NUMBERS

Numbers
- Filho. 2017. Computer Science Distilled, p 165
- Eames Labs. 1977. Powers of Ten (10m16s)
-
Sample from among
- MathCrazyTutoring (2007), Binary Numbers in 60 Seconds (1m35s)
- Khan Academy. 2011. "Binary Numbers" (10m33s)
- Khan Academy. 2014. "Introduction to number systems and binary" (9m59s)
- Cope (2017), Binary Numbers Explained for Beginners (14m25s)
- The Organic Chemistry Tutor. 2018. "Number Systems Introduction - Decimal, Binary, Octal, Hexadecimal & BCD Conversions" (30m4s)
- Khan Academy. 2014. "Adding in Binary" (2m47s)
Materials and Handouts
What You Need to Know
-
CL01 Binary: Concept of base 2; notation; count to 10; dec2bin, bin2dec; first 10 powers of 2; binary arithmetic
-
CL02 Hexadecimal: Concept of base 16; notation; hex2bin, bin2hex, hex2dec; ASCII encoding; URL encoding; HTML color encoding
-
CL03 Counting by Powers: exponents, graphing, logarithms
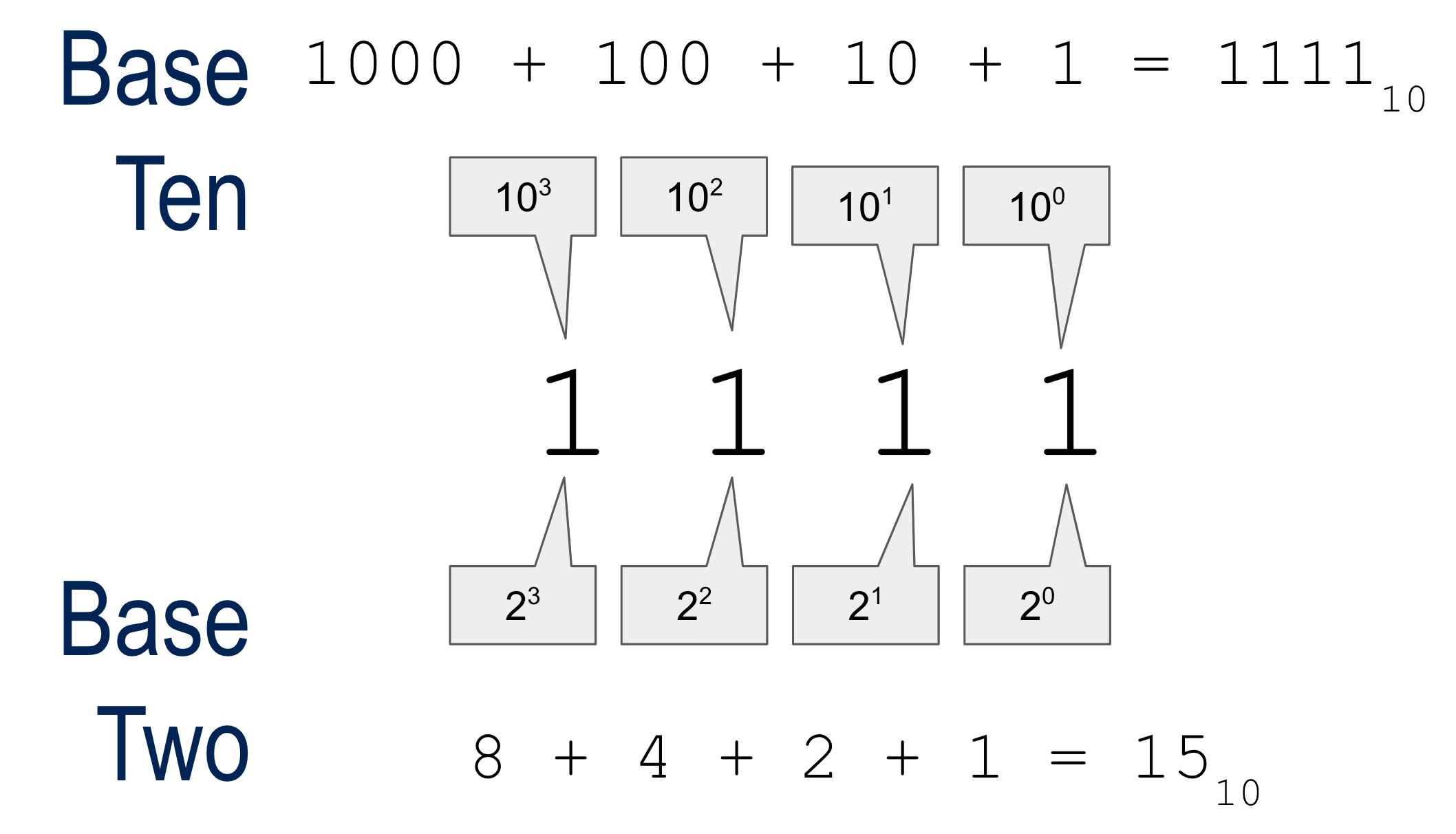
Numbers Basics
- Decimal to Binary
- Binary to Decimal
- Binary to Hexadecimal
- Binary coded decimal


