How do machines keep secrets?
Dan Ryan
Lecture content licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Edited July 2025
Playlist
Intro: Asymmetric Encryption
REFERENCES/RESOURCES
See Also
IMAGES
Outline
Hashing
CHAPTER 0

CHAPTER 1

What is blockchain? Depends whom you ask.
Computer Scientist
What is blockchain? Depends whom you ask.

Accountant
DISTRIBUTED
PUBLIC LEDGER of PEER-TO-PEER TRANSACTIONS.
What is blockchain? Depends whom you ask.

Activist
TRUSTLESS, BORDERLESS, OPEN, DECENTRALIZED, PUBLIC, UNCHANGEABLE record of TRANSACTIONS
BORDERLESS
OPEN
TRUSTLESS
DECENTRALIZED
UNCHANGEABLE
PUBLIC
PEER-TO-PEER
DISTRIBUTED
LEDGER
TRANSACTIONS
TRUSTLESS participants do not need relational connection with transaction partners as any behavior they'd want a guarantee about is guaranteed by the system
BORDERLESS a blockchain is not physically located in one place and so it's unbound by geography and jurisdiction
OPEN refers to the software that runs the system being open
DECENTRALIZED: there is not a host or company or government in charge of the thing.
UNCHANGEABLE: once a transaction has been recorded in the ledger it cannot be changed without unraveling the whole thing.
PEER-TO-PEER means the transactions are between sender and receiver without a "middle man"
DISTRIBUTED means the software and the ledger does not reside on a single server. Everyone can have a copy of the ledger.
a LEDGER is a record of all the transactions in a system
TRANSACTIONS: anything we want a record of can be a transaction, but for now, A sends $X to B
LINKED LIST a data structure in which each element "points" to its predecessor and/or successor.
PUBLIC refers to the fact that the information on the blockchain is visible to the public - it can be hashed or encrypted but the outline of the transaction is visible
Chapter 2: Cryptography 101

