深入看每行細節,只要看「這個函式叫什麼名字」就知道功能。
方便維護和修改
-
如果程式需要修改,只要改 函式內部的程式碼。
提高程式的結構化與模組化
-
函式讓你的程式像拼積木一樣,一塊一塊組成,容易管理。

結構
沒有參數沒有回傳值
void 函式名(){
//程式碼;
}有參數沒有回傳值
void 函式名(宣告 變數){
//程式碼;
}結構
有參數有回傳值
宣告 函式名(){ //根據要回傳的東西宣告資料型態
//程式碼;
return 咚咚;
}全域整數
宣告 變數;
int main(){
//主程式;
}