Binary = Base 2
Positional Number Systems
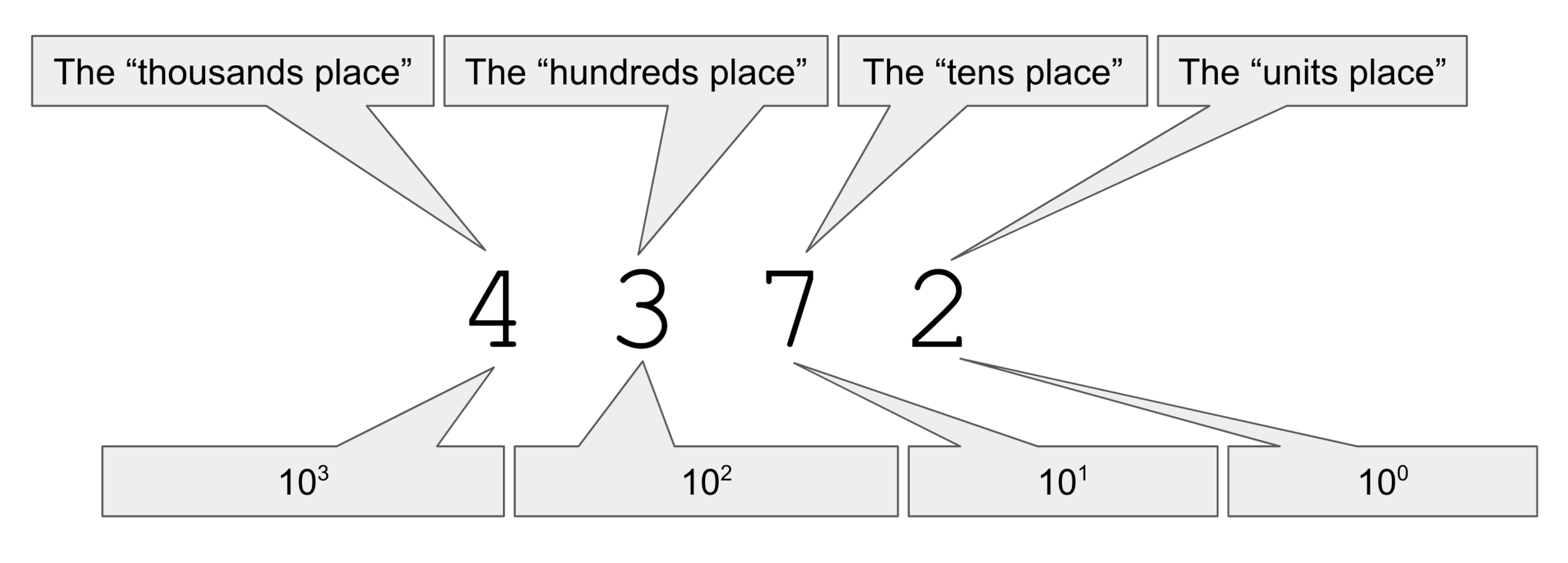
Positional Number Systems
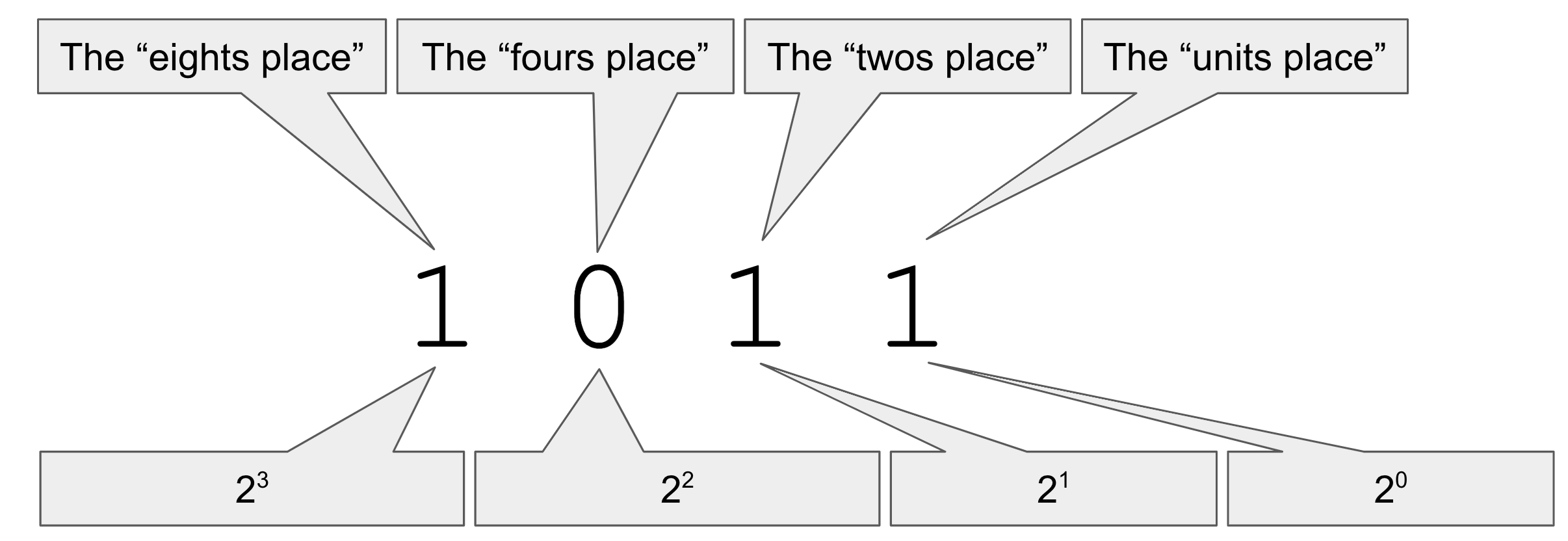
Positional Number Systems
STOP+THINK. Count to ten in binary
0000
0001
0010
0011
0100
0101
0110
0111
1000
1001
1010
1x20
1x21+0
1x21+1x20
1x22+0+0
1x22+0+1x20
1x22+1x21+0
1x22+1x21+1x20
1x23+0+0+0
1x23+0+0+1x20
1x23+0+1x21+0
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
How to convert dec to bin?
Start with decimal number, "D"
Divide by 2.
Note the result.
Write down the remainder.
Repeat process with the result.
Continue until nothing left.
D=6
610 =
Example: What is 610 in binary?
divide by 2
result = 3, remainder = 0
divide by 2
result = 1, remainder = 1
divide by 2
result = 0, remainder = 1
1
1
0
2
DEC2BIN Algorithm
Start with decimal number, "D"
Divide by 2.
Note the result.
Write down the remainder.
Repeat process with the result.
Continue until nothing left.
call decimal number D
divide D by 2
write remainder R to L