Vocabulary
"plaintext"
cyphertext
key
encryption
means taking a message or
transforming it with an algorithm called a
cypher
into a form
called a
that can only be read if you have a
which is a text or number that can b e used to "reverse" the
cypher to
decrypt
the message
Caesar or Shift Cypher
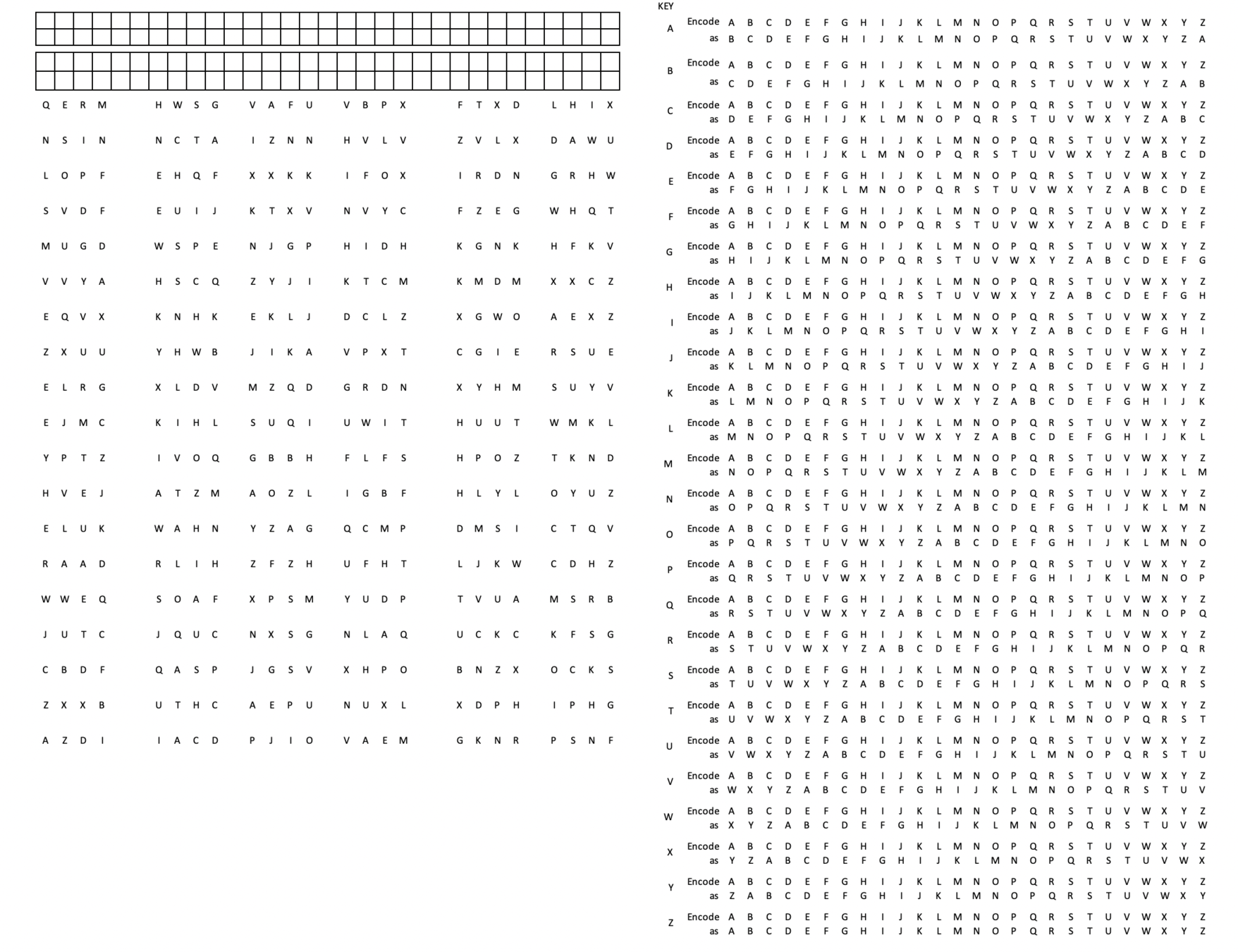
GHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZABCDEF
Encrypt letter with a letter N locations away
Weakness: cryptanalyzable with statistics
ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ
GHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZABCDEF
ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ
For N=6
my secret > seykixkz
Better: Use a "KEY"
Shift Cypher with Key
Shift each letter in plaintext by different amount
9, 14, 6, 15
Select a key phrase.
Note alphabet position of each letter.
info
ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ JKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZABCDEFGHI
ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ
OPQRSTUVWXYZABCDEFGHIJKLMN
ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ
GHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZABCDEF
ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ
PQRSTUVWXYZABCDEFGHIJKLMNO
i
n
f
o
in foinfo
NOTE: Lots of ways to do this. Here the rule is "rotate alphabet N positions to the left"
my secret >
i
k
f
l
t
y
m
v
STOP+THINK
If the key is
starry starry night
what is the cyphertext of
seven pm
s e v e n p m s t a r r y s
S ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ
TUVWXYZABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRS
T ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ
UVWXYZABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRST
A ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ
BCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZA
R ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ
STUVWXYZABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQR
R ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ
STUVWXYZABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQR
Y ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ
ZABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXY
S ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ
TUVWXYZABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRS
T ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ
UVWXYZABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRST
A ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ
BCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZA
R ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ
STUVWXYZABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQR
R ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ
STUVWXYZABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQR
Y ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ
ZABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXY
N ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ
OPQRSTUVWXYZABCDEFGHIJKLMN
I ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ
JKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZABCDEFGHI
L
Y
W
W
F
O
F
STOP+THINK
If the key is
starry starry night
what is the cyphertext of
seven pm
Decrypt the message
vfbkkhliwwj
STOP+THINK
S ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ
TUVWXYZABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRS
T ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ
UVWXYZABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRST
A ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ
BCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZA
R ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ
STUVWXYZABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQR
R ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ
STUVWXYZABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQR
Y ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ
ZABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXY
S ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ
TUVWXYZABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRS
T ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ
UVWXYZABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRST
A ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ
BCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZA
R ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ
STUVWXYZABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQR
R ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ
STUVWXYZABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQR
Y ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ
ZABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXY
N ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ
OPQRSTUVWXYZABCDEFGHIJKLMN
I ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ
JKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZABCDEFGHI
L
A
S
S
I
S
O
V
C
E
R
Instead of a finite key, how about an infinite supply of random numbers?
From Better to Best
The One-Time Pad
Cryptography 101: One-Time Pads
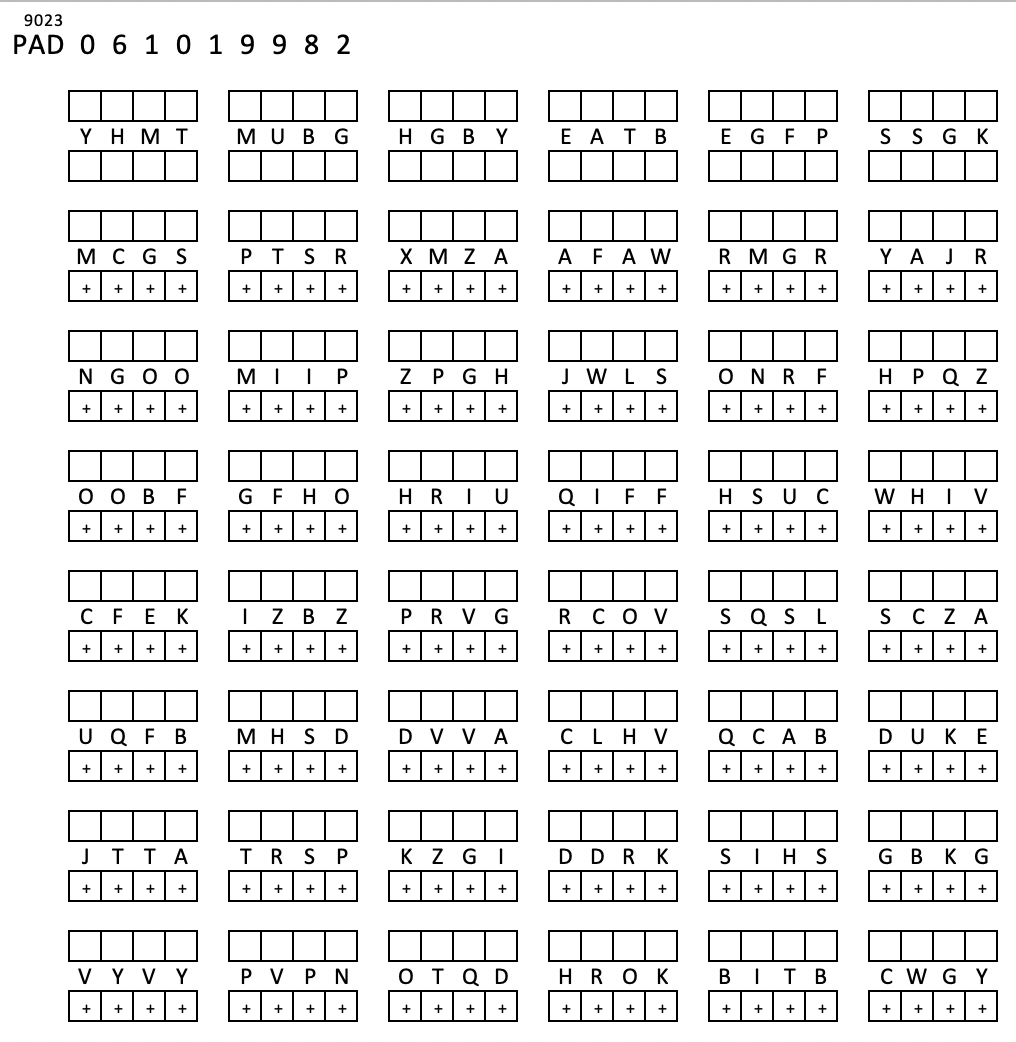
infinite supply of random "numbers"
plaintext here
cyphertext here
You encode your message using the OTP and then you burn the OTP. I can decode because I have a copy of the OTP.
STOP+THINK: Decrypt CWJHJDVOKVXHIATBEGFPSSGK
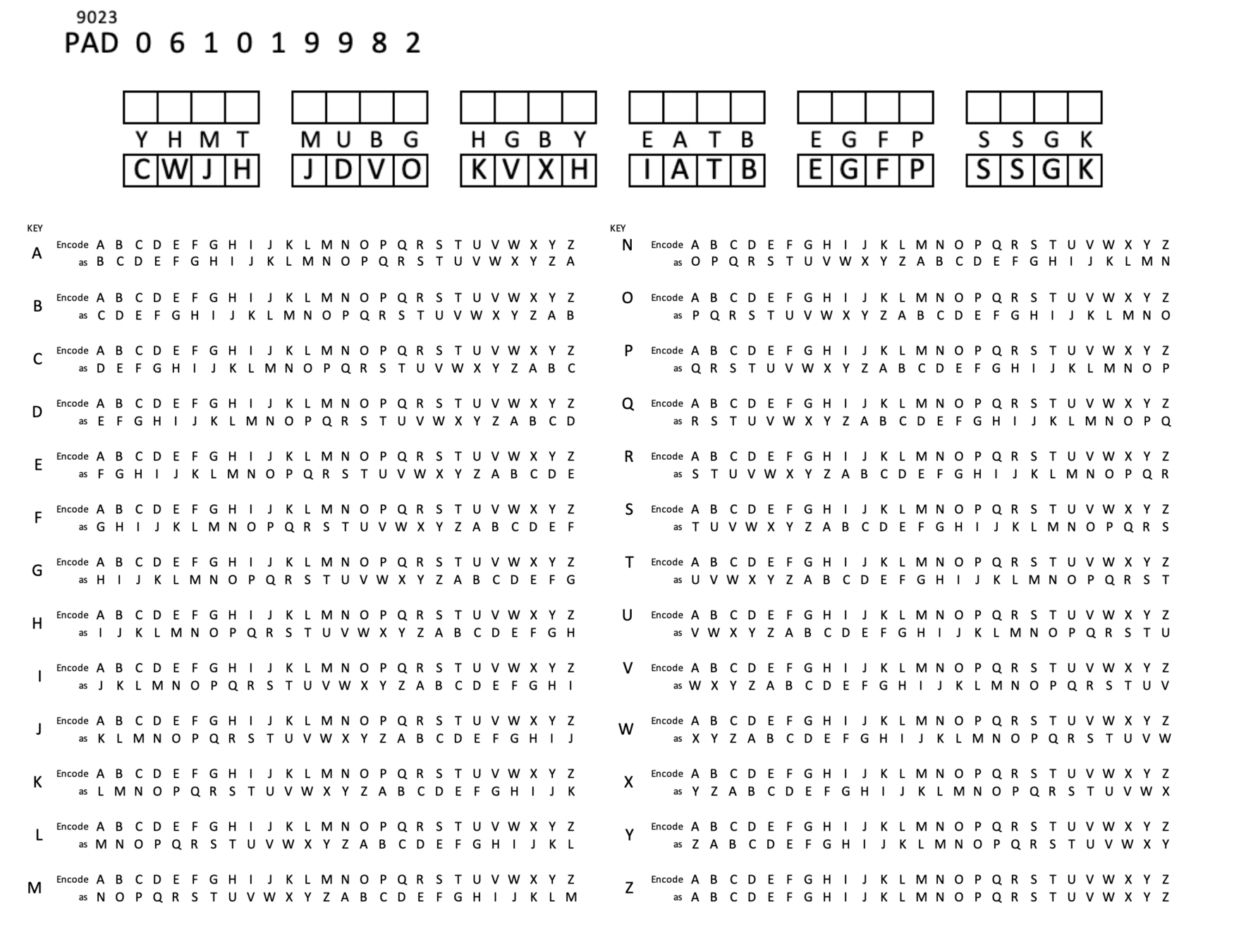
D
1
2
3
4
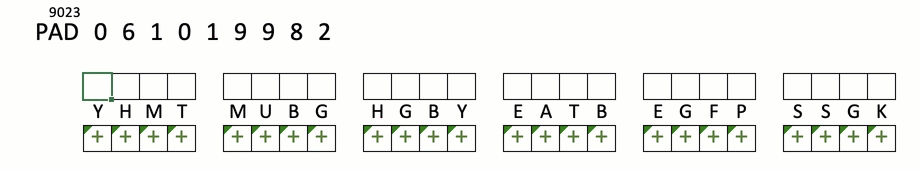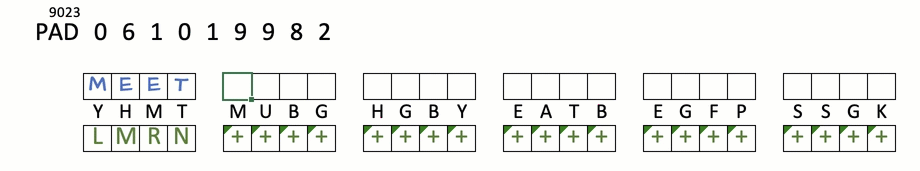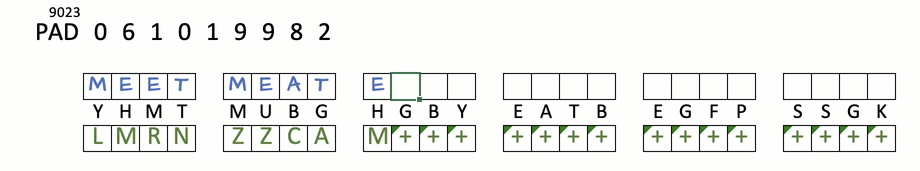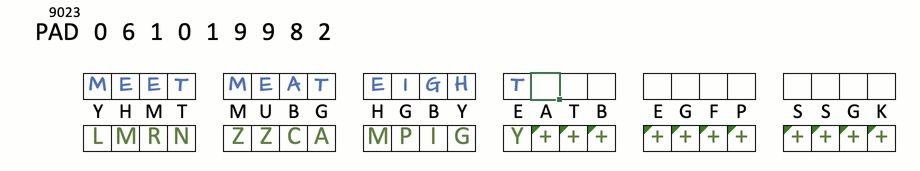

STOP+THINK: Encrypt "meet me at eight"
key:YHMTMUBGHGBYE
STOP+THINK: Decrypt CWJHJDVOKVXHIATBEGFPSSGK

Quick Interlude: Hashing

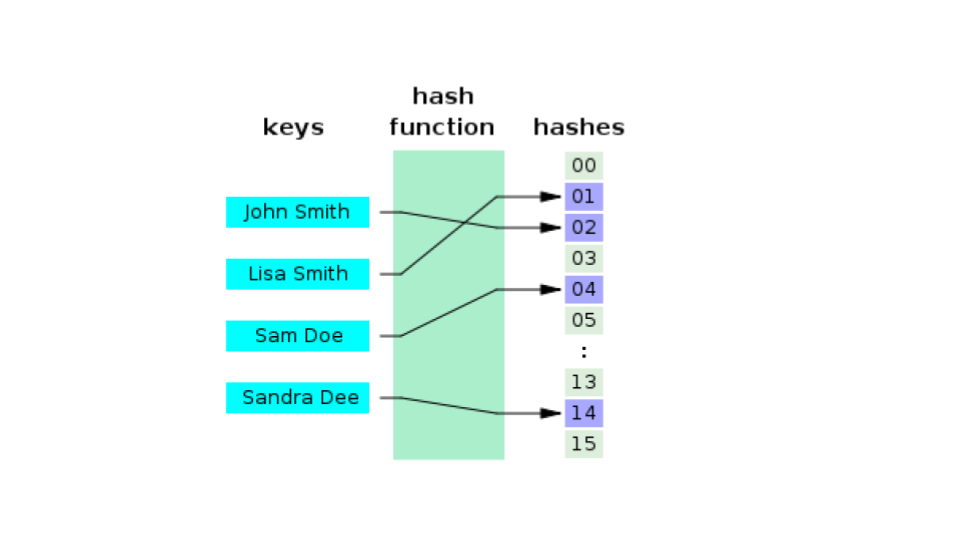
Hashing
- a hash function maps or converts arbitrary data (meaning data of any size) to a fixed sized piece of data in a more or less unique way
- that is, no two things will have the same hash
- in general it is a one way operation
- that is, you can't unhash the hash to find out what the original data was
HASHING REFERENCES
Example


Example
Example
1st letter of first name
3rd letter of first name
3rd letter of last name
1st letter of last name
length of first name
length of last name
dnracdgg
month of birth
date of birth mod 26*
* 1=a, 2=b, ..., 27=a, 28=b, 29=c, 30=d, 31=e
Cryptographic Hash
A cryptographic hash (sometimes called ‘digest’) is a kind of ‘signature’ for a text or a data file.
Cryptographic Hash
aa58b21b01d6b8a99c1a5856962dbac36c758a79dc0a77c2e013ce2c39ecdc8a
da
ec4f2dbb3b140095550c9afbbb69b5d6fd9e814b9da82fad0b34e9fcbe56f1cb

dan
Nam tristique hendrerit iaculis. Ut quis tortor velit. Proin posuere turpis ac mi tincidunt, id vulputate augue semper. Nulla finibus ex nisi, eget feugiat nisl sollicitudin sit amet. Suspendisse dui lorem, sollicitudin eget sodales vitae, gravida vel libero. Morbi elementum id mi non cursus. Proin hendrerit placerat sapien, ut placerat sapien tincidunt vel. Donec pellentesque justo neque, a faucibus odio rhoncus vitae. Quisque viverra aliquet pulvinar. Mauris porta urna vel porttitor rutrum. Quisque dictum finibus neque, ut convallis augue finibus ac. Suspendisse libero lorem, maximus ac tristique et, gravida eget diam. Donec semper dui metus. Pellentesque lobortis porta commodo. Aenean eu augue ultricies, fringilla augue nec, blandit arcu. Nunc consectetur libero tristique, ornare felis consectetur, tincidunt dolor. Nulla facilisi. Sed et feugiat mauris, ac dapibus leo. Etiam eget accumsan lacus. Nam facilisis tortor vel odio sollicitudin auctor. Maecenas quis vulputate enim. Aliquam condimentum justo leo, in bibendum magna fringilla ac. Phasellus a facilisis lorem. Quisque facilisis leo eros, non ultrices tellus volutpat at. Nulla et leo vehicula tellus egestas luctus sed mollis mauris. Maecenas lobortis nec risus sed convallis. Vivamus sit amet imperdiet quam. Cras maximus dui et pellentesque dignissim.
30293f4f02f784c4166a3e17109f01625bd1bfe97de2e017eebf9d23a55d9caf