replace D with result
result=0?
read remainders
STOP+THINK. Convert 123 to binary
123 / 2 Q=61, R=1
1
61 / 2 Q=30, R=1
30 / 2 Q=15, R=0
15 / 2 Q=7, R=1
7 / 2 Q=3, R=1
3 / 2 Q=1, R=1
1 / 2 Q=0, R=1
1
1
0
1
1
1
64
32
+
16
+
8
+
0
+
2
+
1
+
STOP+THINK. Convert 273 to binary
See Also: "How to convert 273 to binary"
STOP+THINK. Convert 2421 to binary
STOP+THINK. Convert 77777 to binary
STOP+THINK. The rest of binary 0 - 15
0000 0100 1000 1100 0001 0101 1001 1101 0010 0110 1010 1110 0011 0111 1011 1111
1011
1100
1111
1110
1101
11
12
13
14
15
Other Bases
What if...
1
2
3
4
5
6
0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, ?
STOP+THINK. What's next?
Base 6
64 63 62 61 60
1296 216 36 6 1
3*36 + 2*6 + 4*1
,10
,15
,14
,13
,12
,11
,20
3246 =
= 12410
= 108 + 12 + 4
Example
The powers of 6
0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 20
STOP+THINK. What's next?
Base 6
64 63 62 61 60
1296 216 36 6 1
3246 = 3*36 + 2*6 + 4*1
= 108 + 12 + 1
= 12110
What if...