We just learned two things
- Different sized inputs produce same size output
- Similarity in input does not mean similarity in output
Cryptographic Hash
A cryptographic hash (aka ‘digest’) is a transformation of a text or a data file into an almost-unique fixed length block of data.
A hash is not ‘encryption’ insofar as it cannot be decrypted back to the original text.
As a ‘one-way’ cryptographic function it can be used on a copy of a document and then compared to a hashed version of an original to verify that the copy is accurate to the original.
SHA-256
an algorithm that generates an almost-unique 256-bit (32-byte) signature for a text input.
Secure Hashing Algorithm 256 bit
SHA256 Pseudocode
SHA-256 Implemented in JS
CH 3 Asymmetric encryption
What did we learn from Eddy Woo?
RSA starts by generating a "key pair" - one private or secret and one public. So we sometimes write SK and PK
We can encrypt with either one.
We can decrypt with the "other" one only.
RSA (Rivest–Shamir–Adleman) is an asymmetric cryptographic algorithm algorithm used to encrypt and decrypt messages.
Asymmetric means one key is used to encrypt and another is used to decrypt.
Why "public" and "private"?
Two kinds of "secret keeping"
I want to create something that only you can read
I want to create something that you can be certain came from me.
ONLINE RSA
"Public Key Cryptography Standards"
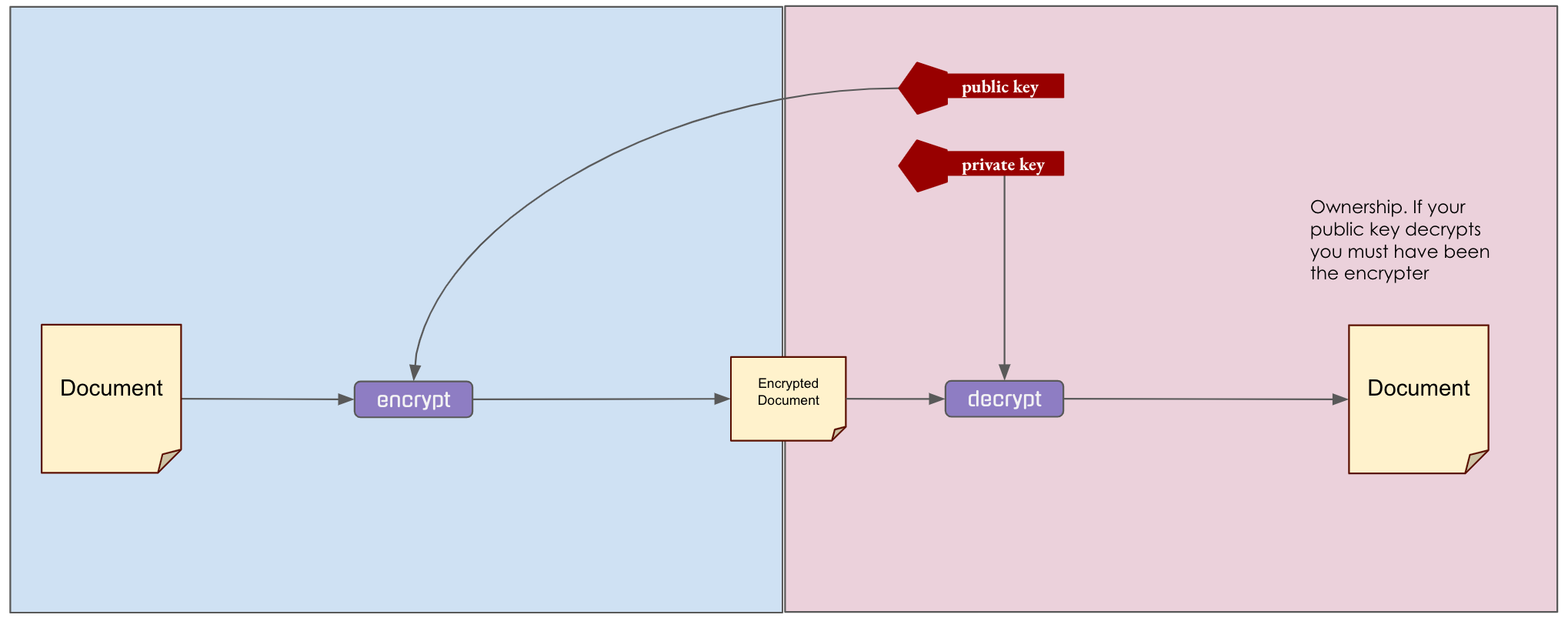
CONFIDENTIALITY
-
You generate public and private key
- You tell me your public key
- I encrypt message with your public key
- I send you the encrypted message
- You decrypt message with your private key

Sending a message for your eyes only
For your eyes only
AUTHENTICATION
-
I generate public and private key
- I encrypt message with my private key
- I tell you my public key
- I send you the encrypted message
- You decrypt message with my public key

Sending a message you know comes from me
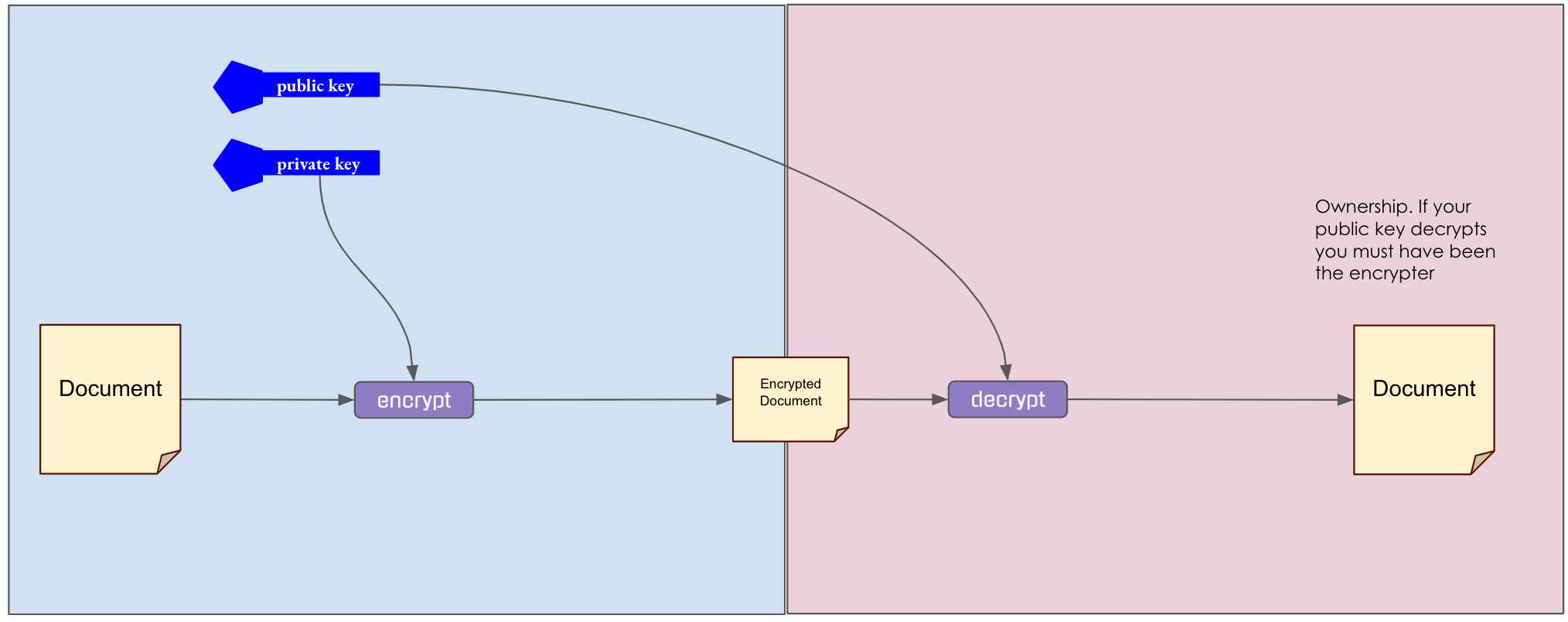
Anyone can read it and know it is from me
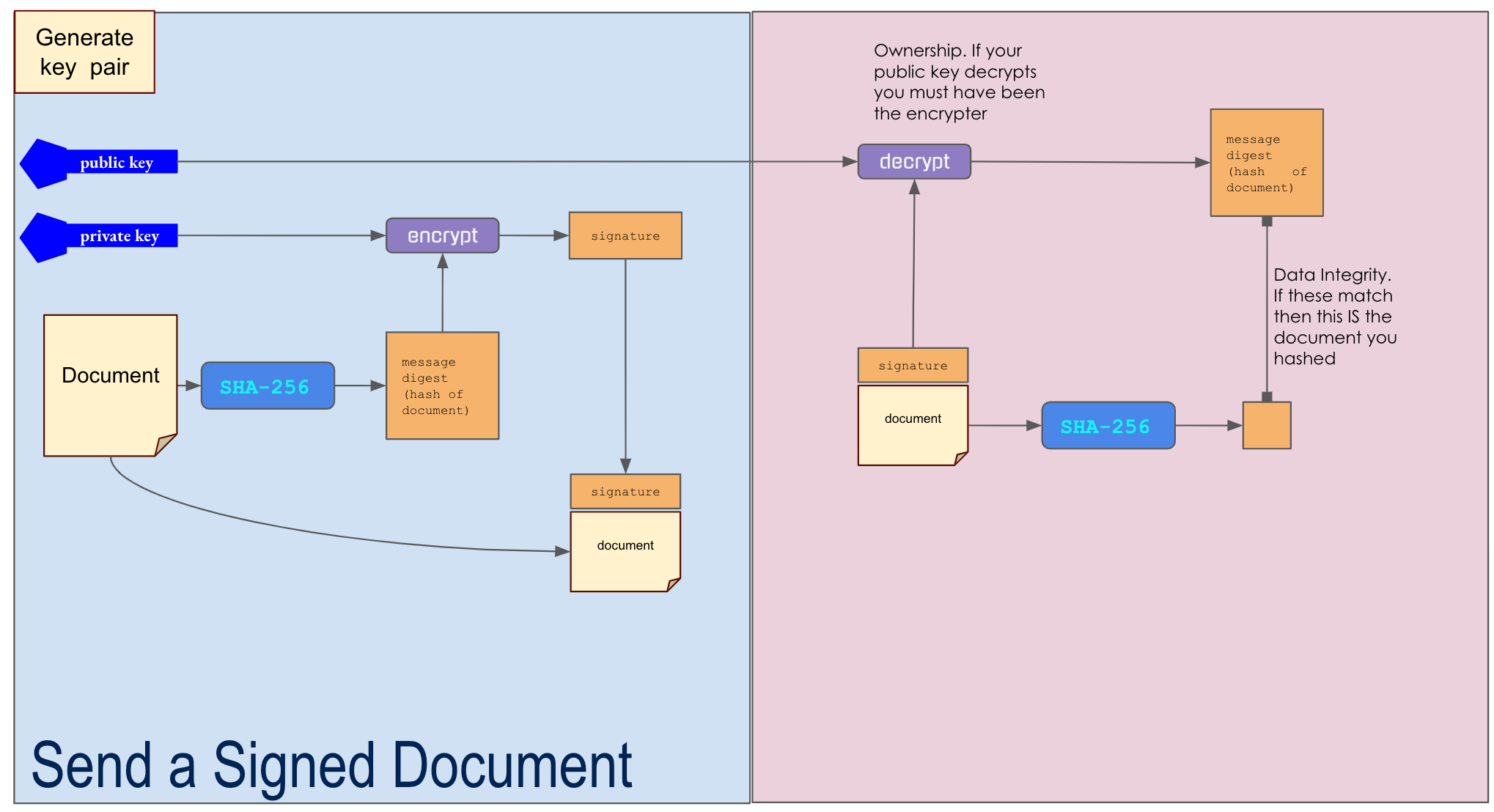
DIGITAL SIGNATURE
-
I generate public and private key
- I create a hash of my document.
- I encrypt the hash with my private key (the signature)
- I tell you my public key
- I send you the message and the encrypted hash
- You hash the message and decrypt the signature with my public key
- If the two hashes match then you have the same document that I signed