0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12
By analogy...
,13
,14
,15
,10
,11...
we need some new symbols
,D
,E
,F
,A
,B
,C
Introducing: HEXADECIMAL NUMBERS
Three Number Systems
Binary Digits: 0,1
Hexadecimal Digits: 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,A,B,C,D,E,F
Decimal Digits: 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9
Positions:
1 s
1 000s
1 00s
1 0s
1 s
8s
4s
2s
Positions:
1 s
4096s
256s
16s
Positions:
BIN & HEX have a special relationship
4 binary digits can represent 16 values
hexadecimal has 16 symbols
Each hexadecimal digit has a 4 bit equivalent
1011
1100
1111
1110
1101
B
C
D
E
F
1010
1001
1000
0111
0110
0101
0100
0000
0001
0010
0011
A
0
1
2
4
3
5
9
7
6
8
BINARY & HEXADECIMAL have a special relationship
24 23 22 21 20
16 8 4 2 1
164 163 162 161 160
65536 4096 256 16 1
BIN2HEX
1011010101010111101010111100
B
1011 0101 0101 0111 1010 1011 1100
{
A
7
5
5
B
C
GROUPS OF FOUR BITS
HEX EQUIVALENT
HEX2BIN
1011010101010111101010111100
1011
B 5 5 7 A B C
{
1100
1011
1010
0111
0101
0101
HEX2DEC
3 x 163 + 10 x 162 + 15 x 161 + 7 x 160
3 x 4096 + 10 x 256 + 15 x 16 + 7 x 1
12288 + 2560 + 240 + 7
15095
3
A
F
7
STOP+THINK. HEX2DEC
FF
111
200
ACE
C0DE
1000
=15*16+15=25510
=256+16+1=27310
=2*256=51210
=10*256+12*16+14 =2560+206=276610
=12*4096+13*16+14 =49152+0+208+14 =4937410
=409610
162=256 163=4096
Click for solutions
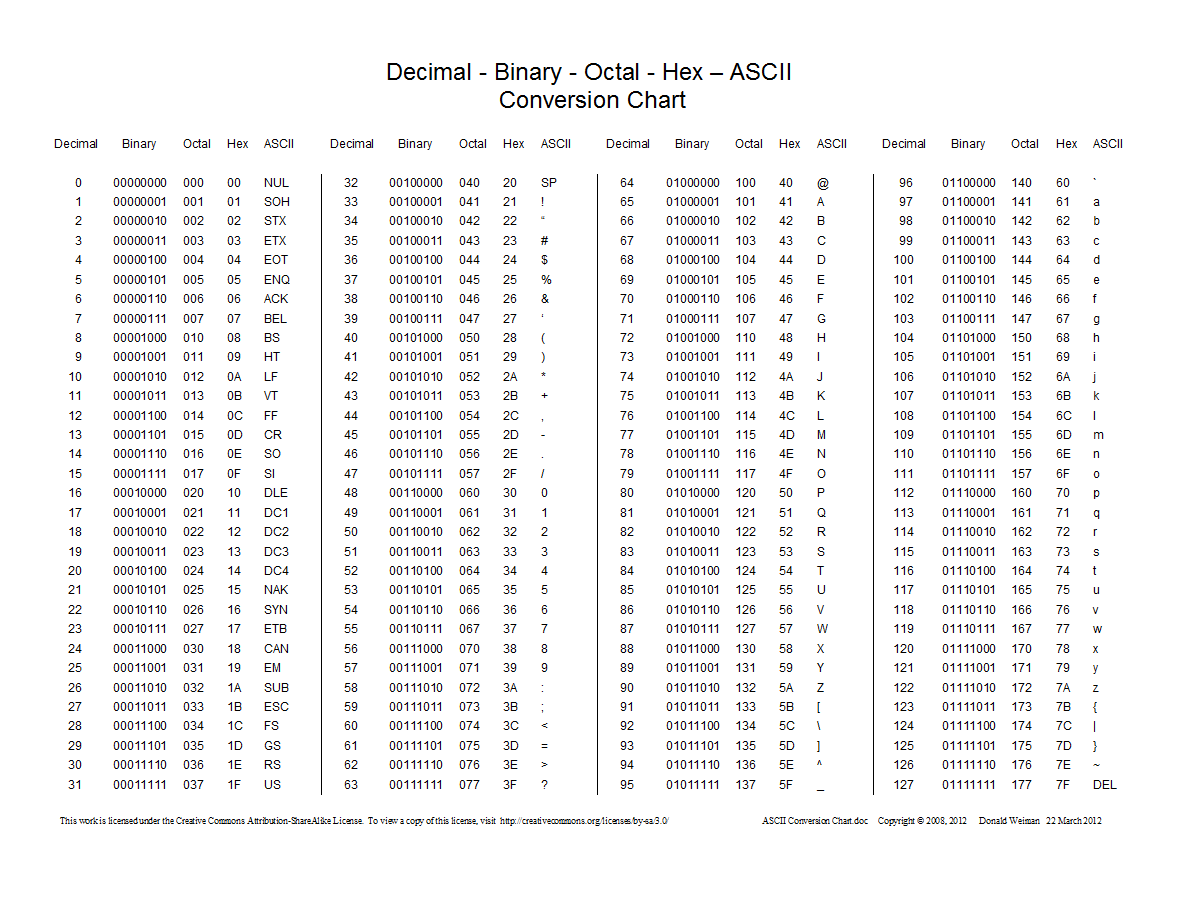
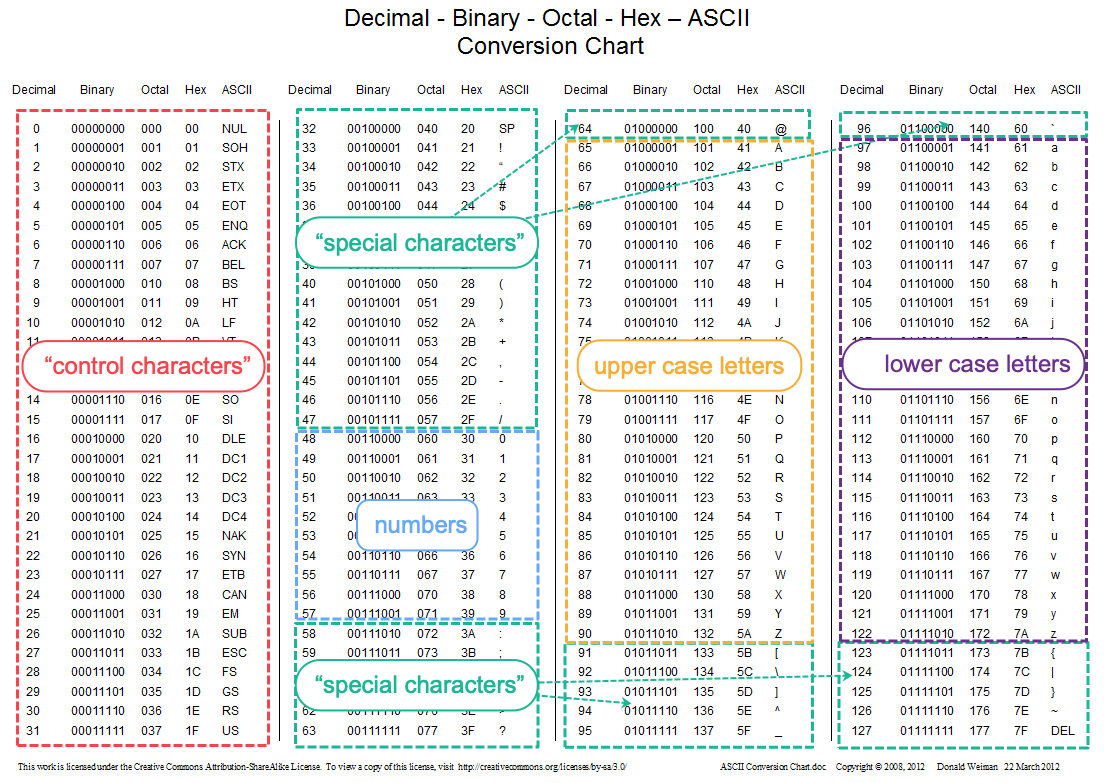
ENCODING
ASCII
American Standard Code for Information Interchange
- Numerical code for letters, digits, symbols
- Goes back to the days of teletype, hence the
control character symbols such as BEL
- Seven binary digits encode 128 symbols