HOW do I guarantee that I signed THIS document?
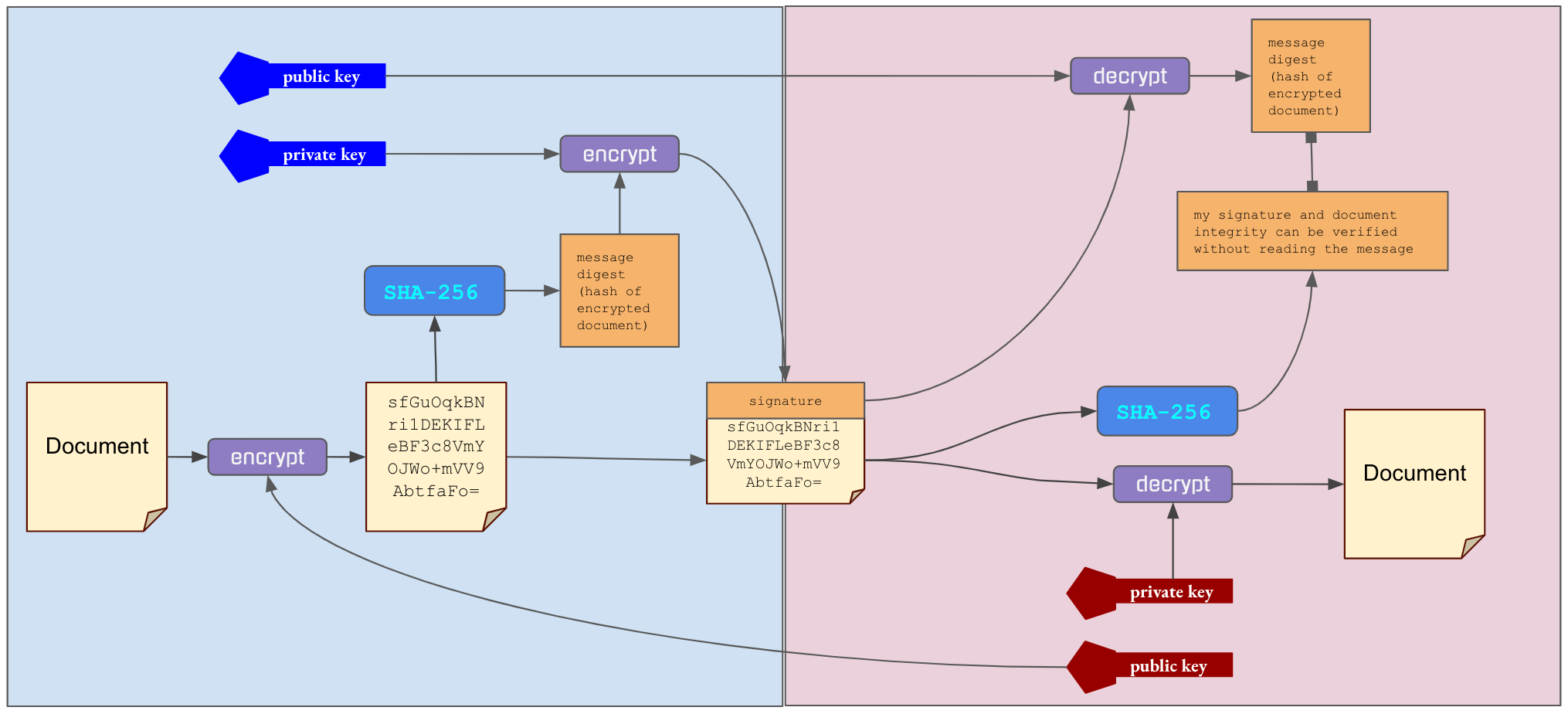
only you can read it
Information Security
- confidentiality: secrecy is maintained
- authenticity: it is from who it says
- integrity: it is what it says
How to operate on lots of data? Break it up into blocks. Blocks always same size. Padding.
Certificates
Start with information about yourself
Ask a trustee to validate and confirm
Trustee signs certificate with private key
Recipient uses trustee's public key to decrypt
If result matches certificate then it's valid.
I am Dan.
This IS Dan.
45ab98de7ff7ced213198005adfe
Skey(trustee)
Web connection receives certificate
Secure Web Exchange
Browser generates keys and sends public as "session" key, encrypted with server's public key.
Server encrypts web page content with session key.
Browser encrypts content to send with private session key.
Browser decrypts content with private key.
Server decrypts content with session key.
Certificate includes server's public key.
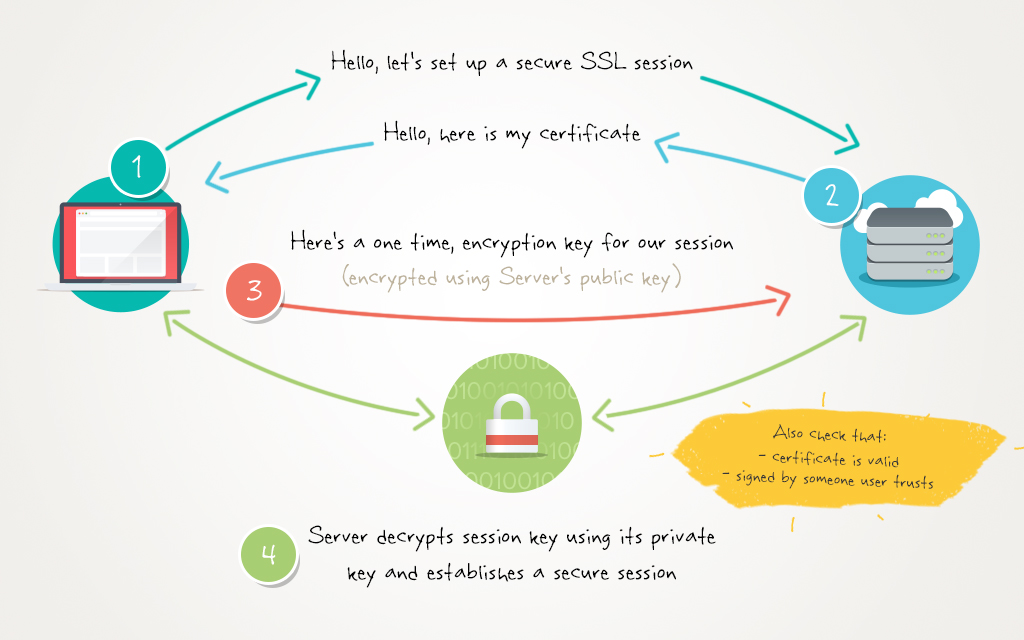
https://www.cloudaccess.net/images/blog/SSLBlog/miraj_blog_post.jpg
Ch 4 Money
4 Money: Can I pay You $10 with Serial Number?
4 Money: Can I pay You $10 with Serial Number?

What if...
on 15Nov2020 Carla gave BTE0000005 to Dan on 10Nov2020 Bri gave BTE0000005 to Carla on 10Oct2020 Ali gave BTE0000005 to Bri on 18JUL2020 GOD gave BTE0000005 to Ali
What if...
on 15Nov2020 Carla gave BTE0000005 to Dan on 10Nov2020 Bri gave BTE0000005 to Carla on 10Oct2020 Ali gave BTE0000005 to Bri on 18JUL2020 GOD gave BTE0000005 to Ali
But how do you know I haven't already given it to someone else?
Answer: you look in the ledger
When I engage in a transaction I tell the whole world about it:
Dan sends Eve $5
What is important to other nodes when they see this message?
They need to know that I am the one who did it.
Transaction: Dan sends Eve $5
Encrypt(
Dan sends Eve $5
, DanPrivateKey
)
This means everyone's copy of the ledger can be correct
Ch 6 Blockchain Again

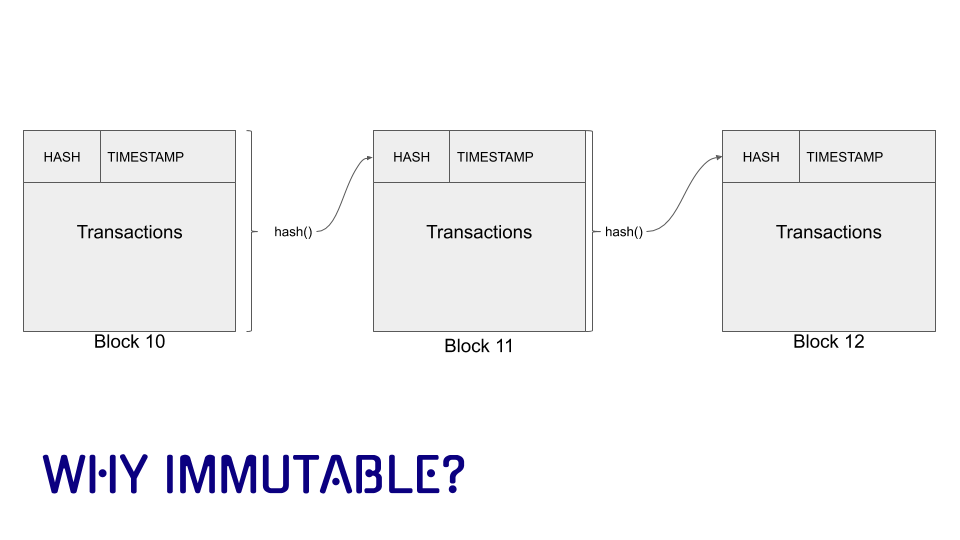
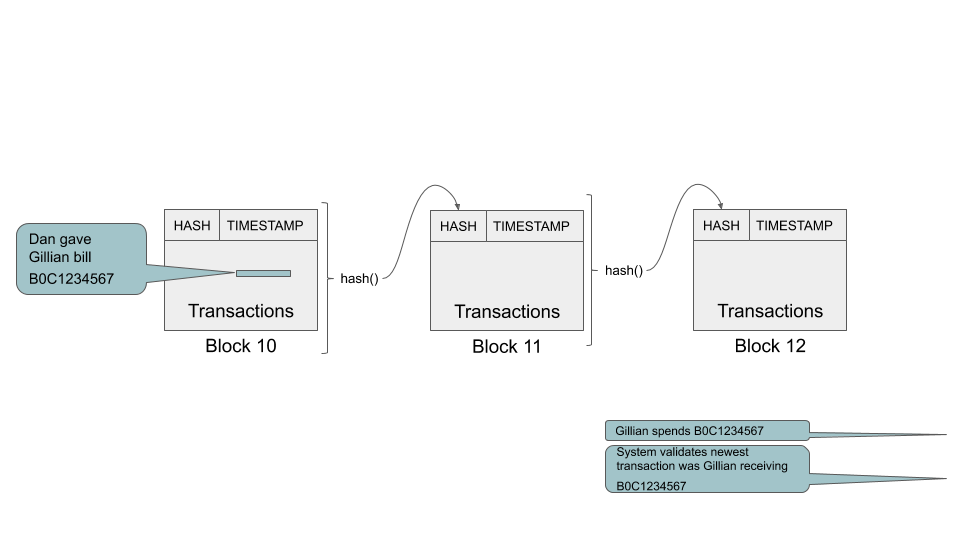

6 Blockchain 2