STOP+THINK. Decode this ASCII text
4465636F 64652074 68697320 41534349 49207465 787460

D
e
c
o
d
e
<sp>
t
h
i
s
C
A
S
<sp>
I
I
.
t
e
x
t
<sp>
STOP+THINK. Decode this ASCII text
Decode this ASCII text.
74=t 65=e 78=x 74=t 60=.
44=D 65=e 63=c 6F=o 64=d 65=e 20=SP
74=t 68=h 69=i 73=s 20=SP
41=A 53=S 43=C 49=I 49=I 20=SP
Other Notations
subscripts: 15916 159hex 159h
prefix: 0x1F9
special characters in URLs as hex pairs prefixed with %
characters in XML and HTML as hex pairs with ode;
colors in HTML & CSS: 3 hex pairs* (red, green and blue) prefixed with #
http://www.example.com/name%20with%20spaces
’ = character U+2019 (’).
This Orange = #FFAA33
*CSS allows 3-hex digit abbreviation, one per component: #FA3 = #FFAA33.
COLORS in HTML
colors in HTML & CSS: 3 hex pairs* (red, green and blue) prefixed with #
This Orange = #FFAA33
*CSS allows 3-hex digit abbreviation, one per component: #FA3 = #FFAA33.
255/255 RED
51/255 BLUE
255/255 GREEN
STOP+THINK: CSS Colors

#17e71e

#abcdef
#8800FF

Which color is
#17e71e
#abcdef
#8800FF

STOP+THINK: HTML &codes
Text
N.B. 16110 = 0xA1
Wait, there's more...
Part 2: Practice
How to Do Negative Numbers in Binary?
One's Complement
Represent number in N bits, e.g., 10210=0110 01102 Invert each bit: 1001 1001
DEC BIN 1's Comp DEC 0 0000 0000 >> 1111 1111 -0 1 0000 0001 >> 1111 1110 -1 2 0000 0010 >> 1111 1101 -2 .. 126 0111 1110 >> 1000 0001 -126 127 0111 1111 >> 1000 0000 -127
Sum of X and -X is 2N-1
"Two's Complement"
How many bits?
Write the positive binary value for the negative number.
Invert each bit in the number.
Add 1.
0101
Find two's complement for -25 in 8 bits
Find two's complement for -25 in 4 bits
Can't be done because 4 bit two's complement goes from 1000 (-8) to 1111 (-1)
0001 1001
Find two's complement for -5 in 4 bits
0101 1010
0101 1010 +1
0101 1010 +1 1011
0001 1001 1110 0110
0001 1001
1110 0110
+1
0001 1001
1110 0110
+1
1110 0111
"Two's Complement"
-17
001 0001
0001 0001 0111 1110 +1 0111 1111
This is a One Pixel PNG File
0000000 89 50 4e 47 0d 0a 1a 0a 00 00 00 0d 49 48 44 52
0000010 00 00 00 02 00 00 00 02 08 06 00 00 00 72 b6 0d
0000020 24 00 00 00 01 73 52 47 42 00 ae ce 1c e9 00 00
0000030 00 78 65 58 49 66 4d 4d 00 2a 00 00 00 08 00 04
0000040 01 1a 00 05 00 00 00 01 00 00 00 3e 01 1b 00 05
0000050 00 00 00 01 00 00 00 46 01 28 00 03 00 00 00 01
0000060 00 02 00 00 87 69 00 04 00 00 00 01 00 00 00 4e
0000070 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 90 00 00 00 01 00 00 00 90
0000080 00 00 00 01 00 03 a0 01 00 03 00 00 00 01 00 01
0000090 00 00 a0 02 00 04 00 00 00 01 00 00 00 02 a0 03
00000a0 00 04 00 00 00 01 00 00 00 02 00 00 00 00 3f 95
00000b0 04 0b 00 00 00 09 70 48 59 73 00 00 16 25 00 00
00000c0 16 25 01 49 52 24 f0 00 00 00 0b 49 44 41 54 08
00000d0 1d 63 60 40 07 00 00 12 00 01 80 14 ca cc 00 00
00000e0 00 00 49 45 4e 44 ae 42 60 82
00000ea
Resources
https://www.csfieldguide.org.nz/en/interactives/pixel-viewer/
BINARY ARITHMETIC
- ADDING SINGLE BITS TOGETHER
- THE CARRY BIT
- MULTIPLYING IN BINARY
Binary
Arithmetic
1
+1
10
Arithmetic in Binary
0 + 0 = 0
0 + 1 = 1
1 + 1 = 10
10 + 1 = 11
10 + 10 = 100
STOP+THINK
Could we write
numbers
with TimBits?


STOP+THINK
Could we do math
with TimBits?

1
+0
01
0
+1
01
0
+0
00
1
+1
10
A
+B
WX
A B W X
1 1 1 0
1 0 0 1
0 1 0 1
0 0 0 0

1. Fill in the missing figures
2. Multiply
111
x101
1010
x1010
3. Add
1111
1011
+10011
4. Compute the 3 bit 2's complement of the numbers -8 to -1
-8
1000
0111
0111 +1 1000
-7
0111
1000
1000 +1 1001
-6
0110
1001
1001 +1 1010
-5
0101
1010
1010 +1 1011
-4
0100
1011
1011 +1 1100
-3
1100
1100 +1 1101
-2
1101
1101 +1 1110
-1
1110
1110 +1 1111
0001
0010
0011
5. Use 2's complement to compute
0101
+1101
1 0010
0011
+1011
1110
0110
+1010
0000
1011
+1101
1000
6. Write -127 and -128 as 8-bit 2's complement numbers. Examine the 7 right-most bits separately from the left-most or "most significant" bit. If you treat these as an ordinary binary number, what value does a 1 in the most significant bit position seem to have in 2s complement notation?

7. Write -32 and -31 as 6-bit 2's complement numbers. Examine the 5 right-most bits separately from the left-most or "most significant" bit. If you treat these as an ordinary binary number, what value does a 1 in the most significant bit position seem to have in 2s complement notation?
8. Make an addition table for 3 bit binary numbers.
| 000 | 001 | 010 | 011 | 100 | 101 | 110 | 111 | |
| 000 | ||||||||
| 001 | ||||||||
| 010 | ||||||||
| 011 | 0110 | |||||||
| 100 | 1000 | |||||||
| 101 | 1010 | 1011 | 1100 | |||||
| 110 | 1100 | 1101 | ||||||
| 111 | 1101 | 1110 |
9. Suppose you had a black box that could add two or three bits together and produce two results, a sum bit and a carry bit. Can you figure out how you might arrange a set of such black boxes to add two 2-bit binary numbers?
A
B
C
D
W
X
Y
AB +CD XYZ
10. Make a multiplication table for 2 bit binary numbers.
AB +CD WXYZ
| 00 | 01 | 10 | 11 | |
| 00 | ||||
| 01 | ||||
| 10 | ||||
| 11 |
11. Put the multiplication results into this table
AB xCD WXYZ
| A | B | C | D | W | X | Y | Z |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |